The Different Faces of the Pancreatic Islet
- PMID: 27586419
- PMCID: PMC12336862
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-39824-2_2
The Different Faces of the Pancreatic Islet
Abstract
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) patients who receive pancreatic islet transplant experience significant improvement in their quality-of-life. This comes primarily through improved control of blood sugar levels, restored awareness of hypoglycemia, and prevention of serious and potentially life-threatening diabetes-associated complications, such as kidney failure, heart and vascular disease, stroke, nerve damage, and blindness. Therefore, beta cell replacement through transplantation of isolated islets is an important option in the treatment of T1D. However, lasting success of this promising therapy depends on durable survival and efficacy of the transplanted islets, which are directly influenced by the islet isolation procedures. Thus, isolating pancreatic islets with consistent and reliable quality is critical in the clinical application of islet transplantation.Quality of isolated islets is important in pre-clinical studies as well, as efforts to advance and improve clinical outcomes of islet transplant therapy have relied heavily on animal models ranging from rodents, to pigs, to nonhuman primates. As a result, pancreatic islets have been isolated from these and other species and used in a variety of in vitro or in vivo applications for this and other research purposes. Protocols for islet isolation have been somewhat similar across species, especially, in mammals. However, given the increasing evidence about the distinct structural and functional features of human and mouse islets, using similar methods of islet isolation may contribute to inconsistencies in the islet quality, immunogenicity, and experimental outcomes. This may also contribute to the discrepancies commonly observed between pre-clinical findings and clinical outcomes. Therefore, it is prudent to consider the particular features of pancreatic islets from different species when optimizing islet isolation protocols.In this chapter, we explore the structural and functional features of pancreatic islets from mice, pigs, nonhuman primates, and humans because of their prevalent use in nonclinical, preclinical, and clinical applications.
Keywords: ATP; Autocrine signaling; Basement membrane; Endocrine cells; Endocrine pancreas; GABA; Glucagon; Glutamate; Insulin; Islet cytoarchitecture; Islet innervation; Islet isolation; Islet microcirculation; Islet transplantation; Islet vasculature; Neurotransmitter; Paracrine signaling; Parasympathetic; Signaling hierarchy; Somatostatin; Sympathetic; T1D; T2D; Type 1 diabetes; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
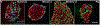
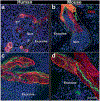
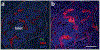
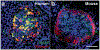
Similar articles
-
The extra-islet pancreas supports autoimmunity in human type 1 diabetes.Elife. 2025 Apr 15;13:RP100535. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100535. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40232951 Free PMC article.
-
Type 1 Diabetes: A Guide to Autoimmune Mechanisms for Clinicians.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Aug;27 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):40-56. doi: 10.1111/dom.16460. Epub 2025 May 15. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 40375390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
Cited by
-
NOD Mice-Good Model for T1D but Not Without Limitations.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720939127. doi: 10.1177/0963689720939127. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32762460 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexing DNA methylation markers to detect circulating cell-free DNA derived from human pancreatic β cells.JCI Insight. 2020 Jul 23;5(14):e136579. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.136579. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32573495 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Metabolomics and Proteomics Analyses in the Local Milieu of Islet Allografts in Rejection versus Tolerance.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 15;22(16):8754. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168754. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445459 Free PMC article.
-
Stem Cells as a Source of Pancreatic Cells for Production of 3D Bioprinted Bionic Pancreas in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes.Cells. 2021 Jun 18;10(6):1544. doi: 10.3390/cells10061544. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34207441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pancreatic islet: a micro-organ in control.CellR4 Repair Replace Regen Reprogram. 2021;9:e3093. doi: 10.32113/cellr4_20213_3093. Epub 2021 Mar 19. CellR4 Repair Replace Regen Reprogram. 2021. PMID: 33816651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grauslund J. Eye complications and markers of morbidity and mortality in long-term type 1 diabetes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011;89(Thesis 1):1–19. - PubMed
-
- Scheen AJ. Pharmacokinetics and clinical use of incretin-based therapies in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014;53:773–85. - PubMed
-
- Narayan KM, Boyle JP, Geiss LS, Saaddine JB, Thompson TJ. Impact of recent increase in incidence on future diabetes burden: U.S., 2005–2050. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(9):2114–6. - PubMed
-
- Pugliese A. The multiple origins of type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2013;30(2):135–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

