Small Molecule-Photoactive Yellow Protein Labeling Technology in Live Cell Imaging
- PMID: 27589715
- PMCID: PMC6273459
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21091163
Small Molecule-Photoactive Yellow Protein Labeling Technology in Live Cell Imaging
Abstract
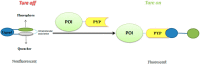
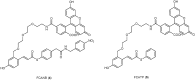
Characterization of the chemical environment, movement, trafficking and interactions of proteins in live cells is essential to understanding their functions. Labeling protein with functional molecules is a widely used approach in protein research to elucidate the protein location and functions both in vitro and in live cells or in vivo. A peptide or a protein tag fused to the protein of interest and provides the opportunities for an attachment of small molecule probes or other fluorophore to image the dynamics of protein localization. Here we reviewed the recent development of no-wash small molecular probes for photoactive yellow protein (PYP-tag), by the means of utilizing a quenching mechanism based on the intramolecular interactions, or an environmental-sensitive fluorophore. Several fluorogenic probes have been developed, with fast labeling kinetics and cell permeability. This technology allows quick live-cell imaging of cell-surface and intracellular proteins without a wash-out procedure.
Keywords: imaging; live cell; photo active yellow protein; protein labeling; small molecule.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



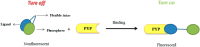
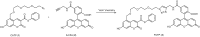



Similar articles
-
Small-molecule-based protein-labeling technology in live cell studies: probe-design concepts and applications.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Jan 21;47(1):247-56. doi: 10.1021/ar400135f. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 23927788 Review.
-
Side-chain specific isotopic labeling of proteins for infrared structural biology: the case of ring-D4-tyrosine isotope labeling of photoactive yellow protein.Protein Expr Purif. 2012 Sep;85(1):125-32. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2012.06.011. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Protein Expr Purif. 2012. PMID: 22800658
-
Development of fluorogenic probes for quick no-wash live-cell imaging of intracellular proteins.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Aug 21;135(33):12360-5. doi: 10.1021/ja405745v. Epub 2013 Aug 8. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23927377
-
Excitation-Wavelength-Dependent Photocycle Initiation Dynamics Resolve Heterogeneity in the Photoactive Yellow Protein from Halorhodospira halophila.Biochemistry. 2018 Mar 20;57(11):1733-1747. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01114. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29465990
-
The growing family of photoactive yellow proteins and their presumed functional roles.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2012 Oct;11(10):1495-514. doi: 10.1039/c2pp25090j. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22911088 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of Large Stokes Shift Fluorescent Proteins Based on Excited State Proton Transfer of an Engineered Photobase.J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Sep 22;143(37):15091-15102. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c05039. Epub 2021 Sep 13. J Am Chem Soc. 2021. PMID: 34516091 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Absorption and Emission in a Protein/Fluorophore Complex.ACS Chem Biol. 2024 Aug 16;19(8):1725-1732. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.4c00125. Epub 2024 Jul 24. ACS Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39046136 Free PMC article.
-
Near-infrared fluorescent probes: a next-generation tool for protein-labeling applications.Chem Sci. 2020 Oct 23;12(10):3437-3447. doi: 10.1039/d0sc04792a. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 34163617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

