Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic considerations in the treatment of critically Ill patients infected with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae
- PMID: 27589330
- PMCID: PMC5477717
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1221021
Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic considerations in the treatment of critically Ill patients infected with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae
Abstract
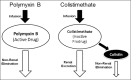
Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) are an emerging healthcare crisis. Infections due to CRE are associated with high morbidity and mortality, especially in critically ill patients. Due to the multi-drug resistant nature of these infections only limited treatment options are available. Antimicrobials that have been described for the treatment of CRE infections include carbapenems, polymyxins, fosfomycin, tigecycline, aminoglycosides, and ceftazidime-avibactam. Given the limited treatment options it is imperative the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics (PK-PD) characteristics of these agents are considered to optimize treatment regimens. This review will focus on the PK-PD challenges of the current treatment options for CRE infections.
Keywords: carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2013. Atlanta, GA: CDC. Retrieved from: http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/pdf/ar-threats-2013...
-
- Tzouvelekis LS, Markogiannakis A, Psichogiou M, Tassios PT, Daikos GL. Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae and other Enterobacteriaceae: an evolving crisis of global dimensions. Clin Microbiol Rev 2012; 25:682-707; PMID:23034326; https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.05035-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Daikos GL, Tsaousi S, Tzouvelekis LS, Anyfantis I, Psichogiou M, Argyropoulou A, Stefanou I, Sypsa V, Miriagou V, Nepka M, et al.. Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections: Lowering mortality by antibiotic combination schemes and the role of carbapenems. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014; 58:2322-8; PMID:24514083; https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02166-13 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qureshi ZA, Paterson DL, Potoski BA, Kilayko MC, Sandovsky G, Sordillo E, Polsky B, Adams-Haduch JM, Doi Y. Treatment outcome of bacteremia due to KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: superiority of combination antimicrobial regimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2012; 56:2108-13; PMID:22252816; https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.06268-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tumbarello M, Viale P, Viscoli C, Trecarichi EM, Tumietto F, Marchese A, Spanu T, Ambretti S, Ginocchio F, Cristini F, et al.. Predictors of mortality in bloodstream infections caused by klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae: importance of combination therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2012; 55:943-50; PMID:22752516; https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cis588 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical