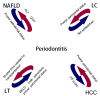
Interaction between periodontitis and liver diseases
- PMID: 27588170
- PMCID: PMC4998044
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2016.718
Interaction between periodontitis and liver diseases
Abstract
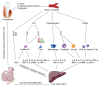
Periodontitis is an oral disease that is highly prevalent worldwide, with a prevalence of 30-50% of the population in developed countries, but only ~10% present with severe forms. It is also estimated that periodontitis results in worldwide productivity losses amounting to ~54 billion USD yearly. In addition to the damage it causes to oral health, periodontitis also affects other types of disease. Numerous studies have confirmed the association between periodontitis and systemic diseases, such as diabetes, respiratory disease, osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease. Increasing evidence also indicated that periodontitis may participate in the progression of liver diseases, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as affecting liver transplantation. However, to the best of our knowledge, there are currently no reviews elaborating upon the possible links between periodontitis and liver diseases. Therefore, the current review summarizes the human trials and animal experiments that have been conducted to investigate the correlation between periodontitis and liver diseases. Furthermore, in the present review, certain mechanisms that have been postulated to be responsible for the role of periodontitis in liver diseases (such as bacteria, pro-inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress) are considered. The aim of the review is to introduce the hypothesis that periodontitis may be important in the progression of liver disease, thus providing dentists and physicians with an improved understanding of this issue.
Keywords: bacteria; cirrhosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver transplantation; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; periodontitis.
Figures
References
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, Aboyans V, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2163–2196. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
