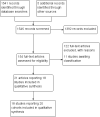
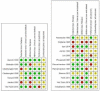
Six months therapy for tuberculous meningitis
- PMID: 27581996
- PMCID: PMC5018659
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012091.pub2
Six months therapy for tuberculous meningitis
Abstract
Background: Tuberculous meningitis (TBM) is the main form of tuberculosis that affects the central nervous system and is associated with high rates of death and disability. Most international guidelines recommend longer antituberculous treatment (ATT) regimens for TBM than for pulmonary tuberculosis disease to prevent relapse. However, longer regimens are associated with poor adherence, which could contribute to increased relapse, development of drug resistance, and increased costs to patients and healthcare systems.
Objectives: To compare the effects of short-course (six months) regimens versus prolonged-course regimens for people with tuberculous meningitis (TBM).
Search methods: We searched the following databases up to 31 March 2016: the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group Specialized Register; the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), published in the Cochrane Library; MEDLINE; EMBASE; LILACS; INDMED; and the South Asian Database of Controlled Clinical Trials. We searched the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (WHO ICTRP) and ClinicalTrials.gov for ongoing trials. We also checked article reference lists and contacted researchers in the field.
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and prospective cohort studies of adults and children with TBM treated with antituberculous regimens that included rifampicin for six months or longer than six months. The primary outcome was relapse, and included studies required a minimum of six months follow-up after completion of treatment.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors (SJ and HR) independently assessed the literature search results for eligibility, and performed data extraction and 'Risk of bias' assessments of the included studies. We contacted study authors for additional information when necessary. Most data came from single arm cohort studies without a direct comparison so we pooled the findings for each group of cohorts and presented them separately using a complete-case analysis. We assessed the quality of the evidence narratively, as using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach was inappropriate with no direct comparisons between short- and prolonged-course regimens.
Main results: Four RCTs and 12 prospective cohort studies met our inclusion criteria, and included a total of 1881 participants with TBM. None of the included RCTs directly compared six months versus longer regimens, so we analysed all data as individual cohorts to obtain relapse rates in each set of cohorts.We included seven cohorts of participants treated for six months, with a total of 458 participants. Three studies were conducted in Thailand, two in South Africa, and one each in Ecuador and Papua New Guinea between the 1980s and 2009. We included 12 cohorts of participants treated for longer than six months (ranging from eight to 16 months), with a total of 1423 participants. Four studies were conducted in India, three in Thailand and one each in China, South Africa, Romania, Turkey and Vietnam, between the late 1970s and 2011.The proportion of participants classified as having stage III disease (severe) was higher in the cohorts treated for six months (33.2% versus 16.9%), but the proportion with known concurrent HIV was higher in the cohorts treated for longer (0/458 versus 122/1423). Although there were variations in the treatment regimens, most cohorts received isoniazid, rifampicin, and pyrazinamide during the intensive phase.Investigators achieved follow-up beyond 18 months after completing treatment in three out of the seven cohorts treated for six months, and five out of the 12 cohorts treated for eight to 16 months. All studies had potential sources of bias in their estimation of the relapse rate, and comparisons between the cohorts could be confounded.Relapse was an uncommon event across both groups of cohorts (3/369 (0.8%) with six months treatment versus 7/915 (0.8%) with longer), with only one death attributed to relapse in each group.Overall, the proportion of participants who died was higher in the cohorts treated for longer than six months (447/1423 (31.4%) versus 58/458 (12.7%)). However, most deaths occurred during the first six months in both treatment cohorts, which suggested that the difference in death rate was not directly related to duration of ATT but was due to confounding. Clinical cure was higher in the group of cohorts treated for six months (408/458 (89.1%) versus longer than six months (984/1336 (73.7%)), consistent with the observations for deaths.Few participants defaulted from treatment with six months treatment (4/370 (1.1%)) versus longer treatment (8/355 (2.3%)), and adherence was not well reported.
Authors' conclusions: In all cohorts most deaths occurred in the first six months; and relapse was uncommon in all participants irrespective of the regimen. Further inferences are probably inappropriate given this is observational data and confounding is likely. These data are almost all from participants who are HIV-negative, and thus the inferences will not apply to the efficacy and safety of the six months regimens in HIV-positive people. Well-designed RCTs, or large prospective cohort studies, comparing six months with longer treatment regimens with long follow-up periods established at initiation of ATT are needed to resolve the uncertainty regarding the safety and efficacy of six months regimens for TBM.
Conflict of interest statement
SJ and HR are employed by the CIDG, which is funded by a grant from the UK Government DFID.
SJ and HR conducted the preliminary work that contributed to the conception and design of this Cochrane Review as part of the evidence review process for the Indian Extra‐Pulmonary TB (INDEX‐TB) Guidelines, a guideline for extrapulmonary TB commissioned by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. Global Health Advocates funded this guideline, and the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi convened it.
RB and MM were part of the technical advisory group on central nervous system TB and took part in discussions that led to the recommendations in the INDEX‐TB Guidelines.
Figures
Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012091
References
References to studies included in this review
Alarcón 1990 {published data only}
-
- Alarcón F, Escalante L, Pérez Y, Banda H, Chacón G, Dueñas G. Tuberculous meningitis. Short course of chemotherapy. Archives of Neurology 1990;47(12):1313‐7. - PubMed
Alvarez‐Uria 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Alvarez‐Uria G, Naik PK, Pakam R, Bachu L, Midde M. Natural history and factors associated with early and delayed mortality in HIV‐infected patients treated of tuberculosis under directly observed treatment short‐course strategy: a prospective cohort study in India. Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Infectious Diseases 2012;2012:502012. [DOI: 10.1155/2012/502012] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Anastasatu 1993 {published data only}
-
- Anastasatu C, Anastasatu O, Murgoci G, Dobre M. [The late results of intensive chemotherapy (9 months) in severe forms of tuberculosis in children]. Pneumoftiziologia 1993;42(4):9‐12. - PubMed
Biddulph 1990 {published data only}
-
- Biddulph J. Short course chemotherapy for childhood tuberculosis. Paediatric Infectious Diseases Journal 1990;9(11):794‐801. - PubMed
Chotmongkol 1991 {published data only}
-
- Chotmongkol V. Treatment of tuberculous meningitis with 6‐month course of chemotherapy. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1991;22(3):372‐4. - PubMed
Chotmongkol 1996 {published data only}
-
- Chotmongkol V, Jitpimolmard S, Thavornpitak Y. Corticosteroid in tuberculous meningitis. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand [Chotmaihet Thangphaet] 1996;79(2):83‐90. - PubMed
Doğanay 1995 {published data only}
-
- Doğanay M, Çalangu S, Turgut H, Bakir M, Aygen B. Treatment of tuberculous meningitis in Turkey. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1989;27(2):135‐8. - PubMed
Donald 1998 {published data only}
-
- Donald PR, Schoeman JF, Zyl LE, Villiers JN, Pretorius M, Springer P. Intensive short course chemotherapy in the management of tuberculous meningitis. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 1998;2(9):704‐11. - PubMed
Iype 2014 {published data only}
Jacobs 1992 {published data only}
-
- Jacobs RF, Sunakorn P, Chotpitayasunonah T, Pope S, Kelleher K. Intensive short course chemotherapy for tuberculous meningitis. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1992;11(3):194‐8. - PubMed
Lau 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lau KK, Yu IT, Chan AC, Wong LK, Tam CM, Sheng B, et al. A registry of tuberculous meningitis in Hong Kong. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2005;9(12):1391‐7. - PubMed
Phuapradit 1987 {published data only}
-
- Phuapradit P, Vejjajiva A. Treatment of tuberculous meningitis: role of short‐course chemotherapy. The Quarterly Journal of Medicine 1987;62(239):249‐58. - PubMed
Ramachandran 1989 {published data only}
-
- Ramachandran P, Duraipandian M, Nagarajan M, Prabhakar R, Ramakrishnan CV, Tripathy SP. Three chemotherapy studies of tuberculous meningitis in children. Tubercle 1986;67(1):17‐29. - PubMed
-
- Ramachandran P, Duraipandian M, Reetha AM, Mahalakshmi SM, Prabhakar R. Long‐term status of children treated for tuberculous meningitis in south India. Tubercle 1989;70(4):235‐9. - PubMed
Ramachandran 1997 {published data only}
-
- Ramachandran P, Duraipandian M, Reetha AM. A 5 year follow‐up study of children treated for tuberculous meningitis with short course chemotherapy. The Indian Journal of Tuberculosis 1997;44:125‐7.
-
- Ramachandran P, Kripasankar AS, Reetha AM, Mahalakshmi SM, Prabhakar R. Short course chemotherapy study in tuberculous meningitis in children. The Indian Journal of Tuberculosis 1997;44:195‐200.
Sharma 2013a {published data only}
Török 2011a {published data only}
-
- Thwaites GE, Nguyen DB, Nguyen HD, Hoang TQ, Do TT, Nguyen TC, et al. Dexamethasone for the treatment of tuberculous meningitis in adolescents and adults. The New England of Journal Medicine 2004;351(17):1741‐51. - PubMed
van Toorn 2014 {published data only}
Visudhiphan 1989 {published data only}
-
- Visudhiphan P, Chiemchanya S. Tuberculous meningitis in children: treatment with isoniazid and rifampicin for twelve months. The Journal of Pediatrics 1989;114(5):875‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Acharya 1985 {published data only}
-
- Acharya VN, Kudva BT, Retnam VJ, Mehta PJ. Adult tuberculous meningitis: comparative study of different chemotherapeutic regimens. The Journal of the Association of Physicians in India 1985;33(9):583‐5. - PubMed
Agrawal 1989 {published data only}
-
- Agrawal M. Prognostic indicators in tubercular meningitis in children. Indian Journal of Tuberculosis 1989;36(3):161‐5.
Alarcón 2013 {published data only}
-
- Alarcón F, Moreira J, Rivera J, Salinas R, Dueñas G, Ende J. Tuberculous meningitis: do modern diagnostic tools offer better prognosis prediction?. The Indian Journal of Tuberculosis 2013;60(1):5‐14. - PubMed
Alvarez‐Uria 2013 {published data only}
-
- Alvarez‐Uria G, Midde M, Pakam R, Naik PK. Initial antituberculous regimen with better drug penetration into cerebrospinal fluid reduces mortality in HIV infected patients with tuberculous meningitis: data from an HIV observational cohort study. Tuberculosis Research and Treatment 2013;2013:242604. - PMC - PubMed
Anuradha 2010 {published data only}
-
- Anuradha HK, Garg RK, Agarwal A, Sinha MK, Verma R, Singh MK, et al. Predictors of stroke in patients of tuberculous meningitis and its effect on the outcome. QJM 2010;103(9):671‐8. - PubMed
Bandyopadhyay 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bandyopadhyay SK, Bandyopadhyay R, Dutta A. Profile of tuberculous meningitis with or without HIV infection and the predicators of adverse outcome. The West Indian Medical Journal 2009;58(6):589‐92. - PubMed
Bhagwati 1986 {published data only}
-
- Bhagwati SN, George K. Use of intrathecal hyaluronidase in the management of tuberculous meningitis with hydrocephalus. Child's Nervous System 1986;2(1):20‐5. - PubMed
Bokade 2014 {published data only}
Cardozo 1976 {published data only}
-
- Cardozo LJ, Raidoo S, Patel BP. Tuberculous meningitis in adult Africans‐problems of diagnosis and management. East African Medical Journal 1976;53(3):134‐42. - PubMed
Chan 1988 {published data only}
-
- Chan KH, Mann KS. Prolonged therapeutic external ventricular drainage: a prospective study. Neurosurgery 1988;23(4):436‐8. - PubMed
Chan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Chan KH, Cheung RT, Lee R, Mak W, Ho SL. Cerebral infarcts complicating tuberculous meningitis. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2005;19(6):391‐5. - PubMed
Chandra 1976 {published data only}
-
- Chandra B. Some aspects of tuberculous meningitis in Surabaya. Proceedings of the Australian Association of Neurologists 1976;13:73‐81. - PubMed
Chugh 2009 {published data only}
-
- Chugh A, Husain M, Gupta RK, Ojha BK, Chandra A, Rastogi M. Surgical outcome of tuberculous meningitis hydrocephalus treated by endoscopic third ventriculostomy: prognostic factors and postoperative neuroimaging for functional assessment of ventriculostomy. Journal of Neurosurgery. Pediatrics 2009;3(5):371‐7. - PubMed
Cotton 1991 {published data only}
-
- Cotton MF, Donald PR, Schoeman JF, Aalbers C, Zyl LE, Lombard C. Plasma arginine vasopressin and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion in tuberculous meningitis. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1991;10(11):837‐42. - PubMed
Cotton 1993 {published data only}
-
- Cotton MF, Donald PR, Schoeman JF, Zyl LE, Aalbers C, Lombard CJ. Raised intracranial pressure, the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion, and arginine vasopressin in tuberculous meningitis. Child's Nervous System 1993;9(1):10‐5; discussion 15‐6. - PubMed
Degefie 2003 {published data only}
-
- Degefie T. Tuberculous meningitis in a district hospital from Southern Ethiopia. Ethiopian Medical Journal 2003;41(4):311‐8. - PubMed
de March‐Ayuela 1994 {published data only}
-
- March‐Ayuela P. Trend in tuberculous meningitis in Barcelona in children aged 0‐4 years: correlation with the annual risk of tuberculous infection. Tubercle and Lung Disease 1994;75(6):423‐8. - PubMed
Dikshit 1976 {published data only}
-
- Dikshit KP, Singh S. Factors influencing prognosis of tuberculous meningitis. Indian Pediatrics 1976;13(8):613‐8. - PubMed
Doğanay 1989 {published data only}
-
- Doğanay M, Bakir M, Dökmetaş I. Treatment of tuberculous meningitis in adults with a combination of isoniazid, rifampicin and streptomycin: a prospective study. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1989;21(1):81‐5. - PubMed
Donald 1986 {published data only}
-
- Donald PR, Burger PJ, Becker WB. Paediatric meningitis in the western Cape. A 3‐year hospital‐based prospective survey. South African Medical Journal 1986;70(7):391‐5. - PubMed
Donald 1996 {published data only}
-
- Donald PR, Cotton MF, Hendricks MK, Schaaf HS, Villiers JN, Willemse TE. Pediatric meningitis in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1996;42(5):256‐61. - PubMed
Eintracht 2000 {published data only}
Elliott 1993 {published data only}
-
- Elliott AM, Halwiindi B, Hayes RJ, Luo N, Tembo G, Machiels L, et al. The impact of human immunodeficiency virus on presentation and diagnosis of tuberculosis in a cohort study in Zambia. The Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1993;96(1):1‐11. - PubMed
Elliott 1995a {published data only}
-
- Elliott AM, Halwiindi B, Hayes RJ, Luo N, Mwinga AG, Tembo G, et al. The impact of human immunodeficiency virus on mortality of patients treated for tuberculosis in a cohort study in Zambia. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1995;89(1):78‐82. - PubMed
Elliott 1995b {published data only}
-
- Elliott AM, Halwiindi B, Hayes RJ, Luo N, Mwinga AG, Tembo G, et al. The impact of human immunodeficiency virus on response to treatment and recurrence rate in patients treated for tuberculosis: two‐year follow‐up of a cohort in Lusaka, Zambia. The Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1995;98(1):9‐21. - PubMed
Erdös 1974 {published data only}
-
- Erdös Z. [Late results (15‐25 years) following therapy of tuberculous meningitis]. Monatsschrift für Kinderheilkunde 1974;122(7):424‐5. - PubMed
Escobar 1975 {published data only}
-
- Escobar JA, Belsey MA, Dueñas A, Medina P. Mortality from tuberculous meningitis reduced by steroid therapy. Pediatrics 1975;56(6):1050‐5. - PubMed
Ganiem 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ganiem AR, Parwati I, Wisaksana R, Zanden A, Beek D, Sturm P, et al. The effect of HIV infection on adult meningitis in Indonesia: a prospective cohort study. AIDS 2009;23(17):2309‐16. - PubMed
Garg 2010 {published data only}
-
- Garg RK, Sharma R, Kar AM, Kushwaha RA, Singh MK, Shukla R, et al. Neurological complications of miliary tuberculosis. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery 2010;112(3):188‐92. - PubMed
Girgis 1978 {published data only}
-
- Girgis NI, Yassin MW, Laughlin LW, Edman DC, Farid Z, Watten RH. Rifampicin in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis. The Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1978;81(12):246‐7. - PubMed
Girgis 1991 {published data only}
-
- Girgis NI, Farid Z, Kilpatrick ME, Sultan Y, Mikhail IA. Dexamethasone adjunctive treatment for tuberculous meningitis. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1991;10(3):179‐83. - PubMed
Girgis 1993 {published data only}
-
- Girgis NI, Sippel JE, Kilpatrick ME, Sanborn WR, Mikhail IA, Cross E, et al. Meningitis and encephalitis at the Abbassia Fever Hospital, Cairo, Egypt, from 1966 to 1989. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1993;48(1):97‐107. - PubMed
Goyal 2014 {published data only}
-
- Goyal P, Srivastava C, Ojha BK, Singh SK, Chandra A, Garg RK, et al. A randomized study of ventriculoperitoneal shunt versus endoscopic third ventriculostomy for the management of tubercular meningitis with hydrocephalus. Child's Nervous System 2014;30(5):851‐7. - PubMed
Guillen 1993 {published data only}
-
- Guillen D, Campos P, Hernández H, Chaparro E. Meningoencefalitis tuberculosa en niños: diez años de experiencia en el Hospital Nacional Cayetano Heredia. Revista Médica Herediana 1993;4(4):182‐7.
Gujjar 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gujjar AR, Srikanth SG, Umamaheshwara Rao GS. HHH regime for arteritis secondary to TB meningitis: a prospective randomized study. Neurocritical Care 2009;10(3):313‐7. - PubMed
Gupta 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gupta A, Garg RK, Singh MK, Verma R, Malhotra HS, Sankhwar SN, et al. Bladder dysfunction and urodynamic study in tuberculous meningitis. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2013;327(1‐2):46‐54. - PubMed
Gupta 2015 {published data only}
Heemskerk 2016 {published data only}
-
- Heemskerk AD, Bang ND, Mai NTH, Chau TTH, Phu NH, Loc PP, et al. Intensified antituberculosis therapy in adults with tuberculous meningitis. The New England Journal of Medicine 2016;374(2):124‐34. - PubMed
Hoose 1990 {published data only}
-
- Hoose C, Eberhardt K, Hartmann W, Wosniok W. Short‐ and long‐term results of tuberculosis therapy with a fixed combination of isoniazid, prothionamide and diaminodiphenylsulfone combined with rifampicin [Kurz‐und Langzeitergebnisse der Tuberkulosetherapie mit einer fixen Kombination aus Isoniazid, Prothionamid und Diaphenylsulfon (IPD) in Verbindung mit Rifampicin]. Pneumologie 1990;44 Suppl 1:458‐9. - PubMed
Immanuel 1990 {published data only}
-
- Immanuel C, Acharyulu GS, Kannapiran M, Segaran R, Sarma GR. Acute phase proteins in tuberculous patients. Indian Journal of Chest Diseases & Allied Sciences 1990;32(1):15‐23. - PubMed
Irfan 1995 {published data only}
-
- Irfan A, Qureshi A. Role of ventriculoperitoneal shunt in post‐tuberculous meningitic hydrocephalous. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 1995;45(2):37‐8. - PubMed
Jain 2011 {published data only}
Jain 2013 {published data only}
Jakka 2005 {published data only}
-
- Jakka S, Veena S, Rao AR, Eisenhut M. Cerebrospinal fluid adenosine deaminase levels and adverse neurological outcome in pediatric tuberculous meningitis. Infection 2005;33(4):264‐6. - PubMed
Jubelt 2006 {published data only}
-
- Jubelt B. Dexamethasone for the treatment of tuberculous meningitis in adolescents and adults. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports 2006;6(6):451‐2. - PubMed
Julka 1998 {published data only}
-
- Julka RK, Deb M, Patwari AK. Tuberculous meningitis and miliary tuberculosis in children: a clinico‐bacteriological profile. Indian Journal of Tuberculosis 1998;45(1):19‐22.
Kalita 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kalita J, Misra UK. Motor and somatosensory evoked potentials in tuberculous meningitis: a clinico‐radiological correlation. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1999;99(4):225‐31. - PubMed
Kalita 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kalita J, Misra UK. Effect of methyl prednisolone on sensory motor functions in tuberculous meningitis. Neurology India 2001;49(3):267‐71. - PubMed
Kalita 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kalita J, Misra UK, Ranjan P. Predictors of long‐term neurological sequelae of tuberculous meningitis: a multivariate analysis. European Journal of Neurology 2007;14(1):33‐7. - PubMed
Kalita 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kalita J, Misra UK, Nair PP. Predictors of stroke and its significance in the outcome of tuberculous meningitis. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2009;18(4):251‐8. - PubMed
Kalita 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kalita J, Misra UK, Prasad S, Bhoi SK. Safety and efficacy of levofloxacin versus rifampicin in tuberculous meningitis: an open‐label randomized controlled trial. The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2014;69(8):2246‐51. - PubMed
Karande 2005a {published data only}
-
- Karande S, Gupta V, Kulkarni M, Joshi A. Prognostic clinical variables in childhood tuberculous meningitis: an experience from Mumbai, India. Neurology India 2005;53(2):191‐5; discussion 195‐6. - PubMed
Karande 2005b {published data only}
-
- Karande S, Gupta V, Kulkarni M, Joshi A, Rele M. Tuberculous meningitis and HIV. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2005;72(9):755‐60. - PubMed
Kingkaew 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kingkaew N, Sangtong B, Amnuaiphon W, Jongpaibulpatana J, Mankatittham W, Akksilp S, et al. HIV‐associated extrapulmonary tuberculosis in Thailand: epidemiology and risk factors for death. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2009;13(6):722‐9. - PubMed
Koh 2007 {published data only}
-
- Koh SB, Kim BJ, Park MH, Yu SW, Park KW, Lee DH. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of cerebral infarction in tuberculous meningitis: a comparative study. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2007;14(11):1073‐7. - PubMed
Kumarvelu 1994 {published data only}
-
- Kumarvelu S, Prasad K, Khosla A, Behari M, Ahuja GK. Randomized controlled trial of dexamethasone in tuberculous meningitis. Tubercle and Lung Disease 1994;75(3):203‐7. - PubMed
Lamprecht 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lamprecht D, Schoeman J, Donald P, Hartzenberg H. Ventriculoperitoneal shunting in childhood tuberculous meningitis. British Journal of Neurosurgery 2001;15(2):119‐25. - PubMed
Lardizabal 1998 {published data only}
-
- Lardizabal DV, Roxas AA Jr. Dexamethasone as adjunctive therapy in adult patients with probable tuberculosis meningitis stage II and III: an open randomized controlled trial. Philippines Journal of Neurology 1998;4:4‐10.
Malhotra 2009 {published data only}
-
- Malhotra HS, Garg RK, Singh MK, Agarwal A, Verma R. Corticosteroids (dexamethasone versus intravenous methylprednisolone) in patients with tuberculous meningitis. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 2009;103(7):625‐34. - PubMed
Marais 2006 {published data only}
-
- Marais BJ, Gie RP, Schaaf HS, Hesseling AC, Enarson DA, Beyers N. The spectrum of disease in children treated for tuberculosis in a highly endemic area. The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2006;10(7):732‐8. - PubMed
Marais 2013 {published data only}
Maree 2007 {published data only}
-
- Maree F, Hesseling AC, Schaaf HS, Marais BJ, Beyers N, Helden P, et al. Absence of an association between Mycobacterium tuberculosis genotype and clinical features in children with tuberculous meningitis. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2007;26(1):13‐8. - PubMed
Mathew 1998 {published data only}
Misra 1996 {published data only}
-
- Misra UK, Kalita J, Srivastava M, Mandal SK. Prognosis of tuberculous meningitis: a multivariate analysis. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1996;137(1):57‐61. - PubMed
Misra 2000 {published data only}
Misra 2010 {published data only}
-
- Misra UK, Kalita J, Nair PP. Role of aspirin in tuberculous meningitis: a randomized open label placebo controlled trial. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2010;293(1‐2):12‐7. - PubMed
Moreira 2008 {published data only}
-
- Moreira J, Alarcon F, Bisoffi Z, Rivera J, Salinas R, Menten J, et al. Tuberculous meningitis: does lowering the treatment threshold result in many more treated patients?. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2008;13(1):68‐75. - PubMed
Nadvi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Nadvi SS, Nathoo N, Annamalai K, Dellen JR, Bhigjee AI. Role of cerebrospinal fluid shunting for human immunodeficiency virus‐positive patients with tuberculous meningitis and hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2000;47(3):644‐9; discussion 649‐50. - PubMed
Narayanan 1982 {published data only}
-
- Narayanan R. Surgical treatment in tuberculous meningitis. Seara Médica Neurocirúrgica 1982;11:33‐9.
Panigatti 2014 {published data only}
-
- Panigatti P, Ratageri VH, Shivanand I, Madhu PK, Shepur TA. Profile and outcome of childhood tuberculosis treated with DOTS ‐ an observational study. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2014;81(1):9‐14. - PubMed
Pardasani 2008 {published data only}
-
- Pardasani V, Shukla G, Singh S, Goyal V, Behari M. Abnormal sleep‐wake cycles in patients with tuberculous meningitis: a case‐control study. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2008;269(1‐2):126‐32. - PubMed
Park 2014 {published data only}
Patwari 1996 {published data only}
-
- Patwari AK, Aneja S, Chandra D, Singhal PK. Long‐term anticonvulsant therapy in tuberculous meningitis‐‐a four‐year follow‐up. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1996;42(2):98‐103. - PubMed
Pepper 2009 {published data only}
-
- Pepper DJ, Marais S, Maartens G, Rebe K, Morroni C, Rangaka MX, et al. Neurologic manifestations of paradoxical tuberculosis‐associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: a case series. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2009;48(11):e96‐107. - PubMed
Phuapradit 1990 {published data only}
Porkert 1997 {published data only}
-
- Porkert MT, Sotir M, Parrott‐Moore P, Blumberg HM. Tuberculous meningitis at a large inner‐city medical center. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences 1997;313(6):325‐31. - PubMed
Radhakrishnan 1990 {published data only}
-
- Radhakrishnan VV, Mathai A. Detection of mycobacterial antigen in cerebrospinal fluid: diagnostic and prognostic significance. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1990;99(1):93‐9. - PubMed
Raghu Raman 1997 {published data only}
Rahajoe 1979 {published data only}
-
- Rahajoe NN, Rahajoe N, Boediman I, Said M, Lazuardi S. The treatment of tuberculosis meningitis in children with a combination of isoniazid rifampicin and streptomycin‐ preliminary report. Tubercle 1979;60(4):245‐50. - PubMed
Rai 2014 {published data only}
Ramzan 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ramzan A, Nayil K, Asimi R, Wani A, Makhdoomi R, Jain A. Childhood tubercular meningitis: an institutional experience and analysis of predictors of outcome. Pediatric Neurology 2013;48(1):30‐5. - PubMed
Ranjan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ranjan P, Kalita J, Misra UK. Serial study of clinical and CT changes in tuberculous meningitis. Neuroradiology 2003;45(5):277‐82. - PubMed
Rao 1982 {published data only}
-
- Rao GR. Tuberculous mortality in an urban complex in central India: a study of long‐term trends. Tubercle 1982;63(3):187‐93. - PubMed
Rao 2013 {published data only}
Raut 2013 {published data only}
-
- Raut T, Garg RK, Jain A, Verma R, Singh MK, Malhotra HS, et al. Hydrocephalus in tuberculous meningitis: incidence, its predictive factors and impact on the prognosis. The Journal of Infection 2013;66(4):330‐7. - PubMed
Rojas‐Echeverri 1996 {published data only}
-
- Rojas‐Echeverri LA, Soto‐Hernández JL, Garza S, Martínez‐Zubieta R, Miranda LI, García‐Ramos G, et al. Predictive value of digital subtraction angiography in patients with tuberculous meningitis. Neuroradiology 1996;38(1):20‐4. - PubMed
Ruslami 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ruslami R, Ganiem AR, Dian S, Apriani L, Achmad TH, Ven AJ, et al. Intensified regimen containing rifampicin and moxifloxacin for tuberculous meningitis: an open‐label, randomised controlled phase 2 trial. The Lancet. Infectious Diseases 2013;13(1):27‐35. - PubMed
Saleem 2011 {published data only}
-
- Saleem K, Shah ZH, Siddique K, Abaidullah S, Iqbal M. Predictors of complications of tuberculous meningitis. Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences 2011;5(2):292‐6.
Saleem 2015 {published data only}
-
- Saleem K, Nasrullah M, Shafiq F. Is CT scan poor predictor of complicated tuberculous meningitis?. Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences 2015;9(1):26‐30.
Salekeen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Salekeen S, Mahmood K, Naqvi IH, Baig MY, Akhter ST, Abbasi A. Clinical course, complications and predictors of mortality in patients with tuberculous meningitis‐‐an experience of fifty two cases at Civil Hospital Karachi, Pakistan. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2013;63(5):563‐7. - PubMed
Savula 1975 {published data only}
-
- Savula MM, Stepanova RV, Piatnochka IT, Shevchuk MP, Rasevich MG. Late observations of patients following tuberculous meningitis. Vrachebnoe Deloe 1975;3:95‐8. - PubMed
Schoeman 1990 {published data only}
-
- Schoeman CJ. The epidemiology and outcome of childhood tuberculous meningitis. The Pelonomi Hospital experience. South African Medical Journal 1990;78(5):245‐7. - PubMed
Schoeman 1991 {published data only}
-
- Schoeman J, Donald P, Zyl L, Keet M, Wait J. Tuberculous hydrocephalus: comparison of different treatments with regard to ICP, ventricular size and clinical outcome. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1991;33(5):396‐405. - PubMed
Schoeman 1997a {published data only}
-
- Schoeman CJ, Herbst I, Nienkemper DC. The effect of tuberculous meningitis on the cognitive and motor development of children. South African Medical Journal 1997;87(1):70‐2. - PubMed
Schoeman 1997b {published data only}
-
- Schoeman JF, Zyl LE, Laubscher JA, Donald PR. Effect of corticosteroids on intracranial pressure, computed tomographic findings, and clinical outcome in young children with tuberculous meningitis. Pediatrics 1997;99(2):226‐31. - PubMed
Schoeman 2000a {published data only}
-
- Schoeman JF, Laubscher JA, Donald PR. Serial lumbar CSF presure measurements and cranial computed tomographic findings in childhood tuberculous meningitits. Child's Nervous System 2000;16(4):203‐8; discussion 209. - PubMed
Schoeman 2000b {published data only}
-
- Schoeman JF, Springer P, Ravenscroft A, Donald PR, Bekker LG, Rensburg AJ, et al. Adjunctive thalidomide therapy of childhood tuberculous meningitis: possible anti‐inflammatory role. Journal of Child Neurology 2000;15(8):497‐503. - PubMed
Schoeman 2002 {published data only}
-
- Schoeman J, Wait J, Burger M, Zyl F, Fertig G, Rensburg AJ, et al. Long‐term follow up of childhood tuberculous meningitis. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 2002;44(8):522‐6. - PubMed
Schoeman 2004 {published data only}
-
- Schoeman JF, Springer P, Rensburg AJ, Swanevelder S, Hanekom WA, Haslett PA, et al. Adjunctive thalidomide therapy for childhood tuberculous meningitis: results of a randomized study. Journal of Child Neurology 2004;19(4):250‐7. - PubMed
Schoeman 2011 {published data only}
-
- Schoeman JF, Janse van Rensburg A, Laubscher JA, Springer P. The role of aspirin in childhood tuberculous meningitis. Journal of Child Neurology 2011;26(8):956‐62. - PubMed
Shah 2014 {published data only}
-
- Shah I, Meshram L. High dose versus low dose steroids in children with tuberculous meningitis. Journal of Clin Neuroscience 2014;21(5):761‐4. - PubMed
Shahbaz 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shahbaz N, Hassan Y, Kashif S, Abdullah M. Middle cerebral artery infarction in central nervous system tuberculosis. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences 2011;27(4):802‐5.
Sharma 2013b {published data only}
-
- Sharma HK, Gupta SK, Sudan SS, Sharma R. Tuberculous meningitis ‐ a clinico‐radiological study. JK Science 2013;15(4):198‐201.
Shor 1973 {published data only}
-
- Shor IIa. Work capacity of adolescents and adults with tuberculous meningitis. Problemy Tuberkuleza 1973;51(5):12‐4. - PubMed
Simmons 2006 {published data only}
-
- Simmons CP, Thwaites GE, Quyen NTH, Torok E, Hoang DM, Chau TTH, et al. Pretreatment intracerebral and peripheral blood immune responses in vietnamese adults with tuberculous meningitis: diagnostic value and relationship to disease severity and outcome. Journal of Immunology 2006;176(3):2007‐14. - PubMed
Singh 1994 {published data only}
-
- Singh BS, Patwari AK, Deb M. Serum sodium and osmolal changes in tuberculous meningitis. Indian Pediatrics 1994;31(11):1345‐50. - PubMed
Singh 1998 {published data only}
-
- Singh SK, Chandra J, Patwari AK, Aneja S, Anand VK, Dutta AK. Tuberculous meningitis in early infancy. Indian Pediatrics 1998;35(9):887‐90. - PubMed
Springer 2009 {published data only}
-
- Springer P, Swanevelder S, Toorn R, Rensburg AJ, Schoeman J. Cerebral infarction and neurodevelopmental outcome in childhood tuberculous meningitis. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology 2009;13(4):343‐9. - PubMed
Swamy 1987 {published data only}
-
- Swamy R, Acharyulu GS, Duraipandian M, Jawahar MS, Ramachandran R, Sarma GR. Liver function tests during treatment of tuberculosis with short‐course regimens containing isoniazid, rifampicin & pyrazinamide. Indian Journal of Medical Research 1987;86:549‐57. - PubMed
Te Brake 2015 {published data only}
-
- Brake L, Dian S, Ganiem AR, Ruesen C, Burger D, Donders R, et al. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis of an intensified regimen containing rifampicin and moxifloxacin for tuberculous meningitis. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2015;45(5):496‐503. - PubMed
Thwaites 2002 {published data only}
-
- Thwaites GE, Chau TT, Caws M, Phu NH, Chuong LV, Sinh DX, et al. Isoniazid resistance, mycobacterial genotype and outcome in Vietnamese adults with tuberculous meningitis. The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2002;6(10):865‐71. - PubMed
Thwaites 2003a {published data only}
-
- Thwaites GE. The diagnosis and pathophysiology of tuberculous meningitis in Vietnamese adults [PhD Thesis]. Ann Arbor (USA): Open University (United Kingdom), 2003.
Thwaites 2003b {published data only}
-
- Thwaites GE, Simmons CP, Quyen NTH, Chau TTH, Mai PP, Dung NT, et al. Pathophysiology and prognosis in Vietnamese adults with tuberculous meningitis. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2003;188(8):1105‐15. - PubMed
Thwaites 2005b {published data only}
-
- Thwaites GE, Lan NT, Dung NH, Quy HT, Oanh DT, Thoa NT, et al. Effect of antituberculosis drug resistance on response to treatment and outcome in adults with tuberculous meningitis. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2005;192(1):79‐88. - PubMed
Thwaites 2005c {published data only}
-
- Thwaites GE, Duc Bang N, Huy Dung N, Thi Quy H, Thi Tuong Oanh D, Thi Cam Thoa N, et al. The influence of HIV infection on clinical presentation, response to treatment, and outcome in adults with tuberculous meningitis. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2005;192(12):2134‐41. - PubMed
Thwaites 2007 {published data only}
Thwaites 2011 {published data only}
Torok 2008 {published data only}
Török 2011b {published data only}
van der Merwe 2009 {published data only}
-
- Merwe DJ, Andronikou S, Toorn R, Pienaar M. Brainstem ischemic lesions on MRI in children with tuberculous meningitis: with diffusion weighted confirmation. Child's Nervous System 2009;25(8):949‐54. - PubMed
van Toorn 2012 {published data only}
-
- Toorn R, Springer P, Laubscher JA, Schoeman JF. Value of different staging systems for predicting neurological outcome in childhood tuberculous meningitis. The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2012;16(5):628‐32. - PubMed
Wait 2010 {published data only}
-
- Wait JW, Schoeman JF. Behaviour profiles after tuberculous meningitis. Journal of Trop Pediatrics 2010;56(3):166‐71. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Caliman‐Sturdza 2010 {published data only}
-
- Caliman‐Sturdza OA, Mihalache D, Luca CM, Dorobăţ C. [Clinical aspects of tuberculous meningitis in children]. Revista medico‐chirurgicală̆ a Societă̆ţ̜ii de Medici ş̧i Naturaliş̧ti din Iaş̧i 2010;114(3):743‐7. - PubMed
Carrasco 1988 {published data only}
-
- Carrasco CE. Nuevas expectativas en el tratamiento y pronóstico de la meningitis tuberculosa. Enfermedades Respiratorias y Cirugía Torácica 1988;4(3):122‐3.
Das Gupta 2005 {published data only}
-
- Das Gupta A, Mania RN, Sahu GN. Treatment of HIV related tuberculosis: experience from a tertiary care hospital in eastern India. Lung India 2005;22(1):5‐11.
Gunawardhana 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gunawardhana SA, Somaratne SC, Fernando MA, Gunaratne PS. Tuberculous meningitis in adults: a prospective study at a tertiary referral centre in Sri Lanka. The Ceylon Medical Journal 2013;58(1):21‐5. - PubMed
Kilincoglu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kilincoglu BF, Dalkilic T, Dincbal MN, Aydin Y. Shunting in hydrocephalus due to tuberculous meningitis. Cases presenting with high cerebrospinal fluid proteins in pediatric age. Journal of Neurosurgical Sciences 2009;53(2):49‐53. - PubMed
Mahadevan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mahadevan B, Mahadevan S, Serane V T. Prognostic factors in childhood tuberculous meningitis. The Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2002;48(6):362‐5. - PubMed
Mahajan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Mahajan SK, Sood BR, Machhan P, Gupta D, Sharma A. Tubercular meningitis: a blessing?. Indian Practitioner 2004;57(4):265‐6.
Nair 2005 {published data only}
-
- Nair PK, Bobade O, Kappikar GV. Tuberculous meningitis. Indian Practitioner 2005;58(6):379‐81.
Rahman 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rahman ML, Basher A, Rashid M, Islam M, Kuddus R, Arif SM, et al. Central nervous system tuberculosis and adjuvant corticosteroid therapy. Mymensingh Medical Journal 2009;18(1):47‐51. - PubMed
Yadav 2004 {published data only}
-
- Yadav YR, Pande S, Raina VK, Singh M. Lumboperitoneal shunts: review of 409 cases. Neurology India 2004;52(2):188‐90. - PubMed
Yadav 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yadav YR, Parihar V, Agrawal M, Bhatele PR. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in tubercular meningitis with hydrocephalus. Neurology India 2011;59(6):855‐60. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
NCT02454569 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02454569. Vicente Ferrer HIV Cohort Study (VFHCS). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02454569?term=Vicente+Ferrer+HIV+Cohort+S... (first received 15 May 2015). [NCT02454569]
Additional references
Alvarez‐Uria 2015
American Thoracic Society 2003
-
- American Thoracic Society, CDC, Infectious Diseases Society of America. Treatment of tuberculosis. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Recommendations and Reports 2003;52(RR‐11):1‐77. - PubMed
Conde 2009
CPG 2009
-
- Working Group of the Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Tuberculosis, Centro Cochrane Iberoamericano (Iberoamerican Cochrane Centre), coordinator. Clinical Practice Guideline on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Tuberculosis. Quality Plan for the Spanish National Healthcare System of the Spanish Ministry for Health, Social Policy and Equality; Agència d’Informació, Avaluació i Qualitat en Salut de Catalunya (AIAQS ‐ Agency for Information, Evaluation, and Quality in Health of Catalonia); 2009. Clinical Practice Guidelines in the Spanish National Healthcare System: CAHTA n.º 2007/26. http://www.guiasalud.es/GPC/GPC_473_Tuberculosis_AIAQS_compl_en.pdf (accessed 15 May 2015).
Department of Health South Africa 2014
-
- Department of Health South Africa. National Tuberculosis Management Guidelines 2014. http://www.sahivsoc.org/upload/documents/NTCP_Adult_TB%20Guidelines%2027... (accessed 25 July 2015).
Donald 2010a
Donald 2010b
Downs 1998
Gordon 1972
-
- Gordon A, Parsons M. The place of corticosteroids in the management of tuberculous meningitis. British Journal of Hospital Medicine 1972;7:651‐5.
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383‐94. - PubMed
Heemskerk 2011
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
INDEX‐TB 2016
-
- INDEX‐TB Guidelines Group. INDEX‐TB Guidelines ‐ Guidelines on Extra‐Pulmonary Tuberculosis for India. INDEX‐TB Guidelines ‐ Guidelines on Extra‐Pulmonary Tuberculosis for India. First Edition. New Delhi: World Health Organization Country Office India, 2016.
IUATLD 2010
-
- International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. Management of Tuberculosis. A Guide to the Essentials of Good Practice. 6th edition, 2010. http://www.theunion.org/what‐we‐do/publications/technical/english/pub_or... (accessed 25 July 2015).
Jullien 2015
-
- Jullien S. Length of treatment for TB meningitis: from evidence to recommendation in India [Master dissertation]. Liverpool, UK: Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, 2015.
Marais 2010
-
- Marais S, Thwaites G, Schoeman JF, Török ME, Misra UK, Prasad K, et al. Tuberculous meningitis: a uniform case definition for use in clinical research. The Lancet. Infectious Diseases 2010;10(11):803‐12. - PubMed
Migliori 2012
MRC 1948
-
- Medical Research Council. Streptomycin treatment of tuberculous meningitis. The Lancet 1948;1(6503):582‐96. - PubMed
NICE 2011
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Tuberculosis: clinical diagnosis and management of tuberculosis, and measures for its prevention and control. NICE guidelines [CG117]. March 2011. http://doctor‐ru.org/main/1000/1025.pdf (accessed 1 February 2016). - PubMed
Prasad 2016
Principi 2012
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
RNTCP 2005
-
- Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme. Technical and Operational Guidelines for Tuberculosis Control, 2005. http://www.tbonline.info/media/uploads/documents/technical_&_operati... (accessed 31 July 2015).
RNTCP 2012
-
- Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme. National guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of pediatric tuberculosis. 2012. http://tbcindia.nic.in/WriteReadData/l892s/3175192227Paediatric%20guidel... (accessed 19 August 2015).
SEIP 2008
-
- Sociedad Española de Infectología Pediátrica. Treatment of extrapulmonary tuberculosis and complicated forms of pulmonary tuberculosis [Documento de concenso sobre el tratamiento de la tuberculosis extrapulmonar y formas complicadas de tuberculosis pulmonar]. Anales de Pediatría 2008;69(3):271‐8. - PubMed
Sterne 2016
-
- Sterne JAC, Higgins JPT, Reeves BC on behalf of the development group for ROBINS‐I. A tool for assessing Risk Of Bias In Non‐randomized Studies of Interventions, Version 7 March 2016. http://www.riskofbias.info (accessed 7 August 2016).
TB CARE I 2014
-
- TB CARE I. International Standards for Tuberculosis Care. 3rd edition, 2014. https://www.thoracic.org/members/assemblies/assemblies/mtpi/resources/is... (accessed 15 May 2015).
Teasdale 1974
-
- Teasdale G, Jennett B. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. The Lancet 1974;2(7872):81‐4. - PubMed
Thwaites 2005a
-
- Thwaites GE, Hien TT. Tuberculous meningitis: many questions, too few answers. The Lancet. Neurology 2005;4(3):160‐70. - PubMed
Thwaites 2009
-
- Thwaites G, Fisher M, Hemingway C, Scott G, Solomon T, Innes J, British Infection Society. British Infection Society guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis of the central nervous system in adults and children. The Journal of Infection 2009;59(3):167‐87. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2009.06.011] - DOI - PubMed
Thwaites 2013
Török 2015
van Loenhout‐Rooyackers 2001
-
- Loenhout‐Rooyackers JH, Keyser A, Laheij RJF, Verbeek ALM, Meer JWM. Tuberculosis meningitis: is a 6‐month treatment regimen sufficient?. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2001;5(11):1028‐35. - PubMed
WHO 2010a
-
- World Health Organization. Treatment of tuberculosis guidelines. 4th edition, 2010. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44165/1/9789241547833_eng.pdf?u... (accessed 15 May 2015).
WHO 2010b
-
- World Health Organization. Rapid advice. Treatment of tuberculosis in children. 2010. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44444/1/9789241500449_eng.pdf (accessed 26 May 2015). - PubMed
WHO 2013
-
- World Health Organization. Definitions and reporting framework for tuberculosis ‐ 2013 revision (updated December 2014). http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/79199/1/9789241505345_eng.pdf (accessed 01 February 2016).
WHO 2014
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2014. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/137094/1/9789241564809_eng.pdf (accessed 21 September 2015).
WHO 2015
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2015. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/191102/1/9789241565059_eng.pdf?... (accessed 22 March 2016).
Woodfield 2008
Yaramiş 1998
-
- Yaramiş A, Gurkan F, Elevli M, Söker M, Haspolat K, Kirbaş G, et al. Central nervous system tuberculosis in children: a review of 214 cases. Pediatrics 1998;102(5):E49. - PubMed
Ziganshina 2013
Zumla 2014
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous