Comprehensive Transcriptome Analyses of the Fructose-Fed Syrian Golden Hamster Liver Provides Novel Insights into Lipid Metabolism
- PMID: 27589064
- PMCID: PMC5010245
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162402
Comprehensive Transcriptome Analyses of the Fructose-Fed Syrian Golden Hamster Liver Provides Novel Insights into Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
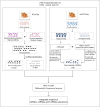
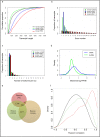
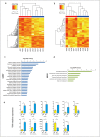
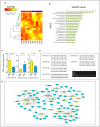
Dyslipidemia has been widely proven to contribute to cardiovascular diseases and other metabolic disorders, especially in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. The overproduction of VLDL is a significant characteristic of dyslipidemia, indicating the dysfunction of hepatic lipid metabolism, from triglyceride synthesis to transport. The fructose-fed Syrian golden hamster is an established animal model for the study of VLDL assembly with insulin resistance, however, it remains unknown how VLDL production is regulated at the transcriptional level due to the absence of a complete hamster genome. Here, we performed deep sequencing and constructed an mRNA-miRNA-lncRNA interaction network of Syrian golden hamster liver in order to reveal the global transcription profile and find potential RNA molecular regulation of VLDL production. We identified 4,450 novel multi-exon hamster lncRNAs and 755 miRNAs expressed in liver. Additionally, 146 differentially expressed coding genes, 27 differentially expressed lncRNA genes, as well as 16 differentially expressed miRNAs were identified. We then constructed an mRNA-miRNA-lncRNA interaction network that may potentially regulate VLDL production, and interestingly found several microRNA-centered regulatory networks. In order to verify our interpretation, miR-486 was selected for further experiments. Overexpression or down-regulation of miR-486 in fructose-fed hamsters resulted in altered hepatic expression of proteins involved in VLDL production, and in modulated levels of circulating VLDL. Our findings implicated that miR-486 is a potential regulator of circulating VLDL levels. These results provide new insights and a valuable resource for further study of the molecular mechanisms of VLDL secretion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Shelness GS, Sellers JA. Very-low-density lipoprotein assembly and secretion. Current opinion in lipidology. 2001;12(2):151–7. WOS:000167817800008. - PubMed
-
- Rutledge AC, Su Q, Adeli K. Apolipoprotein B100 biogenesis: a complex array of intracellular mechanisms regulating folding, stability, and lipoprotein assemblyThis paper is one of a selection of papers published in this special issue entitled “Canadian Society of Biochemistry, Molecular & Cellular Biology 52nd Annual Meeting—Protein Folding: Principles and Diseases” and has undergone the Journal's usual peer review process. Biochemistry and Cell Biology. 2010;88(2):251–67. - PubMed
-
- Swift LL. Assembly of Very-Low-Density Lipoproteins in Rat-Liver—a Study of Nascent Particles Recovered from the Rough Endoplasmic-Reticulum. Journal of lipid research. 1995;36(3):395–406. WOS:A1995QP34500001. - PubMed
-
- Stillemark P, Boren J, Andersson M, Larsson T, Rustaeus S, Karlsson KA, et al. The assembly and secretion of apolipoprotein B-48-containing very low density lipoproteins in McA-RH7777 cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2000;275(14):10506–13. 10.1074/jbc.275.14.10506. WOS:000086345600083. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

