Cognitive rehabilitation for memory deficits after stroke
- PMID: 27581994
- PMCID: PMC6457594
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002293.pub3
Cognitive rehabilitation for memory deficits after stroke
Abstract
Background: Memory problems are a common cognitive complaint following stroke and can potentially affect ability to complete functional activities. Cognitive rehabilitation programmes either attempt to retrain lost or poor memory functions, or teach patients strategies to cope with them.Some studies have reported positive results of cognitive rehabilitation for memory problems, but the results obtained from previous systematic reviews have been less positive and they have reported inconclusive evidence. This is an update of a Cochrane review first published in 2000 and most recently updated in 2007.
Objectives: To determine whether participants who have received cognitive rehabilitation for memory problems following a stroke have better outcomes than those given no treatment or a placebo control.The outcomes of interest were subjective and objective assessments of memory function, functional ability, mood, and quality of life. We considered the immediate and long-term outcomes of memory rehabilitation.
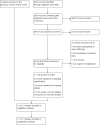
Search methods: We used a comprehensive electronic search strategy to identify controlled studies indexed in the Cochrane Stroke Group Trials Register (last searched 19 May 2016) and in the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL2016, Issue 5), MEDLINE (2005 to 7 March 2016), EMBASE 2005 to 7 March 2016), CINAHL (2005 to 5 February 2016), AMED (2005 to 7 March 2016), PsycINFO (2005 to 7 March 2016), and nine other databases and registries. Start dates for the electronic databases coincided with the last search for the previous review. We handsearched reference lists of primary studies meeting the inclusion criteria and review articles to identify further eligible studies.
Selection criteria: We selected randomised controlled trials in which cognitive rehabilitation for memory problems was compared to a control condition. We included studies where more than 75% of the participants had experienced a stroke, or if separate data were available from those with stroke in mixed aetiology studies. Two review authors independently selected trials for inclusion, which was then confirmed through group discussion.
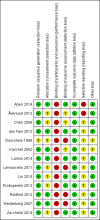
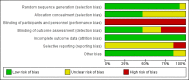
Data collection and analysis: We assessed study risk of bias and extracted data. We contacted the investigators of primary studies for further information where required. We conducted data analysis and synthesis in accordance with the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. We performed a 'best evidence' synthesis based on the risk of bias of the primary studies included. Where there were sufficient numbers of similar outcomes, we calculated and reported standardised mean differences (SMD) using meta-analysis.
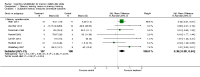
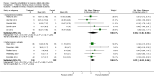
Main results: We included 13 trials involving 514 participants. There was a significant effect of treatment on subjective reports of memory in the short term (standard mean difference (SMD) 0.36, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.08 to 0.64, P = 0.01, moderate quality of evidence), but not the long term (SMD 0.31, 95% CI -0.02 to 0.64, P = 0.06, low quality of evidence). The SMD for the subjective reports of memory had small to moderate effect sizes.The results do not show any significant effect of memory rehabilitation on performance in objective memory tests, mood, functional abilities, or quality of life.No information was available on adverse events.
Authors' conclusions: Participants who received cognitive rehabilitation for memory problems following a stroke reported benefits from the intervention on subjective measures of memory in the short term (i.e. the first assessment point after the intervention, which was a minimum of four weeks). This effect was not, however, observed in the longer term (i.e. the second assessment point after the intervention, which was a minimum of three months). There was, therefore, limited evidence to support or refute the effectiveness of memory rehabilitation. The evidence was limited due to the poor quality of reporting in many studies, lack of consistency in the choice of outcome measures, and small sample sizes. There is a need for more robust, well-designed, adequately powered, and better-reported trials of memory rehabilitation using common standardised outcome measures.
Conflict of interest statement
Roshan das Nair: was involved in one of the trials included in this review. Heather Cogger: none known. Esme Worthington: none known. Nadina B Lincoln: was involved in one of the trials included in this review.
Figures





Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Aben 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Aben L. Metamemory intervention in chronic stroke patients: long‐term effects on social participation and quality of life. http://www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=1656 2008.
-
- Aben L, Heijenbrok‐Kal M, Ponds R, Busschbach J, Ribbers G. Long term effects of a memory self‐efficacy training program for stroke patients in the chronic stage: a randomized controlled trial. Brain Injury 2012;26(4‐5):414‐5.
-
- Aben L, Heijenbrok‐Kal MH, Ponds RWHM, Busschbach JV, Ribbers GM. Long‐lasting effects of a new memory self‐efficacy training for stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2014;28(3):199‐206. - PubMed
-
- Aben L, Heijenbrok‐Kal MH, Loon EM, Groet E, Ponds RW, Busschbach JJ, et al. Training memory self‐efficacy in the chronic stage after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2013;27(2):110‐7. [PUBMED: 22895620] - PubMed
-
- Heijenbrok‐Kal MH. Email communication 2016.
Åkerlund 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Björkdahl A. Email communication 2016.
-
- Åkerlund E, Esbjörnsson E, Sunnerhagen KS, Björkdahl A. Can computerized working memory training improve impaired working memory, cognition and psychological health?. Brain Injury 2013;27(13‐4):1649‐57. - PubMed
Chen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Chen S. Email communication 2016.
-
- Chen S, Jiang Q, Liu P, Huang D, Ding J. Effect of the cognitive rehabilitation on the functional independence of hemiplegic patients with stroke. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;10(18):14‐6.
das Nair 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- O'Brien MC, das Nair R, Lincoln NB. A comparison of the content of memory rehabilitation groups for patients with neurological disabilities. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 2013;23(3):321‐32. - PubMed
-
- das Nair R, Lincoln N, Kontou E, Vella K, O'Brien MC. A comparison of the effectiveness of two types of memory rehabilitation strategies following brain damage: a single blind, randomised control trial. Proceedings of the Oliver Zangwill 10th Anniversary Conference. 16‐17 November 2006. Cambridge, UK. 2006.
-
- das Nair R, Lincoln NB. Evaluation of rehabilitation of memory in neurological disabilities (ReMiND): a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2012;26(10):894‐903. - PubMed
Doornhein 1998 {published data only}
-
- Doornhein K, deHaan EHF. Cognitive training for memory deficits in stroke patients. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 1998;8(4):393‐400.
Kaschel 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kaschel R, Della Sala S, Cantagallo A, Fahlbock A, Laaksonen R, Kazen M. Imagery mnemonics for the rehabilitation of memory: a randomised group controlled trial. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 2002;12(2):127‐53.
Lannin 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Carr B, Allaous J, Lannin N, MacKenzie B, Falcon A, Tate R, et al. Efficacy of using handheld computers plus occupational therapy training to compensate for memory and planning difficulties after brain injury: a randomised control trial. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2012;26(6):687.
-
- Lannin N. Email communication 2016.
-
- Lannin N, Carr B, Allaous J, Mackenzie B, Falcon A, Tate R. A randomized controlled trial of the effectiveness of handheld computers for improving everyday memory functioning in patients with memory impairments after acquired brain injury. Clinical Rehabilitation 2014;28(5):470‐81. - PubMed
-
- Lannin NA, Schmidt J, Carr B, Allaous J, Falcon A, Tate R. Occupational therapy training to use handheld personal digital assistant (PDA) devices to address memory and planning difficulties after acquired brain injury: a randomised controlled trial. Stroke 2014;45(12):296.
Lemoncello 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lemoncello R. Email communication 2016.
-
- Lemoncello R, Sohlberg MM, Fickas S, Prideaux J. A randomised controlled crossover trial evaluating Television Assisted Prompting (TAP) for adults with acquired brain injury. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 2011;21(6):825‐46. - PubMed
Lin 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lin ZC, Tao J, Gao YL, Yin DZ, Chen AZ, Chen LD. Analysis of central mechanism of cognitive training on cognitive impairment after stroke: resting‐state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of International Medical Research 2014;42(3):659‐68. - PubMed
Prokopenko 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mozheyko EY. Email communication 2016.
-
- Prokopenko SV, Mozheyko EY, Petrova MM, Koryagina TD, Kaskaeva DS, Chernykh TV, et al. Correction of post‐stroke cognitive impairments using computer programs. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2013;325(1):148‐53. - PubMed
Radford 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Miller L. Email communication 2016.
-
- Radford K, Lah S, Thayer Z, Say MJ, Miller LA. Improving memory in outpatients with neurological disorders using a group‐based training program. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society 2012;18(04):738‐48. - PubMed
Westerberg 2007 {published data only}
-
- Westerberg H, Jacobaeus H, Hirvikoski T, Clevberger P, Ostenson ML, Bartfai A, et al. Computerised training of working memory ‐ a new method for cognitive rehabilitation after stroke. Proceedings of the Karolinska Stroke Update Meeting. 15‐16 November 2004. Stockholm, Sweden. 2004.
-
- Westerberg H, Jacobaeus H, Hirvikoski T, Clevberger P, Östensson ML, Bartfai A, et al. Computerized working memory training after stroke ‐ a pilot study. Brain Injury 2007;21(1):21‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Barker‐Collo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Barker‐Collo SL, Feigin VL, Lawes CMM, Parag V, Senior H, Rodgers A. Reducing attention deficits after stroke using attention process training: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2009;40(10):3293‐8. - PubMed
Blanchet 2016 {published data only}
-
- Blanchet S. Impact of combined aerobic and cognitive training on cognitive functioning in individuals with vascular cognitive impairment: a pilot study [Abstract]. Proceedings of the 8th World Stroke Congress. Brasilia, Brazil, 10‐13 October 2012.
-
- Blanchet S, Richards CL, Leblond J, Olivier C, Maltais DB. Cardiorespiratory fitness and cognitive functioning following short‐term interventions in chronic stroke survivors with cognitive impairment: a pilot study. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 2016;39(2):153‐9. - PubMed
Brainin 2015 {published data only}
-
- Brainin M. Email communication 2016.
-
- Brainin M, Matz K, Nemec M, Teuschl Y, Dachenhausen A, Asenbaum‐Nan S, et al. Prevention of poststroke cognitive decline: ASPIS ‐ a multicenter, randomized, observer‐blind, parallel group clinical trial to evaluate multiple lifestyle interventions ‐ study design and baseline characteristics. International Journal of Stroke 2015;10(4):627‐35. - PubMed
-
- Matz K, Teuschl Y, Firlinger B, Dachenhausen A, Keindl M, Seyfang L, et al. Multidomain lifestyle interventions for the prevention of cognitive decline after ischemic stroke randomized trial. Stroke 2015;46(10):2874‐80. - PubMed
Bushnick 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bushnick T, Englander J, Oggins J, Levinson R, Halper D. A randomized clinical trial of a cognitive orthotic with executive planning capability in individuals with cognitive dysfunction. Brain Injury 2010;24(3):392‐3.
Chen 2011 {published data only}
Chen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Chen CX, Mao RH, Li SX, Zhao YN, Zhang M. Effect of visual training on cognitive function in stroke patients. International Journal of Nursing Sciences 2015;2(4):329‐33.
de Joode 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Joode EA, Heugten CM, Verhey FRJ, Boxtel MPJ. Effectiveness of an electronic cognitive aid in patients with acquired brain injury: a multicentre randomised parallel‐group study. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 2013;23(1):133‐56. - PubMed
-
- Joode EA. Email communication 2016.
de Luca 2014 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Calabrò RS. Email communication 2016.
-
- Luca R, Calabrò RS, Gervasi G, Salvo S, Bonanno L, Corallo F, et al. Is computer‐assisted training effective in improving rehabilitative outcomes after brain injury? A case‐control hospital‐based study. Disability and Health Journal 2014;7(3):356‐60. - PubMed
Evans 2000 {published data only}
-
- Evans JJ, Wilson BA, Schuri U, Andrade J, Baddeley A, Bruna O, et al. A comparison of 'errorless' and 'trial‐and‐error' learning methods for teaching individuals with acquired memory deficits. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 2000;10(1):67‐101.
Fish 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fish J, Emslie H, Evans JJ, Manly T, Wilson BA. Further investigations into the NeuroPage system for memory and planning disorders. Proceedings of the 34th International Neuropsychological Society Annual Meeting: From Plasticity to Rehabilitation, 26‐29 July. Zurich, Switzerland. 2006:17.
-
- Fish J, Manly T, Emslie H, Evans JJ, Wilson BA. Compensatory strategies for acquired disorders of memory and planning: differential effects of a paging system for patients with brain injury of traumatic versus cerebrovascular aetiology. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 2008;79(8):930‐5. - PubMed
Fong 2009 {published data only}
-
- Fong KNK, Howie DR. Effects of an explicit problem‐solving skills training program using a metacomponential approach for outpatients with acquired brain injury. American Journal of Occupational Therapy 2009;63(5):525‐34. - PubMed
Gamito 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gamito P, Oliveira J, Santos N, Pacheco J, Morais D, Saraiva T, et al. Virtual exercises to promote cognitive recovery in stroke patients: the comparison between head mounted displays versus screen exposure methods. International Journal of Disability and Human Development 2014;13(3):337‐42.
Gasparrini 1979 {published data only}
-
- Gasparrini B. Personal communication 2007.
-
- Gasparrini B, Satz P. A treatment for memory problems in left hemisphere CVA patients. Journal of Clinical Neuropsychology 1979;1(2):137‐50.
Hildebrandt 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hildebrandt H, Bussmann‐Mork B, Schwendemann G. Group therapy for memory impaired patients: a partial remediation is possible. Journal of Neurology 2006;253:512‐9. - PubMed
Imes 1984 {published data only}
-
- Imes C. Interventions with stroke patients: EMG biofeedback, group activities, cognitive retraining. Cognitive Rehabilitation 1984;2(5):4‐17.
Klonoff 2007 {published data only}
-
- Klonoff PS, Talley MC, Dawson LK, Myles SM, Watt LM, Gehrels JA, et al. The relationship of cognitive retraining to neurological patients' work and school status. Brain Injury 2007;21(11):1097‐107. - PubMed
Liu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Liu KPY. Use of mental imagery to improve task generalisation after a stroke. Hong Kong Medical Journal/Xianggang yi xue za zhi 2009;15(3 Suppl 4):37‐41. - PubMed
Lundqvist 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lundqvist A. Email communication 2016.
-
- Lundqvist A, Grundström K, Samuelsson K, Rönnberg J. Computerized training of working memory in a group of patients suffering from acquired brain injury. Brain Injury 2010;24(10):1173‐83. - PubMed
Man 2006 {published data only}
-
- Man DWK, Soong WYL, Tam SF, Hui‐Chan CWY. A randomized clinical trial study on the effectiveness of a tele‐analogy‐based problem‐solving programme for people with acquired brain injury (ABI). NeuroRehabilitation 2006;21(3):205‐17. - PubMed
Markle‐Reid 2011 {published data only}
-
- Markle‐Reid M, Orridge C, Weir R, Browne G, Gafni A, Lewis M, et al. Interprofessional stroke rehabilitation for stroke survivors using home care. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 2011;38(02):317‐34. - PubMed
McDonald 2011 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Haslam C. Email communication 2016.
-
- McDonald A, Haslam C, Yates P, Gurr B, Leeder G, Sayers A. Google Calendar: a new memory aid to compensate for prospective memory deficits following acquired brain injury. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 2011;21(6):784‐807. - PubMed
McEwan 2014 {published data only}
-
- McEwen SE, Wolf T, Baum C, Polatajko H. Combined task‐specific and cognitive strategy training in subacute stroke: a phase II randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2014;45(Suppl 1):ATP110.
McEwen 2015 {published data only}
Miller 2014 {published data only}
-
- Miller LA, Radford K. Testing the effectiveness of group‐based memory rehabilitation in chronic stroke patients. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 2014;24(5):721‐37. - PubMed
Ownsworth 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ownsworth TL, McFarland K. Memory remediation in long‐term acquired brain injury: two approaches in diary training. Brain Injury 1999;13(8):605‐26. - PubMed
Polatajko 2012 {published data only}
-
- Polatajko HJ, McEwen SE, Ryan JD, Baum CM. Pilot randomized controlled trial investigating cognitive strategy use to improve goal performance after stroke. American Journal of Occupational Therapy 2012;66(1):104‐9. - PubMed
Rasmussen 2016 {published data only}
-
- Rasmussen RS, Overgaard K, Østergaard A, Kjær P, Skerris A, Skou C, et al. Post‐stroke rehabilitation at home reduced disability and improved quality of life: a randomized controlled trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2013;35 Suppl 3:94‐5.
-
- Rasmussen RS, Østergaard A, Kjær P, Skerris A, Skou C, Christoffersen J, et al. Stroke rehabilitation at home before and after discharge reduced disability and improved quality of life: a randomised controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2016;30(3):225‐36. - PubMed
Schupp 2002 {published data only}
-
- Schupp W, Rohring S, Kulke H, Peetz H. Home‐based neuropsychological training using tele therapy ‐ practicability and first results. [Abstract]. Proceedings of the 3rd World Congress in Neurological Rehabilitation. 2‐6 April 2002. Venice, Italy, 2002.
Skidmore 2015 {published data only}
Sohlberg 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sohlberg MM, Fickas S, Hung P‐F, Fortier A. A comparison of four prompt modes for route finding for community travellers with severe cognitive impairments. Brain Injury 2007;21(5):531‐8. - PubMed
Tailby 2003 {published data only}
-
- Tailby R, Haslam C. An investigation of errorless learning in memory‐impaired patients: improving the technique and clarifying theory. Neuropsychologia 2003;41(9):1230‐40. - PubMed
Thickpenny‐Davis 2007 {published data only}
-
- Thickpenny‐Davis KL, Barker‐Collo SL. Evaluation of a structured group format memory rehabilitation program for adults following brain injury. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation 2007;22(5):303‐13. - PubMed
Thoene 1995 {published data only}
-
- Thoene AI, Glisky EL. Learning of name‐face associations in memory impaired patients: a comparison of different training procedures. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society 1995;1(1):29‐38. - PubMed
Wilson 2001 {published data only}
Wolf 2015 {unpublished data only}
-
- Wolf TJ. Cognitive Oriented Strategy Training Augmented Rehabilitation (COSTAR) treatment approach for stroke. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01910454. - PMC - PubMed
Yu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Yu J, Hu Y, Wu Y, Chen W, Zhu Y, Cui X, et al. The effects of community‐based rehabilitation on stroke patients in China: a single blind, randomized controlled multicentre trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2009;23(5):408‐17. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Bezdenezhnykh 2014 {published data only}
-
- Bezdenezhnykh A, Prokopenko S, Mozheyko E, Koryagina T, Chernukh T, Shvetsova I, et al. Computer cognitive training for patients with cognitive impairments in acute ischemic stroke. International Journal of Stroke 2014;9:218.
Bezdenezhnykh 2015 {published data only}
-
- Bezdenezhnykh A, Prokopenko S, Mozheiko E, Petrova M, Grippa E, Lipatnikova S, et al. Neuropsychological computer training versus entertaining computer games in patients with post‐stroke cognitive impairments: randomized clinical study. International Journal of Stroke 2015;10 Suppl S2:412.
Matz 2007 {published data only}
-
- Matz K, Brainin M, Teuschl Y, Eckhardt R, Herbst A, Dachenhausen A. Prevention of post‐stroke cognitive decline ‐ a randomized pilot trial testing cognitive training in patients with first lacunar stroke. International Journal of Stroke 2008;23 Suppl 1:400.
-
- Matz K, Teuschl Y, Eckhardt R, Herbst A, Dachenhausen A, Brainin M. Cognitive training in patients with first lacunar stroke ‐ a randomized pilot trial for the prevention of post‐stroke cognitive decline. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2007;23 Suppl 2:42.
Prokopenko 2011 {published data only}
-
- Prokopenko SV, Mozheĭko E, Levin OS, Koriagina TD, Chernykh TV, Berezovskaia MA. Cognitive disorders and its correction in the acute period of ischemic stroke. Zhurnal nevrologii i psikhiatrii imeni SS Korsakova/Ministerstvo zdravookhraneniia i meditsinskoi promyshlennosti Rossiiskoi Federatsii, Vserossiiskoe obshchestvo nevrologov [i] Vserossiiskoe obshchestvo psikhiatrov 2011;112(8 Pt 2):35‐9. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
ISRCTN45171788 {unpublished data only}
-
- Frommelt P. Email communication 2016.
-
- Frommelt P. Neuropsychological rehabilitation: modular cognitive retraining versus compensatory skills training. http://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN45171788.
ISRCTN59754564 {unpublished data only}
-
- Manly T, Peers P. Progressive home‐based working memory and attention training following stroke, implications for spatial bias: a preliminary study. http://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN59754564.
NCT01674790 {published data only}
-
- Mackay‐Lyons M. Combined effects of aerobic exercise and cognitive training on cognition after stroke. ClinicalTrials.gov 2012.
NCT02384057 {unpublished data only}
-
- Shin JH. Cognitive rehabilitation for participants with stroke or brain injury using C8 sciences. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02384057.
NCT02482688 {unpublished data only}
-
- Humphreys GW, Barutchu A. A new rehabilitation treatment following stroke. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02482688.
Sahakian 2016 {unpublished data only}
-
- Sahakian B. Investigation into the efficacy of cognitive training on cognition in adults with brain injury. https://www.ukctg.nihr.ac.uk/trials/trial‐details/trial‐details?trialId=.... [IRAS ID 159857]
Yang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Yang S. Email communication 2016.
-
- Yang S, Ye H, Huang J, Tao J, Jiang C, Lin Z, et al. The synergistic effect of acupuncture and computer‐based cognitive training on post‐stroke cognitive dysfunction: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial of 2x2 factorial design. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2014;14(1):290. - PMC - PubMed
Additional references
Baddeley 1994
-
- Baddeley A, Emslie H, Nimmo‐Smith I. The Doors and People Test: A Test of Visual and Verbal Recall and Recognition. Bury St Edmunds: Thames Valley Test Company, 1994.
Beck 1990
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA. Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) Manual. Oxford: Pearson, 1990.
Beck 2003
-
- Beck AT, Steer R, Brown G. Beck Depression Inventory‐Fast Screen for Medical Patients. San Antonio: Psychological Corporation, 2003.
Broadbent 1982
-
- Broadbent DE, Cooper PF, FitzGerald P, Parkes KR. The Cognitive Failures Questionnaire (CFQ) and its correlates. British Journal of Clinical Psychology 1982;21:1‐16. - PubMed
Cicerone 2000
-
- Cicerone KD, Dahlberg C, Kalmar K, Langenbahn DM, Malec JF, Bergquist TF, et al. Evidence‐based cognitive rehabilitation: recommendations for clinical practice. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2000;81:1596‐615. - PubMed
Cicerone 2005
-
- Cicerone KD, Dahlberg C, Malec JF, Langenbahn DM, Felicetti T, Kneipp S, et al. Evidence‐based cognitive rehabilitation: updated review of the literature from 1998 through 2002. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2005;86:1681‐92. - PubMed
Cicerone 2011
-
- Cicerone KD, Langenbahn DM, Braden C, Malec JF, Kalmar K, Fraas M, et al. Evidence‐based cognitive rehabilitation: updated review of the literature from 2003 through 2008. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2011;92:519‐30. - PubMed
Coughlan 1988
-
- Coughlan A, Storey P. The Wimbledon Self‐Report Scale: emotional and mood appraisal. Clinical Rehabilitation 1988;2(3):207‐13.
Crook 1992
-
- Crook TH, Feher EP, Larrabee GJ. Assessment of memory complaint in age‐associated memory impairment: the MAC‐Q. International Psychogeriatrics 1992;4(02):165‐76. - PubMed
Cumming 2013
-
- Cumming TB, Marshall RS, Lazar RM. Stroke, cognitive deficits, and rehabilitation: still an incomplete picture. International Journal of Stroke 2013;8(1):38‐45. - PubMed
Davis 1995
-
- Davis AM, Cockburn AM, Wade DT, Smith PT. A subjective memory assessment questionnaire for use with elderly people after stroke. Clinical Rehabilitation 1995;9(3):238‐44.
Duncan 1999
-
- Duncan PW, Wallace D, Lai SM, Johnson D, Embretson S, Laster LJ. The stroke impact scale version 2.0 evaluation of reliability, validity, and sensitivity to change. Stroke 1999;30(10):2131‐40. - PubMed
Gillespie 2015
-
- Gillespie DC, Bowen A, Chung CS, Cockburn J, Knapp P, Pollock A. Rehabilitation for post‐stroke cognitive impairment: an overview of recommendations arising from systematic reviews of current evidence. Clinical Rehabilitation 2015;29(2):120‐8. - PubMed
Goldberg 1988
-
- Goldberg DP, Williams PA. User's Guide to the GHQ. Windsor: NFER Nelson, 1988.
GRADEpro [Computer program]
-
- GRADE Working Group, McMaster University. GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed May 2015. Hamilton (ON): GRADE Working Group, McMaster University, 2014.
Hall 1997
-
- Hall KM. The Functional Assessment Measure (FAM). Journal of Rehabilitation Outcomes Measurement 1997;1(3):63‐5.
Hamilton 1987
-
- Hamilton BB, Granger CV, Sherwin FS, Zielezny M, Tashman JS. A uniform national data system for medical rehabilitation. In: Fuhrer JM editor(s). Rehabilitation Outcomes: Analysis and Measurement. Baltimore: Brookes, 1987:137‐47.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Lamb 2013
-
- Lamb F, Anderson J, Saling M, Dewey H. Predictors of subjective cognitive complaint in postacute older adult stroke patients. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2013;94(9):1747‐52. - PubMed
Lincoln 2012
-
- Lincoln NB, Kneebone II, Macniven JAB, Morris RC. Psychological Management of Stroke. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
Mahoney 1965
-
- Mahoney FI. Functional evaluation: the Barthel Index. Maryland State Medical Journal 1965;14:61‐5. - PubMed
Middleton 2014
-
- Middleton LE, Lam B, Fahmi H, Black SE, McIlroy WE, Stuss T, et al. Frequency of domain‐specific cognitive impairment in sub‐acute and chronic stroke. Neurorehabilitation 2014;34(2):305‐12. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman DG. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendation for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomised trials. Lancet 2001;357:1191‐4. - PubMed
Moher 2010
-
- Moher D, Hopewell S, Schulz KF, Montori V, Gøtzsche PC, Devereaux PJ, et al. CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2010;63(8):e1‐e37. - PubMed
Nouri 1987
-
- Nouri FM, Lincoln NB. An extended activities of daily living scale for stroke patients. Clinical Rehabilitation 1987;1(4):301‐5.
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Robertson 2001
-
- Robertson IH, Wilson A. Neuropsychological rehabilitation. In: Fawcett JW, Rosser AE, Dunnett SB editor(s). Brain Damage, Brain Repair. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2001.
Schaapsmeerders 2013
-
- Schaapsmeerders P, Maaijwee NA, Dijk EJ, Rutten‐Jacobs LC, Arntz RM, Schoonderwaldt HC, et al. Long‐term cognitive impairment after first‐ever ischemic stroke in young adults. Stroke 2013;44(6):1621‐8. - PubMed
Snaphaan 2007
-
- Snaphaan L, Leeuw FE. Poststroke memory function in nondemented patients a systematic review on frequency and neuroimaging correlates. Stroke 2007;38(1):198‐203. - PubMed
Sunderland 1983
-
- Sunderland A, Harris JE, Baddeley AD. Do laboratory tests predict everyday memory? A neuropsychological study. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior 1983;22(3):341‐57.
van Rijsbergen 2014
-
- Rijsbergen MWA, Mark RE, Kort PLM, Sitskoorn MM. Subjective cognitive complaints after stroke: a systematic review. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2014;23(3):408‐20. - PubMed
Ware 2001
-
- Ware JE, Kosinski M. SF‐36 Physical & Mental Health Summary Scales: A Manual for Users of Version 1. Quality Metric, 2001.
Wechsler 1997
-
- Wechsler D. Wechsler Memory Scale ‐ Third edition (WMSIII). San Antonio: Harcourt Assessment, 1997.
WHOQoL 1993
-
- WHOQoL Group. Study protocol for the World Health Organization project to develop a Quality of Life assessment instrument (WHOQOL). Quality of Life Research 1993;2(2):153‐9. - PubMed
Williams 1999
-
- Williams LS, Weinberger M, Harris LE, Clark DO, Biller J. Development of a stroke‐specific quality of life scale. Stroke 1999;30(7):1362‐9. - PubMed
Wilson 1985
-
- Wilson BA, Cockburn J, Baddeley A. The Rivermead Behavioural Memory Test. Bury St. Edmunds: Thames Valley Test Company, 1985.
Wilson 2005
-
- Wilson BA, Shiel A, Foley J, Emslie H, Groot Y, Hawkins K, et al. Cambridge Test of Prospective Memory (CAMPROMPT). San Antonio: Pearson Assessment, 2005.
Zigmond 1983
-
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;67(6):361‐70. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
das Nair 2007
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

