Latanoprost-Eluting Contact Lenses in Glaucomatous Monkeys
- PMID: 27586444
- PMCID: PMC8519348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.06.038
Latanoprost-Eluting Contact Lenses in Glaucomatous Monkeys
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the ability of latanoprost-eluting contact lenses to lower the intraocular pressure (IOP) of glaucomatous eyes of cynomolgus monkeys.
Design: Preclinical efficacy study of 3 treatment arms in a crossover design.
Participants: Female cynomolgus monkeys with glaucoma induced in 1 eye by repeated argon laser trabeculoplasty.
Methods: Latanoprost-eluting low-dose contact lenses (CLLO) and high-dose contact lenses (CLHI) were produced by encapsulating a thin latanoprost-polymer film within the periphery of a methafilcon hydrogel, which was lathed into a contact lens. We assessed the IOP-lowering effect of CLLO, CLHI, or daily latanoprost ophthalmic solution in the same monkeys. Each monkey consecutively received 1 week of continuous-wear CLLO, 3 weeks without treatment, 5 days of latanoprost drops, 3 weeks without treatment, and 1 week of continuous-wear CLHI. On 2 consecutive days before initiation of each study arm, the IOP was measured hourly over 7 consecutive hours to establish the baseline IOP. Two-tailed Student t tests and repeated-measures analysis of variance were used for statistical analysis.
Main outcome measures: Intraocular pressure.
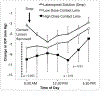
Results: Latanoprost ophthalmic solution resulted in IOP reduction of 5.4±1.0 mmHg on day 3 and peak IOP reduction of 6.6±1.3 mmHg on day 5. The CLLO reduced IOP by 6.3±1.0, 6.7±0.3, and 6.7±0.3 mmHg on days 3, 5, and 8, respectively. The CLHI lowered IOP by 10.5±1.4, 11.1±4.0, and 10.0±2.5 mmHg on days 3, 5, and 8, respectively. For the CLLO and CLHI, the IOP was statistically significantly reduced compared with the untreated baseline at most time points measured. The CLHI demonstrated greater IOP reduction than latanoprost ophthalmic solution on day 3 (P = 0.001) and day 5 (P = 0.015), and at several time points on day 8 (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Sustained delivery of latanoprost by contact lenses is at least as effective as delivery with daily latanoprost ophthalmic solution. More research is needed to determine the optimal continuous-release dose that would be well tolerated and maximally effective. Contact lens drug delivery may become an option for the treatment of glaucoma and a platform for ocular drug delivery.
Copyright © 2016 American Academy of Ophthalmology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ghate D, Edelhauser H. Barriers to glaucoma drug delivery. J Glaucoma. 2008;17(2):147. - PubMed
-
- Hennessy AL, Katz J, Covert D, Kelly CA, Suan EP, Speicher MA, et al. A video study of drop instillation in both glaucoma and retina patients with visual impairment. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011. December;152(6):982–8. - PubMed
-
- Stone JL, Robin AL, Novack GD, Covert DW, Cagle GD. An objective evaluation of eyedrop instillation in patients with glaucoma. Archives of Ophthalmology. 2009. June;127(6):732–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

