Interplay between RNA-binding protein HuR and microRNA-125b regulates p53 mRNA translation in response to genotoxic stress
- PMID: 27592685
- PMCID: PMC5100343
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1229734
Interplay between RNA-binding protein HuR and microRNA-125b regulates p53 mRNA translation in response to genotoxic stress
Abstract
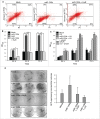
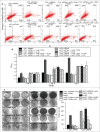
Tumor suppressor protein p53 plays a crucial role in maintaining genomic integrity in response to DNA damage. Regulation of translation of p53 mRNA is a major mode of regulation of p53 expression under genotoxic stress. The AU/U-rich element-binding protein HuR has been shown to bind to p53 mRNA 3'UTR and enhance translation in response to DNA-damaging UVC radiation. On the other hand, the microRNA miR-125b is reported to repress p53 expression and stress-induced apoptosis. Here, we show that UVC radiation causes an increase in miR-125b level in a biphasic manner, as well as nuclear cytoplasmic translocation of HuR. Binding of HuR to the p53 mRNA 3'UTR, especially at a site adjacent to the miR-125b target site, causes dissociation of the p53 mRNA from the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and inhibits the miR-125b-mediated translation repression of p53. HuR prevents the oncogenic effect of miR-125b by reversing the decrease in apoptosis and increase in cell proliferation caused by the overexpression of miR-125b. The antagonistic interplay between miR-125b and HuR might play an important role in fine-tuning p53 gene expression at the post-transcriptional level, and thereby regulate the cellular response to genotoxic stress.
Keywords: Cancer; DNA damage; HuR; RNA-binding protein; miR-125b; microRNA; p53; translation regulation.
Figures





References
-
- Giaccia AJ, Kastan MB. The complexity of p53 modulation: emerging patterns from divergent signals. Genes Dev 1998; 12:2973-83; PMID:9765199; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.12.19.2973 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Horn HF, Vousden KH. Coping with stress: multiple ways to activate p53. Oncogene 2007; 26:1306-16; PMID:17322916; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210263 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ray PS, Grover R, Das S. Two internal ribosome entry sites mediate the translation of p53 isoforms. EMBO Rep 2006; 7:404-10; PMID:16440000; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400623 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vilborg A, Wilhelm MT, Wiman KG. Regulation of tumor suppressor p53 at the RNA level. J Mol Med (Berl) 2010; 88:645-52; PMID:20306257; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00109-010-0609-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takagi M, Absalon MJ, McLure KG, Kastan MB. Regulation of p53 translation and induction after DNA damage by ribosomal protein L26 and nucleolin. Cell 2005; 123:49-63; PMID:16213212; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.034 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
