Clinical application of DEX/CRH test and multi-channel NIRS in patients with depression
- PMID: 27582123
- PMCID: PMC5007847
- DOI: 10.1186/s12993-016-0108-x
Clinical application of DEX/CRH test and multi-channel NIRS in patients with depression
Abstract
Background: To reduce the number of patients with depression, biomarkers for clarifying psychiatric disorders are warranted. Numerous candidates have been proposed; however, near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) with multi-channel probes and a dexamethasone/corticotropin-releasing hormone (DEX/CRH) test are still surviving for practical demand. Thirty-one outpatients with depressed moods were analyzed using both biological tests.
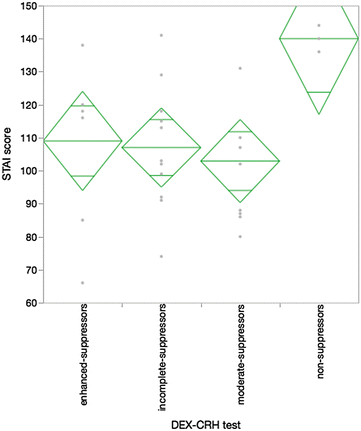
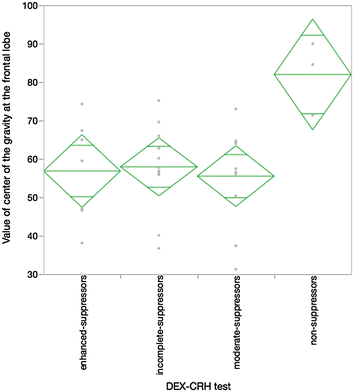
Results: The non-suppressors, as indicated by the DEX/CRH test, exhibited a high severity on the Hamilton Depression Scale and severe anxiety on the State Trait Anxiety Scale. In addition, a unique response was identified via NIRS in the same group suggested by the DEX/CRH assessment.
Conclusions: The results obtained from these biological tests did not fit well with the category defined by operative diagnostic criteria, such as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders or The International Classification of Diseases. Thus, it is critical that the utility evaluations of candidate biomarkers not be assessed by comparisons with the categorized criteria for a specific psychiatric disorder. Trial registration UMIN000013214, Registered 21 February 2014.
Keywords: Biomarker; DEX/CRH test; Depression; HAMD; NIRS.
Figures

References
-
- Berman RM, Fava M, Thase ME, Trivedi MH, Swanink R, Mcquade RD, Carson WH, Adson D, Taylor L, Hazel J, Marcus RN. Aripiprazole augmentation in major depressive disorder: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with inadequate response to antidepressants. CNS Spectr. 2009;14:197–206. doi: 10.1017/S1092852900020216. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

