Effects of the κ-opioid receptor on the inhibition of 100 Hz electroacupuncture on cocaine-induced conditioned place preference
- PMID: 27588082
- PMCID: PMC4997994
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3504
Effects of the κ-opioid receptor on the inhibition of 100 Hz electroacupuncture on cocaine-induced conditioned place preference
Abstract
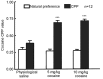
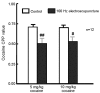
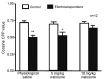
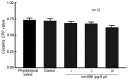
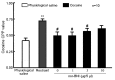
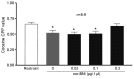
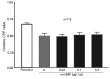
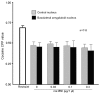
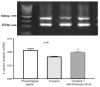
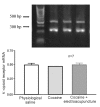
The administration of 100 Hz electroacupuncture has been demonstrated to suppress cocaine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) in rats, and there is evidence that the κ-opioid receptor may have a role in cocaine addiction. The present study sought to explore the mechanisms underlying the inhibitory effects of 100 Hz electroacupuncture on cocaine-induced CPP in rats. A rat model of cocaine-induced CPP was used in the present study to investigate the following: i) Naloxone treatment (5 and 10 mg/kg) following 100 Hz electroacupuncture-mediated inhibition on cocaine-induced CPP, revealing that a high dose (10 mg/kg) of naloxone blocked the inhibitory effects of 100 Hz electroacupuncture on cocaine-induced CPP; ii) nor-binaltorphimine (nor-BNI) on 100 Hz electroacupuncture-mediated inhibition on cocaine-induced CPP, which indicated that administration of 10 µg/5 µl and 0.3 µg/1 µl nor-BNI intracerebroventricularly and via the nucleus accumbens, respectively, reversed the inhibitory effects of 100 Hz electroacupuncture on cocaine-induced CPP, and that injection of nor-BNI in different brain areas of rats blocks the inhibitory effects of electroacupuncture on cocaine-induced CPP; and iv) 100 Hz electroacupuncture on the mRNA expression levels of the κ-opioid receptor in the rat nucleus accumbens and amygdala, which established that mRNA expression levels of κ-opioid receptor in the nucleus accumbens were increased with 100 Hz electroacupuncture plus cocaine-induced CPP. Overall, the results of the present study indicated that 100 Hz electroacupuncture was able to suppress cocaine-induced CPP via the κ-opioid receptor in the nucleus accumbens.
Keywords: cocaine; conditioned place preference; dopamine pathway; electroacupuncture; nor-binaltorphimine; κ-opioid receptor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats is inhibited by electroacupuncture at 2 Hz: role of enkephalin in the nucleus accumbens.Neuropharmacology. 2010 Jan;58(1):233-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.07.007. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Neuropharmacology. 2010. PMID: 19596017
-
Peripheral electric stimulation attenuates the expression of cocaine-induced place preference in rats.Brain Res. 2002 Dec 6;957(1):129-35. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)03614-4. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12443988
-
Electroacupuncture of 2 hz has a rewarding effect: evidence from a conditioned place preference study in rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:730514. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nen043. Epub 2011 Aug 9. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. PMID: 18955347 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivation of cocaine conditioned place preference induced by stress is reversed by cholecystokinin-B receptors antagonist in rats.Brain Res. 2002 Nov 1;954(1):132-40. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)03359-0. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12393241
-
The role of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in cocaine place preference and mu opioid receptor expression in the nucleus accumbens.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Sep;235(9):2675-2685. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4961-1. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29992335
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates the relapse of pain-related aversive memory by activating KOR and inhibiting GABAergic neurons in the insular cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2023 Oct 9;33(20):10711-10721. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhad321. Cereb Cortex. 2023. PMID: 37679857 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
