Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART6-3p inhibits cancer cell metastasis and invasion by targeting long non-coding RNA LOC553103
- PMID: 27584792
- PMCID: PMC5059857
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.253
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART6-3p inhibits cancer cell metastasis and invasion by targeting long non-coding RNA LOC553103
Abstract
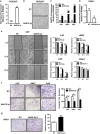
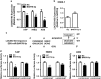
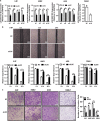
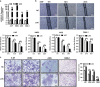
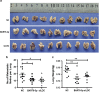
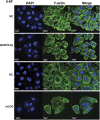
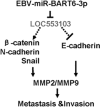
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection is causatively related to a variety of human cancers, including nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and gastric cancer (GC). EBV encodes 44 mature miRNAs, a number of which have been proven to promote carcinogenesis by targeting host genes or self-viral genes. However, in this study, we found that an EBV-encoded microRNA, termed EBV-miR-BART6-3p, inhibited EBV-associated cancer cell migration and invasion including NPC and GC by reversing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process. Using microarray analysis, we identified and validated that a novel long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) LOC553103 was downregulated by EBV-miR-BART6-3p, and LOC553103 knockdown by specific siRNAs phenocopied the effect of EBV-miR-BART6-3p, while LOC553103 overexpression promoted cancer cell migration and invasion to facilitate EMT. In conclusion, we determined that EBV-miR-BART6-3p, a microRNA encoded by oncogenic EBV, inhibited EBV-associated cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting and downregulating a novel lncRNA LOC553103. Thus, our study presents an unreported mechanism underlying EBV infection in EBV-associated cancer carcinogenesis, and provides a potential novel diagnosis and treatment biomarker for NPC and other EBV-related cancers.
Figures

References
-
- Young LS, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 757–768. - PubMed
-
- Young LS, Murray PG. Epstein-Barr virus and oncogenesis: from latent genes to tumours. Oncogene 2003; 22: 5108–5121. - PubMed
-
- He JR, Tang LY, Yu DD, Su FX, Song EW, Lin Y et al. Epstein-Barr virus and breast cancer: serological study in a high-incidence area of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett 2011; 309: 128–136. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

