The worldwide costs of dementia 2015 and comparisons with 2010
- PMID: 27583652
- PMCID: PMC5232417
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.07.150
The worldwide costs of dementia 2015 and comparisons with 2010
Abstract
Introduction: In 2010, Alzheimer's Disease International presented estimates of the global cost of illness (COI) of dementia. Since then, new studies have been conducted, and the number of people with dementia has increased. Here, we present an update of the global cost estimates.
Methods: This is a societal, prevalence-based global COI study.
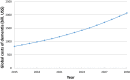
Results: The worldwide costs of dementia were estimated at United States (US) $818 billion in 2015, an increase of 35% since 2010; 86% of the costs occur in high-income countries. Costs of informal care and the direct costs of social care still contribute similar proportions of total costs, whereas the costs in the medical sector are much lower. The threshold of US $1 trillion will be crossed by 2018.
Discussion: Worldwide costs of dementia are enormous and still inequitably distributed. The increase in costs arises from increases in numbers of people with dementia and in increases in per person costs.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Cost; Costs of illness; Dementia; Economics.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Wimo A., Prince M. Alzheimer's Disease International; London: 2010. World Alzheimer Report 2010. The global economic impact of dementia.
-
- Wimo A., Jonsson L., Bond J., Prince M., Winblad B. The worldwide economic impact of dementia 2010. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9 1–11.e3. - PubMed
-
- WHO . WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2012. Dementia: a public health priority.
-
- Prince M., Wimo A., Guerchet M., Ali G.C., Wu Y.-T., Prina M. Alzheimer's Disease International; London: 2015. World Alzheimer Report 2015. The Global Impact of Dementia. An analysis of prevalence, incidence, costs and trends. World Alzheimer's Report.
-
- Hurd M.D., Martorell P., Langa K.M. Monetary costs of dementia in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:489–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical