Deep Brain Stimulation in Huntington's Disease-Preliminary Evidence on Pathophysiology, Efficacy and Safety
- PMID: 27589813
- PMCID: PMC5039467
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci6030038
Deep Brain Stimulation in Huntington's Disease-Preliminary Evidence on Pathophysiology, Efficacy and Safety
Abstract
Huntington's disease (HD) is one of the most disabling degenerative movement disorders, as it not only affects the motor system but also leads to cognitive disabilities and psychiatric symptoms. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the pallidum is a promising symptomatic treatment targeting the core motor symptom: chorea. This article gives an overview of preliminary evidence on pathophysiology, safety and efficacy of DBS in HD.
Keywords: DBS; Huntington; chorea; deep brain stimulation; globus pallidus; recordings; safety pathophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
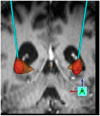
Related to Huntington’s Disease and/or deep brain stimulation: L.W. received consultant honoraria and travel grants from Medtronic, St. Jude Medical, Inomed and Desitin. S.J.G. received coverage of travel expenses and honoraria from Medtronic and Boston Scientific. C.J.H., S.E. and S.O. declare no conflicts of interest. A.S. and J.V. received consultant honoraria and travel grants from Medtronic. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript. Trial NCT02535884 is supported by Medtronic. Medtronic had no role in the design of the review, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. Medtronic provided Figure 1 for this manuscript on request of the authors.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

