Variation in mothers' arginine vasopressin receptor 1a and dopamine receptor D4 genes predicts maternal sensitivity via social cognition
- PMID: 27581946
- PMCID: PMC5290085
- DOI: 10.1111/gbb.12326
Variation in mothers' arginine vasopressin receptor 1a and dopamine receptor D4 genes predicts maternal sensitivity via social cognition
Abstract
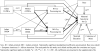
We examined the extent to which the arginine vasopressin receptor 1a (AVPR1a) and dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) were related to sensitive maternal behavior directly or indirectly via maternal social cognition. Participants were 207 (105 European-American and 102 African-American) mothers and their children (52% females). Sensitive maternal behavior was rated and aggregated across a series of tasks when infants were 6 months, 1 year and 2 years old. At 6 months, mothers were interviewed about their empathy, attributions about infant behavior and beliefs about crying to assess their parenting-related social cognition. Mothers with long alleles for AVPR1a and DRD4 engaged in more mother-oriented social cognition (i.e. negative attributions and beliefs about their infants' crying, β = 0.13, P < 0.05 and β = 0.16, P < 0.05, respectively), which in turn predicted less sensitive maternal behavior (β = -0.23, P < 0.01). Both indirect effects were statistically significant independent of one another and covariates [95% confidence interval (CI): -0.22, -0.03 and β = -0.03 for AVPR; 95% CI: -0.20, -0.03 and β = -0.04 for DRD4]. There were no significant direct effects of AVPR1a or DRD4 on maternal sensitivity (β = 0.02, P = .73 and β = -0.10, P = .57, respectively). The results did not vary for African-American and European-American mothers (Δχ2 = 18.76, Δdf = 16, P = 0.28). Results support the view that one mechanism by which maternal genes are associated with parental behavior is via social cognition.
Keywords: AVPR1a; Arginine vasopressin; DRD4; dopamine; infants; mothers; sensitivity; social cognition.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd and International Behavioural and Neural Genetics Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arginine vasopressin 1a receptor gene and maternal behavior: evidence of association and moderation.Genes Brain Behav. 2012 Apr;11(3):262-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00769.x. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Genes Brain Behav. 2012. PMID: 22288734
-
DRD4 interacts with adverse life events in predicting maternal sensitivity via emotion regulation.J Fam Psychol. 2018 Sep;32(6):783-792. doi: 10.1037/fam0000454. Epub 2018 Jul 23. J Fam Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30035571 Free PMC article.
-
Mothers' dopamine receptor polymorphism modulates the relation between infant fussiness and sensitive parenting.Dev Psychobiol. 2010 Mar;52(2):149-57. doi: 10.1002/dev.20423. Dev Psychobiol. 2010. PMID: 20175141
-
Molecular genetic studies of the arginine vasopressin 1a receptor (AVPR1a) and the oxytocin receptor (OXTR) in human behaviour: from autism to altruism with some notes in between.Prog Brain Res. 2008;170:435-49. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00434-2. Prog Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18655900 Review.
-
Brain opioids and mother-infant social motivation.Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1994 Jun;397:40-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1994.tb13264.x. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1994. PMID: 7981473 Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal care of heterozygous dopamine receptor D4 knockout mice: Differential susceptibility to early-life rearing conditions.Genes Brain Behav. 2020 Sep;19(7):e12655. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12655. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Genes Brain Behav. 2020. PMID: 32306548 Free PMC article.
-
Empathy and Parental Sensitivity in Child Attachment and Socioemotional Development: A Systematic Review from Emotional, Genetic, and Neurobiological Perspectives.Children (Basel). 2025 Apr 4;12(4):465. doi: 10.3390/children12040465. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40310085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Polymorphisms in Oxytocin and Dopamine Pathway Genes and the Development of Dispositional Compassion Over Time: The Young Finns Study.Front Psychol. 2021 Apr 8;12:576346. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.576346. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33897514 Free PMC article.
-
A Scientometric Review of Infant Cry and Caregiver Responsiveness: Literature Trends and Research Gaps over 60 Years of Developmental Study.Children (Basel). 2023 Jun 10;10(6):1042. doi: 10.3390/children10061042. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Longitudinal Study of Maternal Beliefs About Infant Crying During the Postpartum Period: Interplay With Infant's Temperament.Front Psychol. 2021 Dec 16;12:786391. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.786391. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34975680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ainsworth MDS, Blehar MC, Waters E, Wall S. Patterns of attachment. Erlbaum; Hillsdale, NJ.: 1978.
-
- Anacker K, Enge S, Reif A, Lesch K, Strobel A. Dopamine D4 receptor gene variation impacts self-reported altruism. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18:402–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources