REDIportal: a comprehensive database of A-to-I RNA editing events in humans
- PMID: 27587585
- PMCID: PMC5210607
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw767
REDIportal: a comprehensive database of A-to-I RNA editing events in humans
Abstract
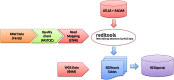
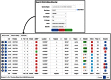
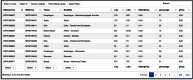
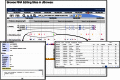
RNA editing by A-to-I deamination is the prominent co-/post-transcriptional modification in humans. It is carried out by ADAR enzymes and contributes to both transcriptomic and proteomic expansion. RNA editing has pivotal cellular effects and its deregulation has been linked to a variety of human disorders including neurological and neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Despite its biological relevance, many physiological and functional aspects of RNA editing are yet elusive. Here, we present REDIportal, available online at http://srv00.recas.ba.infn.it/atlas/, the largest and comprehensive collection of RNA editing in humans including more than 4.5 millions of A-to-I events detected in 55 body sites from thousands of RNAseq experiments. REDIportal embeds RADAR database and represents the first editing resource designed to answer functional questions, enabling the inspection and browsing of editing levels in a variety of human samples, tissues and body sites. In contrast with previous RNA editing databases, REDIportal comprises its own browser (JBrowse) that allows users to explore A-to-I changes in their genomic context, empathizing repetitive elements in which RNA editing is prominent.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Gott J.M., Emeson R.B. Functions and mechanisms of RNA editing. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2000;34:499–531. - PubMed
-
- Hogg M., Paro S., Keegan L.P., O'Connell M.A. RNA editing by mammalian ADARs. Adv. Genet. 2011;73:87–120. - PubMed
-
- Gallo A., Locatelli F. ADARs: allies or enemies? The importance of A-to-I RNA editing in human disease: from cancer to HIV-1. Biol. Rev. Cambr. Philos. Soc. 2012;87:95–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

