New concept for the prevention and treatment of metastatic lymph nodes using chemotherapy administered via the lymphatic network
- PMID: 27581921
- PMCID: PMC5007471
- DOI: 10.1038/srep32506
New concept for the prevention and treatment of metastatic lymph nodes using chemotherapy administered via the lymphatic network
Abstract
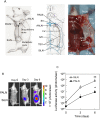
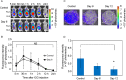
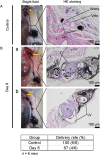
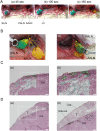
Intravenous chemotherapy has poor access to metastatic lymph nodes (LNs) and is limited by short-lived drug concentrations. Here, we describe the administration of chemotherapy via the lymphatic network as a new concept for the prevention and treatment of metastatic LNs. A metastatic LN can be treated by the injection of drugs into an upstream LN, either the sentinel LN (SLN) or another upstream LN. In a mouse model, tumor cells were inoculated into the subiliac LN (SiLN) to induce metastasis to the proper axillary LN (PALN). Two routes were used for drug delivery to the PALN, namely from the SiLN and from the accessory axillary LN (AALN). We found that tumor masses were formed in lymphatic vessels between the SiLN and PALN. The flow of fluorescent solution injected into the SiLN towards the PALN decreased with tumor mass formation. Delivery from the AALN (free of metastatic tumor cells) to the PALN was identified as an alternative route. Intranodal injection can deliver high concentrations of drugs to secondary metastatic LNs. The study advocates a new concept for the prevention and treatment of metastatic lymph nodes whereby drugs injected into upstream lymph nodes can reach metastatic lymph nodes via the lymphatic network.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study of the physicochemical properties of drugs suitable for administration using a lymphatic drug delivery system.Cancer Sci. 2021 May;112(5):1735-1745. doi: 10.1111/cas.14867. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33629407 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the enhanced permeability and retention effect in the early stages of lymph node metastasis.Cancer Sci. 2017 May;108(5):846-852. doi: 10.1111/cas.13206. Epub 2017 May 22. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28211204 Free PMC article.
-
Protocols for the Evaluation of a Lymphatic Drug Delivery System Combined with Bioluminescence to Treat Metastatic Lymph Nodes.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2524:333-346. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2453-1_27. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35821485
-
Tumor Regulation of Lymph Node Lymphatic Sinus Growth and Lymph Flow in Mice and in Humans.Yale J Biol Med. 2017 Sep 25;90(3):403-415. eCollection 2017 Sep. Yale J Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28955180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of an intranodal drug delivery system using a mouse model with lymphadenopathy: novel discoveries and clinical application.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2025 Apr;22(4):555-564. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2025.2471982. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 39995110 Review.
Cited by
-
Intranodal delivery of modified docetaxel: Innovative therapeutic method to inhibit tumor cell growth in lymph nodes.Cancer Sci. 2022 Apr;113(4):1125-1139. doi: 10.1111/cas.15283. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 35100484 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering and steering population-level response under spatial drug heterogeneity on microhabitat structures.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 17:2025.02.13.638200. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.13.638200. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40027692 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Imaging of the Mouse Lymphatic Sinus during Early Stage Lymph Node Metastasis Using Intranodal Lymphangiography with X-ray Micro-computed Tomography.Mol Imaging Biol. 2019 Oct;21(5):825-834. doi: 10.1007/s11307-018-01303-4. Mol Imaging Biol. 2019. PMID: 30607526
-
Optimization of lymphatic drug delivery system with carboplatin for metastatic lymph nodes.Sci Rep. 2025 May 8;15(1):16037. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99602-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40341825 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Effect of Second Near-Infrared Absorbing Gold Nanorods on Metastatic Lymph Nodes via Lymphatic Delivery System.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 28;13(9):1359. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091359. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mehlen P. & Puisieux A. Metastasis: a question of life or death. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 449–458 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto H. et al.. Micrometastasis volume in lymph nodes determines disease recurrence rate of stage II colorectal cancer: a prospective multicenter trial. Clin. Cancer Res. CCR-15-2199 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Sato T., Mori S., Arai Y. & Kodama T. The combination of intralymphatic chemotherapy with ultrasound and nano-/microbubbles is efficient in the treatment of experimental tumors in mouse lymph nodes. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 40, 1237–1249 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Kato S. et al.. Delivery of molecules to the lymph node via lymphatic vessels using ultrasound and nano/microbubbles. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 41, 1411–1421 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

