Increased extracellular heat shock protein 90α in severe sepsis and SIRS associated with multiple organ failure and related to acute inflammatory-metabolic stress response in children
- PMID: 27583886
- PMCID: PMC5008570
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004651
Increased extracellular heat shock protein 90α in severe sepsis and SIRS associated with multiple organ failure and related to acute inflammatory-metabolic stress response in children
Abstract
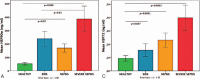
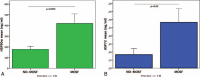
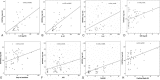
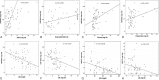
Mammalian heat-shock-protein (HSP) 90α rapidly responses to environmental insults. We examined the hypothesis that not only serum HSP72 but also HSP90α is increased in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), severe-sepsis (SS), and/or sepsis (S) compared to healthy children (H); we assessed HSP90α relation to (a) multiple organ system failure (MOSF) and (b) inflammatory-metabolic response and severity of illness.A total of 65 children with S, SS, or SIRS and 25 H were included. ELISA was used to evaluate extracellular HSP90α and HSP72, chemiluminescence interleukins (ILs), flow-cytometry neutrophil-CD64 (nCD64)-expression.HSP90α, along with HSP72, were dramatically increased among MOSF patients. Patients in septic groups and SIRS had elevated HSP90α compared to H (P < 0.01). HSP90α was independently related to predicted death rate and severity of illness; positively to HSP72, nCD64, ILs, length of stay, days on ventilator, and fever; negatively to HDL and LDL (P < 0.05). The HSP72 was increased in SS/S and related negatively to HDL and LDL (P < 0.05).Serum HSP90α is markedly elevated in children with severe sepsis and is associated with MOSF. Better than the HSP72, also increased in SS, SIRS, and MOSF, HSP90α is related to the inflammatory stress, fever, outcome endpoints, and predicted mortality and inversely related to the low-LDL/low-HDL stress metabolic pattern.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CD64-Neutrophil expression and stress metabolic patterns in early sepsis and severe traumatic brain injury in children.BMC Pediatr. 2013 Mar 1;13:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-13-31. BMC Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 23452299 Free PMC article.
-
Early response roles for prolactin cortisol and circulating and cellular levels of heat shock proteins 72 and 90α in severe sepsis and SIRS.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:803561. doi: 10.1155/2014/803561. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25243181 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine may repress the weak LPS and enhance the strong heat shock induction of monocyte and lymphocyte HSP72 proteins but may not modulate the HSP72 mRNA in patients with sepsis or trauma.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:806042. doi: 10.1155/2015/806042. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26550577 Free PMC article.
-
International pediatric sepsis consensus conference: definitions for sepsis and organ dysfunction in pediatrics.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2005 Jan;6(1):2-8. doi: 10.1097/01.PCC.0000149131.72248.E6. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2005. PMID: 15636651 Review.
-
The epidemiology of the systemic inflammatory response.Intensive Care Med. 2000;26 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S64-74. doi: 10.1007/s001340051121. Intensive Care Med. 2000. PMID: 10786961 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the diagnostic and prognostic values of serum HSP90α in sepsis patients: a retrospective study.PeerJ. 2022 Mar 10;10:e12997. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12997. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35291488 Free PMC article.
-
Chrysophanol promotes M2 polarization and inhibits M1 polarization through the NF-κB signaling pathway to attenuate sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 30;16:1641068. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1641068. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40808684 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Levels of Plasma Extracellular Heat-Shock Proteins 60 and 70 kDa Characterized Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis.Front Pediatr. 2021 Nov 25;9:740274. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.740274. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34900858 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Mechanism of Shengmai Injection on Sepsis by Network Pharmacology Approaches.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Aug 3;2020:4956329. doi: 10.1155/2020/4956329. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32831866 Free PMC article.
-
Ex Vivo Evaluation of Glutamine Treatment in Sepsis and Trauma in a Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Model.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 3;15(1):252. doi: 10.3390/nu15010252. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36615909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson JD, Fleshner M. Releasing signals, secretory pathways, and immune function of endogenous extracellular heat shock protein 72. J Leukoc Biol 2006; 79:425–434.doi:10.1189/jlb.0905523. - PubMed
-
- Sharma HS, Muresanu D, Sharma A, et al. Cerebrolysin treatment attenuates heat shock protein overexpression in the brain following heat stress: an experimental study using immunohistochemistry at light and electron microscopy in the rat. Ann NY Acad Sci 2010; 1199:138–148.doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05330.x. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

