Vif Proteins from Diverse Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Lineages Have Distinct Binding Sites in A3C
- PMID: 27581978
- PMCID: PMC5105656
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01497-16
Vif Proteins from Diverse Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Lineages Have Distinct Binding Sites in A3C
Abstract
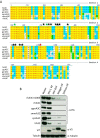
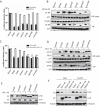
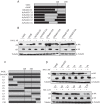
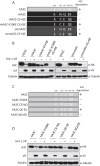
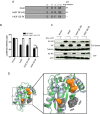
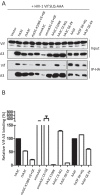
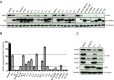
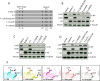
Lentiviruses have evolved the Vif protein to counteract APOBEC3 (A3) restriction factors by targeting them for proteasomal degradation. Previous studies have identified important residues in the interface of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Vif and human APOBEC3C (hA3C) or human APOBEC3F (hA3F). However, the interaction between primate A3C proteins and HIV-1 Vif or natural HIV-1 Vif variants is still poorly understood. Here, we report that HIV-1 Vif is inactive against A3Cs of rhesus macaques (rhA3C), sooty mangabey monkeys (smmA3C), and African green monkeys (agmA3C), while HIV-2, African green monkey simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVagm), and SIVmac Vif proteins efficiently mediate the depletion of all tested A3Cs. We identified that residues N/H130 and Q133 in rhA3C and smmA3C are determinants for this HIV-1 Vif-triggered counteraction. We also found that the HIV-1 Vif interaction sites in helix 4 of hA3C and hA3F differ. Vif alleles from diverse HIV-1 subtypes were tested for degradation activities related to hA3C. The subtype F-1 Vif was identified to be inactive for degradation of hA3C and hA3F. The residues that determined F-1 Vif inactivity in the degradation of A3C/A3F were located in the C-terminal region (K167 and D182). Structural analysis of F-1 Vif revealed that impairing the internal salt bridge of E171-K167 restored reduction capacities to A3C/A3F. Furthermore, we found that D101 could also form an internal interaction with K167. Replacing D101 with glycine and R167 with lysine in NL4-3 Vif impaired its counteractivity to A3F and A3C. This finding indicates that internal interactions outside the A3 binding region in HIV-1 Vif influence the capacity to induce degradation of A3C/A3F.
Importance: The APOBEC3 restriction factors can serve as potential barriers to lentiviral cross-species transmissions. Vif proteins from lentiviruses counteract APOBEC3 by proteasomal degradation. In this study, we found that monkey-derived A3C, rhA3C and smmA3C, were resistant to HIV-1 Vif. This was determined by A3C residues N/H130 and Q133. However, HIV-2, SIVagm, and SIVmac Vif proteins were found to be able to mediate the depletion of all tested primate A3C proteins. In addition, we identified a natural HIV-1 Vif (F-1 Vif) that was inactive in the degradation of hA3C/hA3F. Here, we provide for the first time a model that explains how an internal salt bridge of E171-K167-D101 influences Vif-mediated degradation of hA3C/hA3F. This finding provides a novel way to develop HIV-1 inhibitors by targeting the internal interactions of the Vif protein.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of APOBEC3 proteins by a novel YXXL motif in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vif and simian immunodeficiency virus SIVagm Vif.J Virol. 2009 Mar;83(5):2374-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01898-08. Epub 2008 Dec 24. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19109396 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of specific determinants of human APOBEC3F, APOBEC3C, and APOBEC3DE and African green monkey APOBEC3F that interact with HIV-1 Vif.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(24):12599-608. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01437-10. Epub 2010 Oct 13. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20943965 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved and non-conserved features of HIV-1 and SIVagm Vif mediated suppression of APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases.Cell Microbiol. 2008 Aug;10(8):1662-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01157.x. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Cell Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18419775 Free PMC article.
-
Examination of the APOBEC3 Barrier to Cross Species Transmission of Primate Lentiviruses.Viruses. 2021 Jun 7;13(6):1084. doi: 10.3390/v13061084. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34200141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumultuous relationship between the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral infectivity factor (Vif) and the human APOBEC-3G and APOBEC-3F restriction factors.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Jun;73(2):211-32. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00040-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19487726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Feline APOBEC3s, Barriers to Cross-Species Transmission of FIV?Viruses. 2018 Apr 10;10(4):186. doi: 10.3390/v10040186. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29642583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
APOBEC3-Related Editing and Non-Editing Determinants of HIV-1 and HTLV-1 Restriction.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 12;26(4):1561. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041561. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted HIV-1 Vif interactions with human E3 ubiquitin ligase and APOBEC3s.FEBS J. 2021 Jun;288(11):3407-3417. doi: 10.1111/febs.15550. Epub 2020 Sep 21. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 32893454 Free PMC article.
-
Selection Pressure Regulates the Evolution-Structure-Function Paradigm of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein Family.J Mol Evol. 2025 Apr;93(2):238-256. doi: 10.1007/s00239-025-10235-x. Epub 2025 Feb 5. J Mol Evol. 2025. PMID: 39907741
-
Divergence in Dimerization and Activity of Primate APOBEC3C.J Mol Biol. 2021 Dec 3;433(24):167306. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167306. Epub 2021 Oct 16. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34666043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- LaRue RS, Andresdottir V, Blanchard Y, Conticello SG, Derse D, Emerman M, Greene WC, Jonsson SR, Landau NR, Löchelt M, Malik HS, Malim MH, Münk C, O'Brien SJ, Pathak VK, Strebel K, Wain-Hobson S, Yu XF, Yuhki N, Harris RS. 2009. Guidelines for naming nonprimate APOBEC3 genes and proteins. J Virol 83:494–497. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01976-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

