TH9 cell differentiation, transcriptional control and function in inflammation, autoimmune diseases and cancer
- PMID: 27589682
- PMCID: PMC5342605
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11681
TH9 cell differentiation, transcriptional control and function in inflammation, autoimmune diseases and cancer
Abstract
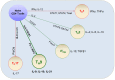
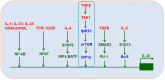
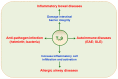
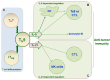
Naïve CD4+T cells differentiate into various T cell subsets depending on the specific cytokine environment. TH9 cells are less well-characterized than other T cell subsets, and factors that control their development and function have only recently been identified. It is now clear that TH9 cells play critical roles in immune-mediated diseases, including allergic airway, autoimmune and inflammatory bowel diseases, and cancer. Thus, the promotion or suppression of TH9 cell differentiation, transcriptional control and function may provide novel treatments for clinical inflammation, autoimmune diseases and tumors.
Keywords: T cell differentiation; TH9; allergic airway inflammation; autoimmune diseases; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

