Solution Structures and Molecular Associations of a Peptide-Based Catalyst for the Stereoselective Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation
- PMID: 27588823
- PMCID: PMC5130343
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b02282
Solution Structures and Molecular Associations of a Peptide-Based Catalyst for the Stereoselective Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation
Abstract
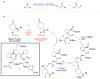
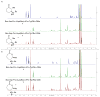
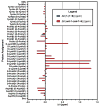
The structural analysis of a peptide-based catalyst for the Baeyer-Villiger oxidation (BVO) is reported. This unique structure is then analyzed in the context of its previously documented facility to control selectivity (both enantioselectivity and migratory aptitude) in catalytic reactions. The effects of additives on the solution conformation of the peptide are found to be dramatic, revealing substrate-specific interactions and a possible "induced fit" model. The experimental observation of dynamic behavior supports the notion that flexibility in stereoselective catalysts can be an advantageous feature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Baeyer A, Villiger V. Berichte de deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 1899;32:3625–3633.
-
- de Gonzalo G, van Berkel WJH, Fraaije MW. Science of Synthesis, Biocatalysis in Organic Synthesis. 2015;3:187–233.
-
- Evan PA, Lawler MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:8642–8643. - PubMed
-
- Michelin RA, Sgarbosa P, Scarso A, Strukul G. Coord Chem Rev. 2010;254:646–660.
-
- Xu S, Wang Z, Zhang X, Ding K. Eur J Org Chem. 2011;1:110–116.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

