Hematopoietic Stem Cells Are the Major Source of Multilineage Hematopoiesis in Adult Animals
- PMID: 27590115
- PMCID: PMC5054720
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.08.007
Hematopoietic Stem Cells Are the Major Source of Multilineage Hematopoiesis in Adult Animals
Abstract
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) sustain long-term reconstitution of hematopoiesis in transplantation recipients, yet their role in the endogenous steady-state hematopoiesis remains unclear. In particular, recent studies suggested that HSCs provide a relatively minor contribution to immune cell development in adults. We directed transgene expression in a fraction of HSCs that maintained reconstituting activity during serial transplantations. Inducible genetic labeling showed that transgene-expressing HSCs gave rise to other phenotypic HSCs, confirming their top position in the differentiation hierarchy. The labeled HSCs rapidly contributed to committed progenitors of all lineages and to mature myeloid cells and lymphocytes, but not to B-1a cells or tissue macrophages. Importantly, labeled HSCs gave rise to more than two-thirds of all myeloid cells and platelets in adult mice, and this contribution could be accelerated by an induced interferon response. Thus, classically defined HSCs maintain immune cell development in the steady state and during systemic cytokine responses.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
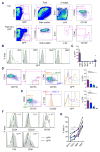
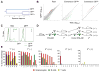
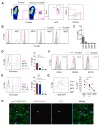
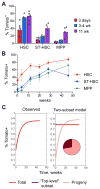
Comment in
-
HSC Contribution in Making Steady-State Blood.Immunity. 2016 Sep 20;45(3):464-466. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.09.002. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 27653597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benz C, Copley MR, Kent DG, Wohrer S, Cortes A, Aghaeepour N, Ma E, Mader H, Rowe K, Day C, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell subtypes expand differentially during development and display distinct lymphopoietic programs. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10:273–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 AI072571/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL132074/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA190400/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL113678/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CIHR/Canada
- T32 HD055165/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI100853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL129506/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008224/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA173861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI115382/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI072571/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG049074/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

