Genome-Wide Analysis of MicroRNA Responses to the Phytohormone Abscisic Acid in Populus euphratica
- PMID: 27582743
- PMCID: PMC4988358
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01184
Genome-Wide Analysis of MicroRNA Responses to the Phytohormone Abscisic Acid in Populus euphratica
Abstract
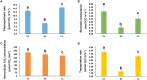
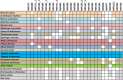
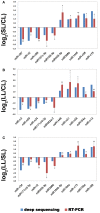
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a type of non-coding small RNA with a regulatory function at the posttranscriptional level in plant growth development and in response to abiotic stress. Previous studies have not reported on miRNAs responses to the phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA) at a genome-wide level in Populus euphratica, a model tree for studying abiotic stress responses in woody plants. Here we analyzed the miRNA response to ABA at a genome-wide level in P. euphratica utilizing high-throughput sequencing. To systematically perform a genome-wide analysis of ABA-responsive miRNAs in P. euphratica, nine sRNA libraries derived from three groups (control, treated with ABA for 1 day and treated with ABA for 4 days) were constructed. Each group included three libraries from three individual plantlets as biological replicate. In total, 151 unique mature sequences belonging to 75 conserved miRNA families were identified, and 94 unique sequences were determined to be novel miRNAs, including 56 miRNAs with miRNA(*) sequences. In all, 31 conserved miRNAs and 31 novel miRNAs response to ABA significantly differed among the groups. In addition, 4132 target genes were predicted for the conserved and novel miRNAs. Confirmed by real-time qPCR, expression changes of miRNAs were inversely correlated with the expression profiles of their putative targets. The Populus special or novel miRNA-target interactions were predicted might be involved in some biological process related stress tolerance. Our analysis provides a comprehensive view of how P. euphratica miRNA respond to ABA, and moreover, different temporal dynamics were observed in different ABA-treated libraries.
Keywords: ABA; Populus euphratica; high-throughput sequencing; microRNA; target.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exploration of ABA Responsive miRNAs Reveals a New Hormone Signaling Crosstalk Pathway Regulating Root Growth of Populus euphratica.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 16;19(5):1481. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051481. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29772702 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide characterization of new and drought stress responsive microRNAs in Populus euphratica.J Exp Bot. 2011 Jul;62(11):3765-79. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err051. Epub 2011 Apr 21. J Exp Bot. 2011. PMID: 21511902 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of salt-responsive and novel microRNAs in Populus euphratica by deep sequencing.BMC Genet. 2014;15 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-15-S1-S6. Epub 2014 Jun 20. BMC Genet. 2014. PMID: 25079824 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory role of abscisic acid on cadmium uptake, accumulation and translocation in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 13;13:953717. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.953717. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36176683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral Roles of Abscisic Acid in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Oct 11;8:1760. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01760. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 29075279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and molecular characterization of miRNAs and their target genes associated with seed development through small RNA sequencing in chickpea.Funct Integr Genomics. 2021 Mar;21(2):283-298. doi: 10.1007/s10142-021-00777-w. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Funct Integr Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33630193
-
Characterization of Conserved and Novel microRNAs in Lilium lancifolium Thunb. by High-Throughput Sequencing.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 13;8(1):2880. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21193-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29440670 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of ABA Responsive miRNAs Reveals a New Hormone Signaling Crosstalk Pathway Regulating Root Growth of Populus euphratica.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 16;19(5):1481. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051481. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29772702 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of miRNA-mediated fertility regulation network of cytoplasmic male sterility during flower bud development in soybean.3 Biotech. 2019 Jan;9(1):22. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1543-1. Epub 2019 Jan 2. 3 Biotech. 2019. PMID: 30622860 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel miRNAs and Their Target Genes in the Response to Abscisic Acid in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 1;22(13):7153. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137153. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 57, 289–300.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

