Long-acting recombinant fusion protein linking coagulation factor IX with albumin (rIX-FP) in children. Results of a phase 3 trial
- PMID: 27583313
- PMCID: PMC5039316
- DOI: 10.1160/TH16-03-0179
Long-acting recombinant fusion protein linking coagulation factor IX with albumin (rIX-FP) in children. Results of a phase 3 trial
Abstract
A global phase 3 study evaluated the pharmacokinetics, efficacy and safety of a recombinant fusion protein linking coagulation factor IX with albumin (rIX-FP) in 27 previously treated male children (1-11 years) with severe and moderately severe haemophilia B (factor IX [FIX] activity ≤2 IU/dl). All patients received routine prophylaxis once every seven days for up to 77 weeks, and treated any bleeding episodes on-demand. The mean terminal half-life of rIX-FP was 91.4 hours (h), 4.3-fold longer than previous FIX treatment and clearance was 1.11 ml/h/kg, 6.4-fold slower than previous FIX treatment. The median (Q1, Q3) annualised spontaneous bleeding rate was 0.00 (0.00, 0.91) and was similar between the <6 years and ≥6 years age groups, with a weekly median prophylactic dose of 46 IU/kg. In addition, patients maintained a median trough level of 13.4 IU/dl FIX activity on weekly prophylaxis. Overall, 97.2 % of bleeding episodes were successfully treated with one or two injections of rIX-FP (95 % CI: 92 % to 99 %), 88.7 % with one injection, and 96 % of the treatments were rated effective (excellent or good) by the Investigator. No patient developed FIX inhibitors and no safety concerns were identified. These results indicate that rIX-FP is safe and effective for preventing and treating bleeding episodes in children with haemophilia B with weekly prophylaxis. Routine prophylaxis with rIX-FP at treatment intervals of up to 14 days are currently being investigated in children with severe and moderately severe haemophilia B. Clinicaltrials.gov (NCT01662531).
Keywords: Haemophilia B; factor IX; on-demand treatment; prophylactic regimen; rIX-FP.
Conflict of interest statement
G.K., H.C., C.M., T.L., S.H., T.C., M.E.M, J.C. and E.S. received research support from CSL Behring to conduct the study. G.K. received honoraria for speaking and/or for consulting from Opko Biologics, Alnylam, Bayer, Pfizer, Novo Nordisk and research grants from BPL, Baxalta, Pfizer, Opko Biologics. H.C. received honoraria for speaking and/or for consulting from CSL Behring, Bayer Healthcare, Baxter Biosciences, LFB, Novo Nordisk and Pfizer. C.M. has received honoraria for speaking and travel support from Baxter, Bayer, Biotest, CSL Behring, Novo Nordisk and Pfizer. T.L. has received honoraria for speaking and/or for consulting from Baxalta, Bayer, Biogen Ipsen, CSL Behring, LFB, Novo Nordisk, Octapharma, Pfizer and Roche. S.H. received research grant and speakers honorarium from Bayer Healthcare GmbH, Baxalta Innovations GmbH, Biotest AG, CSL Behring GmbH, LFB GmbH, Novartis Pharma GmbH, Novo Nordisk Pharma GmbH, Octapharma GmbH and Pfizer Pharma GmbH. M.E.M. received speaker and consulting fees from CSL Behring, Bayer Healthcare, Pfizer, Baxalta, Novo Nordisk and Sobi/Biogen Idec. J.C. received honoraria for speaking and/or for consulting from CSL Behring, Baxter Biosciences, Biogen Idec and Novo Nordisk. E.S. received honoraria for speaking and/or for consulting from CSL Behring, Bayer, Baxter/Baxalta, Pfizer, NovoNordisk, Roche, Sobi/Biogen Idec, Biotest, Kedrion, Octapharma and Grifols and received unrestricted research grants from NovoNordisk and Pfizer. C.V., Y.L. and I.J. were employed at CSL Behring.
Figures
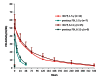
References
-
- Bolton-Maggs PHB, Pasi KJ. Haemophilias A and B. Lancet 2003; 361: 1801–1809. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava A, Brewer AK, Mauser-Bunschoten EP, et al. Guidelines for the management of hemophilia. Haemophilia 2012; 19: e1-e47. - PubMed
-
- RIXUBIS Package Insert. Available at: http://www.rixubis.com/pdf/rixubis_pi.pdf. Accessed 22nd February 2016.
-
- Santagostino E, Mancuso ME. Venous access in haemophilic children: choice and management. Haemophilia 2010; 16: 20–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

