Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene polymorphisms and osteoporosis in Thai menopausal women
- PMID: 27582019
- PMCID: PMC5007848
- DOI: 10.1186/s12952-016-0059-7
Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene polymorphisms and osteoporosis in Thai menopausal women
Abstract
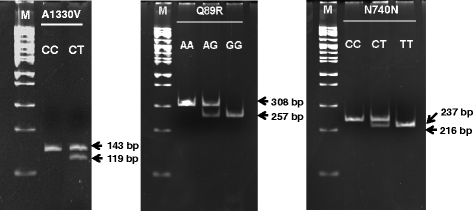
Background: Osteoporosis, characterized by low bone mineral density (BMD) and high bone fracture risk, is prevalent in Thai menopausal women. Genetic factors are known to play a key role in BMD. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5), a co-receptor in the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, is involved in many aspects of bone biology. As coding single nucleotide polymorphisms (cSNPs) of LRP5, including A1330V (rs3736228), and Asian-related Q89R (rs41494349) and N740N (rs2306862), are associated with lowered BMD, this study aimed to determine the relationship between these LRP5 polymorphisms and BMD in 277 Thai menopausal women.
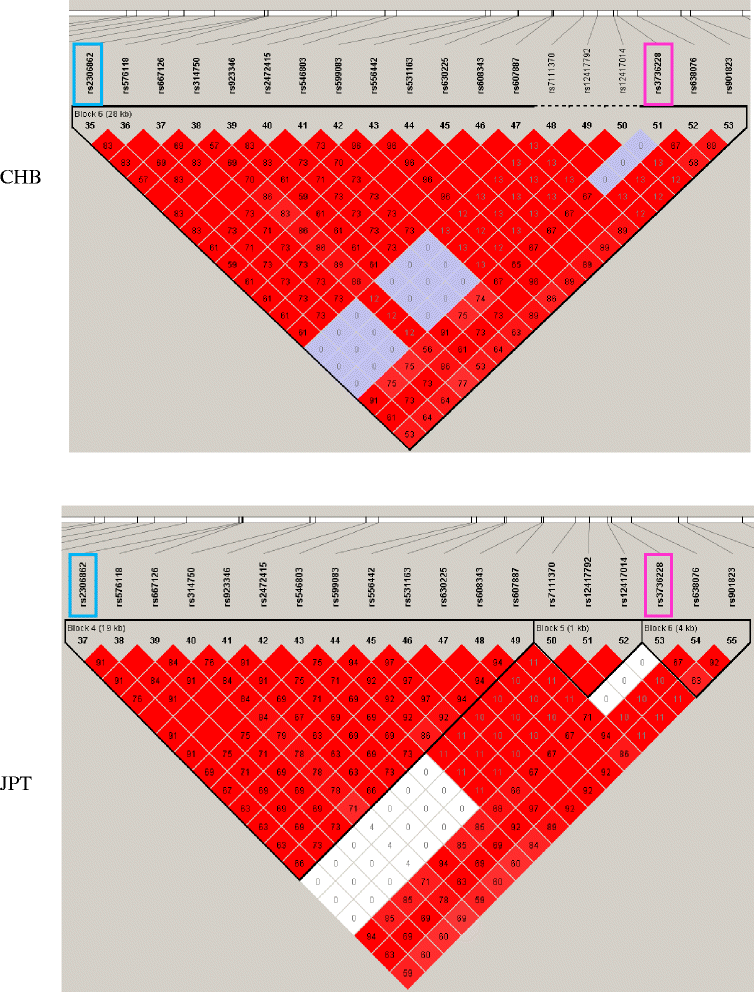
Results: Only rs3736228 deviated from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium of allele frequency (p = 0.022). The median, range and p value for the BMD related to each SNP parameter were compared (Mann-Whitney U test). Significant differences were observed between wild-type and risk alleles for both rs3736228 (total radial, p = 0.011; and radial 33, p = 0.001) and rs2306862 (radial 33: p = 0.015) SNPs, with no significant difference for rs41494349 SNP. Linkage disequilibrium was strong for both rs3736228 and rs2306862 SNPs. Haplotype analysis identified high CC frequency in both normal and osteopenia/osteoporosis groups, with a significant odds ratio for carrying the TT haplotype; however, this was non-significant after adjusting for age. Multivariate binary logistic regression analysis performed for rs3736228 showed that individuals with a body mass index <25 kg/m(2) had an increased risk of osteoporosis for each decade, but the polymorphism had no effect.
Conclusions: This study did not identify LRP5 polymorphisms as a risk factor for osteoporosis in Thai menopausal women. Further studies with larger sample sizes are needed to further clarify the role of LRP5 as a genetic determinant of osteoporosis.
Keywords: Coding single nucleotide polymorphisms; Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5); Menopausal Thai women; Osteopenia; Osteoporosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of the A1330V and V667M polymorphisms of LRP5 with bone mineral density in Greek peri- and postmenopausal women.Maturitas. 2011 Oct;70(2):188-93. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2011.07.016. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Maturitas. 2011. PMID: 21840657
-
Impact of genetic variants of IL-6, IL6R, LRP5, ESR1 and SP7 genes on bone mineral density in postmenopausal Mexican-Mestizo women with obesity.Gene. 2013 Oct 10;528(2):216-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.07.008. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23891823
-
Association of a single-nucleotide variation (A1330V) in the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene (LRP5) with bone mineral density in adult Japanese women.Bone. 2007 Apr;40(4):997-1005. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2005.06.025. Epub 2007 Feb 15. Bone. 2007. PMID: 17306638
-
Common polymorphism in the LRP5 gene may increase the risk of bone fracture and osteoporosis.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:290531. doi: 10.1155/2014/290531. Epub 2014 Dec 14. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25580429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Wnt signaling molecules related to osteoporosis].Clin Calcium. 2013 Jun;23(6):855-60. Clin Calcium. 2013. PMID: 23719498 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Identification of aberrantly expressed long non-coding RNAs in postmenopausal osteoporosis.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jun;41(6):3537-3550. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3575. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29568943 Free PMC article.
-
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway has a healing ability for periapical periodontitis.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 4;11(1):19673. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99231-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34608236 Free PMC article.
-
The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) 4037C>T polymorphism: candidate for susceptibility to type 1 diabetes mellitus.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Aug;62(4):480-484. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000057. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30304114 Free PMC article.
-
LRP5-/6 gene polymorphisms and its association with risk of abnormal bone mass in postmenopausal women.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 May 18;18(1):369. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03829-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37202775 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Genome Sequencing Unravels New Genetic Determinants of Early-Onset Familial Osteoporosis and Low BMD in Malta.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jan 23;13(2):204. doi: 10.3390/genes13020204. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205249 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

