Development and Validation of a Histological Method to Measure Microvessel Density in Whole-Slide Images of Cancer Tissue
- PMID: 27583442
- PMCID: PMC5008750
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161496
Development and Validation of a Histological Method to Measure Microvessel Density in Whole-Slide Images of Cancer Tissue
Abstract
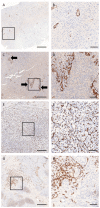
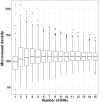
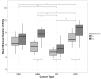
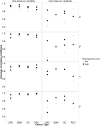
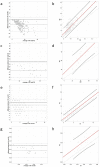
Despite all efforts made to develop predictive biomarkers for antiangiogenic therapies, no unambiguous markers have been identified so far. This is due to among others the lack of standardized tests. This study presents an improved microvessel density quantification method in tumor tissue based on stereological principles and using whole-slide images. Vessels in tissue sections of different cancer types were stained for CD31 by an automated and validated immunohistochemical staining method. The stained slides were digitized with a digital slide scanner. Systematic, uniform, random sampling of the regions of interest on the whole-slide images was performed semi-automatically with the previously published applications AutoTag and AutoSnap. Subsequently, an unbiased counting grid was combined with the images generated with these scripts. Up to six independent observers counted microvessels in up to four cancer types: colorectal carcinoma, glioblastoma multiforme, ovarian carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma. At first, inter-observer variability was found to be unacceptable. However, after a series of consensus training sessions and interim statistical analysis, counting rules were modified and inter-observer concordance improved considerably. Every CD31-positive object was counted, with exclusion of suspected CD31-positive monocytes, macrophages and tumor cells. Furthermore, if interconnected, stained objects were considered a single vessel. Ten regions of interest were sufficient for accurate microvessel density measurements. Intra-observer and inter-observer variability were low (intraclass correlation coefficient > 0.7) if the observers were adequately trained.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: Koen Marien, Valerie Croons, Yannick Waumans, Ellen Sluydts, Stefanie De Schepper, and Luc Andries are employees of HistoGeneX NV (Antwerp, Belgium). Mark Kockx is CEO of HistoGeneX NV, which carries out immunohistochemical testing for pharmaceutical companies as part of (pre-)clinical studies that evaluate new anticancer drugs. Mark Kockx and Wim Waelput are consulting pathologists to Pathomation BVBA. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvements with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed. This does not alter the authors' adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AutoTag and AutoSnap: Standardized, semi-automatic capture of regions of interest from whole slide images.MethodsX. 2015 May 21;2:272-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2015.05.002. eCollection 2015. MethodsX. 2015. PMID: 26150998 Free PMC article.
-
Fully automated microvessel counting and hot spot selection by image processing of whole tumour sections in invasive breast cancer.J Clin Pathol. 1999 Mar;52(3):184-92. doi: 10.1136/jcp.52.3.184. J Clin Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10450177 Free PMC article.
-
Microvessel density and angiogenesis in primary hepatic malignancies: Differential expression of CD31 and VEGFR-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2018 Aug;214(8):1136-1141. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.06.011. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Pathol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 29935812
-
Reconsideration of the clinical and histopathological significance of angiogenesis in prostate cancer: Usefulness and limitations of microvessel density measurement.Int J Urol. 2015 Sep;22(9):806-15. doi: 10.1111/iju.12840. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Int J Urol. 2015. PMID: 26153072 Review.
-
Using virtual microscopy for the development of sampling strategies in quantitative histology and design-based stereology.Anat Histol Embryol. 2022 Jan;51(1):3-22. doi: 10.1111/ahe.12765. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Anat Histol Embryol. 2022. PMID: 34806204 Review.
Cited by
-
Baicalein ameliorates cognitive decline induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion through the SIRT1-mediated Notch1 pathway to improve angiogenesis and suppress neuroinflammation.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Apr 11;17:1521353. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1521353. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40290868 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of ST2 aggravates glioma invasiveness, vascular abnormality, and immune suppression.Neurooncol Adv. 2025 Jan 27;7(1):vdaf010. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdaf010. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2025. PMID: 39931535 Free PMC article.
-
Super-resolution Ultrasound Imaging.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020 Apr;46(4):865-891. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.11.013. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31973952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Microvessel Density as a Potential Predictive Marker for Bevacizumab Benefit: GOG-0218 Biomarker Analyses.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017 Nov 1;109(11):djx066. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx066. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017. PMID: 29059426 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Multiscale modeling of tumor growth and angiogenesis: Evaluation of tumor-targeted therapy.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Jun 23;17(6):e1009081. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009081. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 34161319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weidner N. Current pathologic methods for measuring intratumoral microvessel density within breast carcinoma and other solid tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995;36: 169–80. - PubMed
-
- Vermeulen PB, Gasparini G, Fox SB, Toi M, Martin L, McCulloch P, et al. Quantification of angiogenesis in solid human tumours: an international consensus on the methodology and criteria of evaluation. Eur J Cancer. 1996;32A: 2474–84. - PubMed
-
- Vermeulen PB, Gasparini G, Fox SB, Colpaert C, Marson LP, Gion M, et al. Second international consensus on the methodology and criteria of evaluation of angiogenesis quantification in solid human tumours. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38: 1564–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

