Performance of hemodialysis with novel medium cut-off dialyzers
- PMID: 27587605
- PMCID: PMC5837492
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfw310
Performance of hemodialysis with novel medium cut-off dialyzers
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Performance of Hemodialysis with Novel Medium Cut-Off Dialyzers.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021 Jul 23;36(8):1555-1556. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa322. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34046683 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Compared to high-flux dialysis membranes, novel medium cut-off (MCO) membranes show greater permeability for larger middle molecules.
Methods: In two prospective, open-label, controlled, randomized, crossover pilot studies, 39 prevalent hemodialysis (HD) patients were studied in four dialysis treatments as follows: study 1, three MCO prototype dialyzers (AA, BB and CC with increasing permeability) and one high-flux dialyzer in HD; and study 2, two MCO prototype dialyzers (AA and BB) in HD and high-flux dialyzers in HD and hemodiafiltration (HDF). Primary outcome was lambda free light chain (λFLC) overall clearance. Secondary outcomes included overall clearances and pre-to-post-reduction ratios of middle and small molecules, and safety of MCO HD treatments.
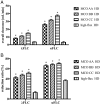
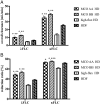
Results: MCO HD provided greater λFLC overall clearance [least square mean (standard error)] as follows: study 1: MCO AA 8.5 (0.54), MCO BB 11.3 (0.51), MCO CC 15.0 (0.53) versus high-flux HD 3.6 (0.51) mL/min; study 2: MCO AA 10.0 (0.58), MCO BB 12.5 (0.57) versus high-flux HD 4.4 (0.57) and HDF 6.2 (0.58) mL/min. Differences between MCO and high-flux dialyzers were consistently significant in mixed model analysis (each P < 0.001). Reduction ratios of λFLC were greater for MCO. Clearances of α1-microglobulin, complement factor D, kappa FLC (κFLC) and myoglobin were generally greater with MCO than with high-flux HD and similar to or greater than clearances with HDF. Albumin loss was moderate with MCO, but greater than with high-flux HD and HDF.
Conclusions: MCO HD removes a wide range of middle molecules more effectively than high-flux HD and even exceeds the performance of high-volume HDF for large solutes, particularly λFLC.
Keywords: beta2-microglobulin; dialysis; hemodiafiltration; hemodialysis; uremic toxins.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
References
-
- Vanholder R, De Smet R, Glorieux G et al. Review on uremic toxins: classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int 2003; 63: 1934–1943 - PubMed
-
- Vanholder RC, Eloot S, Glorieux GL. Future avenues to decrease uremic toxin concentration. Am J Kidney Dis 2016; 67: 664–676 - PubMed
-
- Cohen G, Haag-Weber M, Mai B et al. Effect of immunoglobulin light chains from hemodialysis and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients on polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions. J Am Soc Nephrol 1995; 6: 1592–1599 - PubMed
-
- Cohen G, Rudnicki M, Horl WH. Uremic toxins modulate the spontaneous apoptotic cell death and essential functions of neutrophils. Kidney Int Suppl 2001; 78: S48–S52 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

