Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Promotes Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Survival and Resultant Bone Formation When Entrapped in Photocrosslinked Alginate Hydrogels
- PMID: 27581621
- PMCID: PMC5176258
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201600461
Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Promotes Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Survival and Resultant Bone Formation When Entrapped in Photocrosslinked Alginate Hydrogels
Abstract
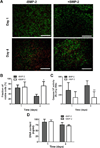
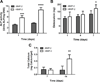
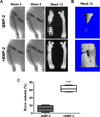
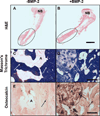
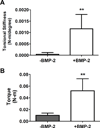
There is a substantial need to prolong cell persistence and enhance functionality in situ to enhance cell-based tissue repair. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) is often used at high concentrations for osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) but can induce apoptosis. Biomaterials facilitate the delivery of lower doses of BMP-2, reducing side effects and localizing materials at target sites. Photocrosslinked alginate hydrogels (PAHs) can deliver osteogenic materials to irregular-sized bone defects, providing improved control over material degradation compared to ionically cross-linked hydrogels. It is hypothesized that the delivery of MSCs and BMP-2 from a PAH increases cell persistence by reducing apoptosis, while promoting osteogenic differentiation and enhancing bone formation compared to MSCs in PAHs without BMP-2. BMP-2 significantly decreases apoptosis and enhances survival of photoencapsulated MSCs, while simultaneously promoting osteogenic differentiation in vitro. Bioluminescence imaging reveals increased MSC survival when implanted in BMP-2 PAHs. Bone defects treated with MSCs in BMP-2 PAHs demonstrate 100% union as early as 8 weeks and significantly higher bone volumes at 12 weeks, while defects with MSC-entrapped PAHs alone do not fully bridge. This study demonstrates that transplantation of MSCs with BMP-2 in PAHs achieves robust bone healing, providing a promising platform for bone repair.
Keywords: bone morphogenetic protein-2; mesenchymal stem cell; osteogenesis; photocrosslinking; survival.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

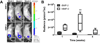
References
-
- Calori GM, Colombo M, Mazza EL, Mazzola S, Malagoli E, Mineo GV. Incidence of donor site morbidity following harvesting from iliac crest or RIA graft. Injury. 2014;45(Suppl 6):S116–S120. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Barrena E, Rosset P, Lozano D, Stanovici J, Ermthaller C, Gerbhard F. Bone fracture healing: cell therapy in delayed unions and nonunions. Bone. 2015;70:93–101. - PubMed
-
- Wen C, Kang H, Shih YR, Hwang Y, Varghese S. In vivo comparison of biomineralized scaffold-directed osteogenic differentiation of human embryonic and mesenchymal stem cells. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2016;6:121–131. - PubMed
-
- Song S, Kim EJ, Bahney CS, Miclau T, Marcucio R, Roy S. The synergistic effect of micro-topography and biochemical culture environment to promote angiogenesis and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2015;18:100–111. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

