Effect of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase on the Modulation of Coronary Reactive Hyperemia: Role of Oxylipins and PPARγ
- PMID: 27583776
- PMCID: PMC5008628
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162147
Effect of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase on the Modulation of Coronary Reactive Hyperemia: Role of Oxylipins and PPARγ
Abstract
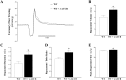
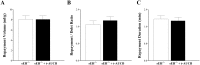
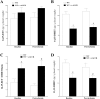
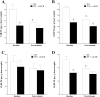
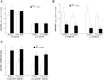
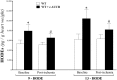
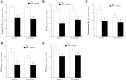
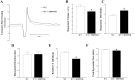
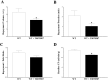
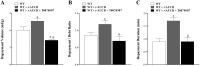
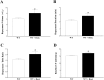
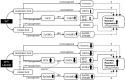
Coronary reactive hyperemia (CRH) is a physiological response to ischemic insult that prevents the potential harm associated with an interruption of blood supply. The relationship between the pharmacologic inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and CRH response to a brief ischemia is not known. sEH is involved in the main catabolic pathway of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), which are converted into dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DHETs). EETs protect against ischemia/reperfusion injury and have numerous beneficial physiological effects. We hypothesized that inhibition of sEH by t-AUCB enhances CRH in isolated mouse hearts through changing the oxylipin profiles, including an increase in EETs/DHETs ratio. Compared to controls, t-AUCB-treated mice had increased CRH, including repayment volume (RV), repayment duration, and repayment/debt ratio (p < 0.05). Treatment with t-AUCB significantly changed oxylipin profiles, including an increase in EET/DHET ratio, increase in EpOME/DiHOME ratio, increase in the levels of HODEs, decrease in the levels of mid-chain HETEs, and decrease in prostanoids (p < 0.05). Treatment with MS-PPOH (CYP epoxygenase inhibitor) reduced CRH, including RV (p < 0.05). Involvement of PPARγ in the modulation of CRH was demonstrated using a PPARγ-antagonist (T0070907) and a PPARγ-agonist (rosiglitazone). T0070907 reduced CRH (p < 0.05), whereas rosiglitazone enhanced CRH (p < 0.05) in isolated mouse hearts compared to the non-treated. These data demonstrate that sEH inhibition enhances, whereas CYP epoxygenases-inhibition attenuates CRH, PPARγ mediate CRH downstream of the CYP epoxygenases-EET pathway, and the changes in oxylipin profiles associated with sEH-inhibition collectively contributed to the enhanced CRH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Campbell WB, Gebremedhin D, Pratt PF, Harder DR. Identification of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids as endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors. Circ Res. 1996;78(3):415–23. - PubMed
-
- Sinal CJ, Miyata M, Tohkin M, Nagata K, Bend JR, Gonzalez FJ. Targeted disruption of soluble epoxide hydrolase reveals a role in blood pressure regulation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(51):40504–10. - PubMed
-
- Seubert J, Yang B, Bradbury JA, Graves J, Degraff LM, Gabel S, et al. Enhanced postischemic functional recovery in CYP2J2 transgenic hearts involves mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channels and p42/p44 MAPK pathway. Circ Res. 2004;95(5):506–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

