The relationship of the oleic acid level and ECHDC3 mRNA expression with the extent of coronary lesion
- PMID: 27586541
- PMCID: PMC5009642
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-016-0312-6
The relationship of the oleic acid level and ECHDC3 mRNA expression with the extent of coronary lesion
Abstract
Background: The fatty acid profile is associated with the risk and progression of several diseases, probably via mechanisms including its influence on gene expression. We previously reported a correlation between ECHDC3 upregulation and the severity of acute coronary syndrome. Here, we assessed the relationship of serum fatty acid profile and ECHDC3 expression with the extent of coronary lesion.
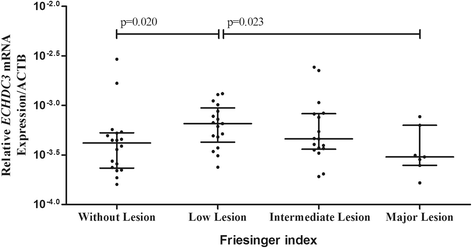
Methods: Fifty-nine individuals aged 30 to 74 years and undergoing elective cinecoronariography for the first time were enrolled in the present study. The extent of coronary lesion was assessed by the Friesinger index and patients were classified as without lesion (n = 18), low lesion (n = 17), intermediate lesion (n = 17) and major lesion (n = 7). Serum biochemistry, fatty acid concentration, and ECHDC3 mRNA expression in blood were evaluated.
Results: Elevated serum levels of oleic acid and total monounsaturated fatty acids were observed in patients with low and intermediate lesion, when compared to patients without lesion (p < 0.05). ECHDC3 mRNA expression was 1.2 fold higher in patients with low lesion than in patients without lesion (p = 0.020), and 1.8 fold lower in patients with major lesion patients than in patients with low lesion (p = 0.023).
Conclusion: Increased levels of monounsaturated fatty acids, especially oleic acid, and ECHDC3 upregulation in patients with coronary artery lesion suggests that these are independent factors associated with the initial progression of cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; ECHDC3; Friesinger index; Monounsaturated fatty acids; Oleic acid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of products made from a high-palmitic acid, trans-free semiliquid fat or a high-oleic acid, low-trans semiliquid fat on the serum lipoprotein profile and on C-reactive protein concentrations in humans.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008 May;62(5):617-24. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602756. Epub 2007 Apr 18. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008. PMID: 17440525 Clinical Trial.
-
A new hypotensive polyunsaturated fatty acid dietary combination regulates oleic acid accumulation by suppression of stearoyl CoA desaturase 1 gene expression in the SHR model of genetic hypertension.FASEB J. 2004 Apr;18(6):773-5. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-0950fje. Epub 2004 Feb 20. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 14977874
-
What limits production of unusual monoenoic fatty acids in transgenic plants?Planta. 2002 Aug;215(4):584-95. doi: 10.1007/s00425-002-0751-3. Epub 2002 Mar 27. Planta. 2002. PMID: 12172841
-
[Protective effect of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids on the development of cardiovascular disease].Nutr Hosp. 2001 May-Jun;16(3):78-91. Nutr Hosp. 2001. PMID: 11475681 Review. Spanish.
-
Direct vascular antiatherogenic effects of oleic acid: a clue to the cardioprotective effects of the Mediterranean diet.Cardiologia. 1999 Jun;44(6):507-13. Cardiologia. 1999. PMID: 10443051 Review.
Cited by
-
The Short Overview on the Relevance of Fatty Acids for Human Cardiovascular Disorders.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 30;10(8):1127. doi: 10.3390/biom10081127. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32751513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of oleic acid supplementation in myotonic dystrophy muscle cell models.Biol Res. 2024 May 17;57(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00496-z. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38760841 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive effect of sericin on hepatic mitochondrial conformation through its regulation of apoptosis, autophagy and energy maintenance: a proteomics approach.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 8;8(1):14943. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33372-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30297713 Free PMC article.
-
TREML4 mRNA Expression and Polymorphisms in Blood Leukocytes are Associated with Atherosclerotic Lesion Extension in Coronary Artery Disease.Sci Rep. 2019 May 10;9(1):7229. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43745-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31076644 Free PMC article.
-
Virgin Olive Oil Ranks First in a New Nutritional Quality Score Due to Its Compositional Profile.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 28;15(9):2127. doi: 10.3390/nu15092127. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432257 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

