HuR silencing elicits oxidative stress and DNA damage and sensitizes human triple-negative breast cancer cells to radiotherapy
- PMID: 27588488
- PMCID: PMC5323119
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11706
HuR silencing elicits oxidative stress and DNA damage and sensitizes human triple-negative breast cancer cells to radiotherapy
Abstract
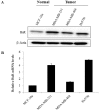
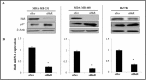
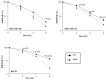
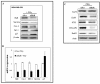
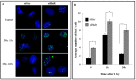
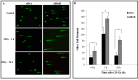
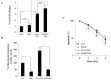
HuR is an mRNA-binding protein whose overexpression in cancer cells has been associated with poor prognosis and resistance to therapy. While reports on HuR overexpression contributing to chemoresistance exist, limited information is available on HuR and radioresistance especially in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).In this study we investigated the role of HuR in radiation resistance in three TNBC (MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468 and Hs578t) cell lines. Endogenous HuR expression was higher in TNBC cells compared to normal cells. siRNA mediated knockdown of HuR (siHuR) markedly reduced HuR mRNA and protein levels compared to scrambled siRNA (siScr) treatment. Further, siHuR treatment sensitized TNBC cells to ionizing radiation at 2 Gy compared to siScr treatment as evidenced by the significant reduction in clonogenic cell survival from 59%, 49%, and 65% in siScr-treated cells to 40%, 33%, and 46% in siHuR-treated MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468 and Hs578t cells, respectively. Molecular studies showed increased ROS production and inhibition of thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) in HuR knockdown cells contributed to radiosensitization. Associated with increased ROS production was evidence of increased DNA damage, demonstrated by a significant increase (p < 0.05) in γ-H2AX foci that persisted for up to 24 h in siHuR plus radiation treated cells compared to control cells. Further, comet assay revealed that HuR-silenced cells had larger and longer-lasting tails than control cells, indicating higher levels of DNA damage. In conclusion, our studies demonstrate that HuR knockdown in TNBC cells elicits oxidative stress and DNA damage resulting in radiosensitization.
Keywords: DNA repair; HuR; breast cancer; radiation; siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Nguyen PL, Taghian AG, Katz MS, Niemierko A, Abi Raad RF, Boon WL, Bellon JR, Wong JS, Smith BL, Harns JR. Breast cancer subtype approximated by estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER-2 is associated with local and distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2373–2378. - PubMed
-
- Kyndi M, Sørensen FB, Knudsen H, Overgaard M, Nielsen HM, Overgaard J Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group. Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, HER-2, and response to postmastectomy radiotherapy in high-risk breast cancer: the Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1419–1426. - PubMed
-
- Goodhead DT. Initial events in the cellular effects of ionizing radiations: clustered damage in DNA. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994;65:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Barzilai A, Yamamoto K. DNA damage responses to oxidative stress. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004;3:1109–15. - PubMed
-
- Riley PA. Free radicals in biology: oxidative stress and the effects of ionizing radiation. Int J Rad Biol. 1994;65:27–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

