Selenium-binding protein 1 in head and neck cancer is low-expression and associates with the prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 27583873
- PMCID: PMC5008557
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004592
Selenium-binding protein 1 in head and neck cancer is low-expression and associates with the prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Selenium-binding protein 1 (SELENBP1) expression is reduced markedly in many types of cancers and low SELENBP1 expression levels are associated with poor patient prognosis.
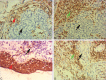
Methods: SELENBP1 gene expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) was analyzed with GEO dataset and characteristics of SELENBP1 expression in paraffin embedded tissue were summarized. Expression of SELENBP1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), laryngeal cancer, oral cancer, tonsil cancer, hypopharyngeal cancer and normal tissues were detected using immunohistochemistry, at last, 99 NPC patients were followed up more than 5 years and were analyzed the prognostic significance of SELENBP1.
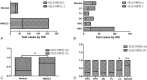
Results: Analysis of GEO dataset concluded that SELENBP1 gene expression in HNSCC was lower than that in normal tissue (P < 0.01), but there was no significant difference of SELENBP1 gene expression in different T-stage and N-stage (P > 0.05). Analysis of pathological section concluded that SELENBP1 in the majority of HNSCC is low expression and in cancer nests is lower expression than surrounding normal tissue, even associated with the malignant degree of tumor. Further study indicated the low SELENBP1 expression group of patients with NPC accompanied by poor overall survival and has significantly different comparing with the high expression group.
Conclusion: SELENBP1 expression was down-regulated in HNSCC, but has no associated with T-stage and N-stage of tumor. Low expression of SELENBP1 in patients with NPC has poor over survival, so SELENBP1 could be a novel biomarker for predicting prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Klein EA. Selenium and vitamin E cancer prevention trial. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2004; 1031:234–241. - PubMed
-
- Davis C, Tsuji PA, Milner JA. Selenoproteins and cancer prevention. Ann Rev Nutr 2012; 32:73–95. - PubMed
-
- Rayman MP. Selenium and human health. Lancet 2012; 379:1256–1268. - PubMed
-
- Jeong JY, Wang Y, Sytkowski AJ. Human selenium binding protein-1 (hSP56) interacts with VDU1 in a selenium-dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 379:583–588. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

