The involvement of proline-rich protein Mus musculus predicted gene 4736 in ocular surface functions
- PMID: 27588265
- PMCID: PMC4990575
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2016.08.06
The involvement of proline-rich protein Mus musculus predicted gene 4736 in ocular surface functions
Abstract
Aim: To research the two homologous predicted proline-rich protein genes, Mus musculus predicted gene 4736 (MP4) and proline-rich protein BstNI subfamily 1 (Prb1) which were significantly upregulated in cultured corneal organs when encountering fungal pathogen preparations. This study was to confirm the expression and potential functions of these two genes in ocular surface.
Methods: A Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis model was established in Balb/c mice. One day post infection, mRNA level of MP4 was measured using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and MP4 protein detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC) or Western blot using a customized polyclonal anti-MP4 antibody preparation. Lacrimal glands from normal mice were also subjected to IHC staining for MP4. An online bioinformatics program, BioGPS, was utilized to screen public data to determine other potential locations of MP4.
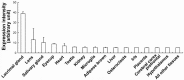
Results: One day after keratitis induction, MP4 was upregulated in the corneas at both mRNA level as measured using real-time PCR and protein levels as measured using Western blot and IHC. BioGPS analysis of public data suggested that the MP4 gene was most abundantly expressed in the lacrimal glands, and IHC revealed that normal murine lacrimal glands were positive for MP4 staining.
Conclusion: MP4 and Prb1 are closely related with the physiology and pathological processes of the ocular surface. Considering the significance of ocular surface abnormalities like dry eye, we propose that MP4 and Prb1 contribute to homeostasis of ocular surface, and deserve more extensive functional and disease correlation studies.
Keywords: Mus musculus predicted gene 4736; Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis; ocular surface; proline-rich protein.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Detection and regulation of cationic amino acid transporters in healthy and diseased ocular surface.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Mar;50(3):1112-21. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2368. Epub 2008 Nov 7. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 18997084
-
Neutralization of ocular surface TNF-α reduces ocular surface and lacrimal gland inflammation induced by in vivo dry eye.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Nov 15;54(12):7557-66. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-11515. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 24052636
-
ST2 is essential for Th2 responsiveness and resistance to pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Oct;48(10):4626-33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0316. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17898286
-
cDNA clones for mouse parotid proline-rich proteins. mRNA regulation by isoprenaline and the nucleotide sequence of proline-rich protein cDNA MP5.Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 1;204(2):591-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16672.x. Eur J Biochem. 1992. PMID: 1339347
-
The pathology of dry eye: the interaction between the ocular surface and lacrimal glands.Cornea. 1998 Nov;17(6):584-9. doi: 10.1097/00003226-199811000-00002. Cornea. 1998. PMID: 9820935 Review.
References
-
- Lu Y, Bennick A. Interaction of tannin with human salivary proline-rich proteins. Arch Oral Biol. 1998;43(9):717–728. - PubMed
-
- Al Kawas S, Rahim ZH, Ferguson DB. Potential uses of human salivary protein and peptide analysis in the diagnosis of disease. Arch Oral Biol. 2012;57(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Holmes AR, Rodrigues E, van der Wielen P, Lyons KM, Haigh BJ, Wheeler TT, Dawes PJ, Cannon RD. Adherence of Candida albicans to silicone is promoted by the human salivary protein SPLUNC2/PSP/BPIFA2. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2014;29(2):90–98. - PubMed
-
- Iavarone F, D'Alessandro A, Tian N, Cabras T, Messana I, Helmerhorst EJ, Oppenheim FG, Castagnola M. High-resolution high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry characterization of a new isoform of human salivary acidic proline-rich proteins named Roma-Boston Ser22 (Phos)→Phe variant. J Sep Sci. 2014;37(14):1896–1902. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manconi B, Castagnola M, Cabras T, Olianas A, Vitali A, Desiderio C, Sanna MT, Messana I. The intriguing heterogeneity of human salivary proline-rich proteins: Short title: Salivary proline-rich protein species. J Proteomics. 2016;134:47–56. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
