SPAI: an interactive platform for indel analysis
- PMID: 27585593
- PMCID: PMC5009558
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-2824-x
SPAI: an interactive platform for indel analysis
Abstract
Background: Insertions and Deletions (Indels) are the most common form of structural variation in human genome. Indels not only contribute to genetic diversity but also cause diseases. Therefore assessing indels in human genome has become an interesting topic to the research community. This increasing interest on indel calling research has resulted into the development of a good number of indel calling tools. However, all of these tools are command line based and require expertise from Computer Science (CS) to execute them which makes it challenging for researchers from non-CS background.
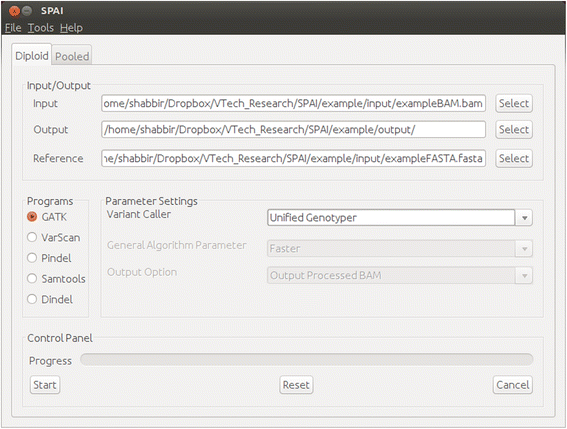
Methods: In this paper, we describe an interactive platform named SPAI which stands for Single Platform for Analyzing Indels.
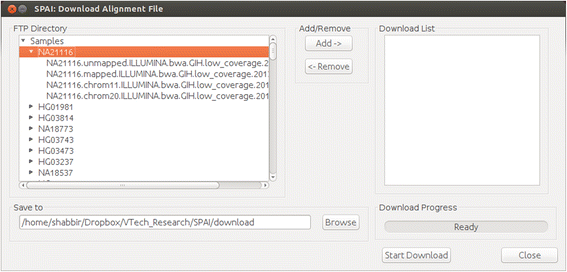
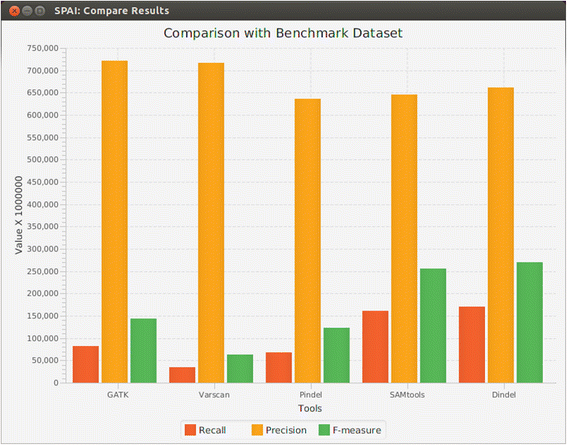
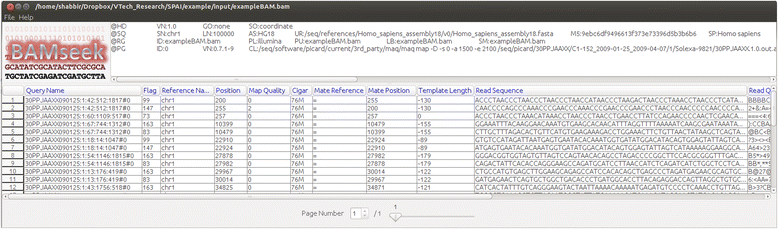
Results: Being a Graphical User Interface (GUI) tool, SPAI facilitates users to run several popular indel calling tools and perform several analyses on the indel calling results without knowing any command line programming.
Conclusions: SPAI is written in Java and tested in Linux operating system.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources