Neurokinin-1 inhibitors in the prevention of nausea and vomiting from highly emetogenic chemotherapy: a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 27583032
- PMCID: PMC4981292
- DOI: 10.1177/1758834016654902
Neurokinin-1 inhibitors in the prevention of nausea and vomiting from highly emetogenic chemotherapy: a network meta-analysis
Abstract
A network meta-analysis of the comparative effectiveness of neurokinin 1 (NK-1) inhibitors in the prophylaxis of highly emetogenic chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting has been conducted. Eligible studies included randomized trials evaluating aprepitant, fosaprepitant, netupitant (NEPA), casopitant and rolapitant containing regimens in the setting of highly emetogenic chemotherapy. Primary outcomes of interest include complete response (CR) and rate of no significant nausea. After preclusion of ineligible studies, 19 studies were included in the final analysis. The majority of the regimens containing NK-1 inhibitors (including NEPA, aprepitant/palonosetron (palono)/dexamethasone (dexa), casopitant/granisetron (grani) or ondansetron (ondan)/dexa, aprepitant/ondan/dexa) are better than regimens not containing them (palono/dexa, ondan/dexa, grani/dexa) in terms of achieving a CR in the overall phase. Moreover, casopitant/grani or ondan/dexa and aprepitant/grani or ondan/dexa are better than rolapitant/ondan or grani/dexa in terms of CR achievement [odds ratio (OR) 1.62, 95% credible interval (CrI) 1.14-2.23, and OR 1.28, 95% CrI 1.01-1.59, respectively]. Taking into consideration the limitations of cross-trial comparisons, regimens containing neurokinin inhibitors are associated with higher CR rates than regimens not containing them. Moreover, casopitant and aprepitant regimens seem to be more effective than rolapitant regimens.
Keywords: chemotherapy; nausea; neurokinin; vomiting.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
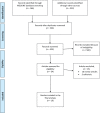


References
-
- Aapro M., Grunberg S., Manikhas G., Olivares G., Suarez T., Tjulandin S., et al. (2006) A phase III, double-blind, randomized trial of palonosetron compared with ondansetron in preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting following highly emetogenic chemotherapy. Ann Oncol 17: 1441–1449. - PubMed
-
- De Wit R., Herrstedt J., Rapoport B., Carides A., Carides G., Elmer M., et al. (2003) Addition of the oral NK1 antagonist aprepitant to standard antiemetics provides protection against nausea and vomiting during multiple cycles of cisplatin-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 21: 4105–4111. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

