Activation of the EIF2α/ATF4 and ATF6 Pathways in DU-145 Cells by Boric Acid at the Concentration Reported in Men at the US Mean Boron Intake
- PMID: 27587023
- PMCID: PMC5344959
- DOI: 10.1007/s12011-016-0824-y
Activation of the EIF2α/ATF4 and ATF6 Pathways in DU-145 Cells by Boric Acid at the Concentration Reported in Men at the US Mean Boron Intake
Abstract
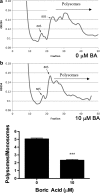
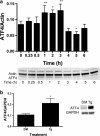
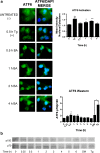
Fruits, nuts, legumes, and vegetables are rich sources of boron (B), an essential plant nutrient with chemopreventive properties. Blood boric acid (BA) levels reflect recent B intake, and men at the US mean intake have a reported non-fasting level of 10 μM. Treatment of DU-145 prostate cancer cells with physiological concentrations of BA inhibits cell proliferation without causing apoptosis and activates eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2α). EIF2α induces cell differentiation and protects cells by redirecting gene expression to manage endoplasmic reticulum stress. Our objective was to determine the temporal expression of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-activated genes in DU-145 prostate cells treated with 10 μM BA. Immunoblots showed post-treatment increases in eIF2α protein at 30 min and ATF4 and ATF6 proteins at 1 h and 30 min, respectively. The increase in ATF4 was accompanied by an increase in the expression of its downstream genes growth arrest and DNA damage-induced protein 34 (GADD34) and homocysteine-induced ER protein (Herp), but a decrease in GADD153/CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP), a pro-apoptotic gene. The increase in ATF6 was accompanied by an increase in expression of its downstream genes GRP78/BiP, calreticulin, Grp94, and EDEM. BA did not activate IRE1 or induce cleavage of XBP1 mRNA, a target of IRE1. Low boron status has been associated with increased cancer risk, low bone mineralization, and retinal degeneration. ATF4 and BiP/GRP78 function in osteogenesis and bone remodeling, calreticulin is required for tumor suppressor p53 function and mineralization of teeth, and BiP/GRP78 and EDEM prevent the aggregation of misfolded opsins which leads to retinal degeneration. The identification of BA-activated genes that regulate its phenotypic effects provides a molecular underpinning for boron nutrition and biology.
Keywords: ATF4; ATF6A; Boric acid; Boron; Calreticulin (CALR); DU-145; EDEM1; GADD153/CHOP (DDIT3); GADD34 (PPP1R15A); GRP78/BiP (HSPa5); GRP94 (HSP90B1); Herp (HERPUD1); Hrd1 (SYVN1); Nutrition; RE1 (ERN1); XBP1; eIF2α (EIF2A).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Boric Acid Activation of eIF2α and Nrf2 Is PERK Dependent: a Mechanism that Explains How Boron Prevents DNA Damage and Enhances Antioxidant Status.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019 Mar;188(1):2-10. doi: 10.1007/s12011-018-1498-4. Epub 2018 Sep 8. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019. PMID: 30196486
-
Boric acid induces cytoplasmic stress granule formation, eIF2α phosphorylation, and ATF4 in prostate DU-145 cells.Biometals. 2015 Feb;28(1):133-41. doi: 10.1007/s10534-014-9809-5. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Biometals. 2015. PMID: 25425213 Free PMC article.
-
Gene regulatory network of unfolded protein response genes in endoplasmic reticulum stress.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013 Jan;18(1):11-23. doi: 10.1007/s12192-012-0351-5. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013. PMID: 22802018 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP Signaling Pathway in Tumor Progression During Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Curr Mol Med. 2016;16(6):533-44. doi: 10.2174/1566524016666160523143937. Curr Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27211800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the ATF4 pathway in cancer therapy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012 Dec;16(12):1189-202. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2012.728207. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012. PMID: 23009153 Review.
Cited by
-
Anticancer effect of caudatin in diethylnitrosamine‑induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Aug;22(2):697-706. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11135. Epub 2020 May 7. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32626931 Free PMC article.
-
Borate Ameliorates Sodium Nitrite-Induced Oxidative Stress Through Regulation of Oxidant/Antioxidant Status: Involvement of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB Pathways.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022 Jan;200(1):197-205. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02613-5. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022. PMID: 33559025
-
In vitro cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of boric acid on endometrial adenocarcinoma cell lines (HEC-1B and Ischikawa).Med Oncol. 2025 Feb 19;42(3):79. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02625-4. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39971813 Free PMC article.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum stress response in prostate cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2022 Dec;19(12):708-726. doi: 10.1038/s41585-022-00649-3. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Nat Rev Urol. 2022. PMID: 36168057 Review.
-
Astragaloside IV ameliorates endoplasmic reticulum stress‑induced apoptosis of Aβ25‑35‑treated PC12 cells by inhibiting the p38 MAPK signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Mar;19(3):2005-2012. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9855. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30664172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cui Y, Winton M, Zhang Z, Rainey C, Marshall J, et al. Dietary boron intake and prostate cancer risk. Oncol Rep. 2004;11:887–892. - PubMed
-
- Muezzinoglu T, Korkmaz M, Nese N, Bakirdere S, Arslan Y, et al. (2011) Prevalence of prostate cancer in high boron-exposed population: a community-based study. Biol Trace Elem Res - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

