A tri-coil bellows-type round window transducer with improved frequency characteristics for middle-ear implants
- PMID: 27594098
- PMCID: PMC5266591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2016.08.013
A tri-coil bellows-type round window transducer with improved frequency characteristics for middle-ear implants
Abstract
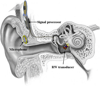
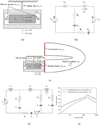
A number of methods to drive the round window (RW) using a floating mass transducer (FMT) have been reported. This method has attracted attention because the FMT is relatively easy to implant in the RW niche. However, the use of an FMT to drive the RW has been proven to produce low outputs at frequencies below approximately 1 kHz. In this study, a new tri-coil bellows-type transducer (TCBT), which has excellent low frequency output and is easy to implant, is proposed. To design the frequency characteristics of the TCBT, mechanical and electrical simulations were performed, and then a comparative analysis was conducted between a floating mass type transducer (like the FMT) and a fixed type transducer (like the TCBT). The features of the proposed TCBT are as follows. First, the TCBT's housing is fixed to the RW niche so that it does not vibrate. Second, the internal end of a tiny bellows is connected to a vibrating three-pole permanent magnet located within three field coils. Finally, the rim of the bellows bottom is attached to the end of the housing that hermetically encloses the three field coils. In this design, the only vibrating element is the bellows itself, which efficiently drives the RW membrane. To evaluate the characteristics of this newly developed TCBT, the transducer was installed in the RW niche of temporal bones and the velocity of the stapes was measured using a laser Doppler vibrometer. The experimental results indicate that the TCBT can produce 100, 111, and 129 dB SPL equivalent pressure outputs at below 1 kHz, 1-3 kHz, and above 3 kHz, respectively. Thus, the TCBT with one side coupled to the RW via a bellows will be easy to implant and offer better performance than an FMT.
Keywords: Middle-ear implants; Round window (RW); Tri-coil bellows-type transducer (TCBT).
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
-
- ASTM International. Standard Practice for Describing System Output of Implantable Middle Ear Hearing Devices, Designation. 2005. pp. F2504–F2505.
-
- Arnold A, Kompis M, Candreia C, Pfiffner F, Häusler R, Stieger C. The floating mass transducer at the round window: direct transmission or bone conduction? Hear. Res. 2010a;263:120–127. - PubMed
-
- Arnold A, Stieger C, Candreia C, Pfiffner F, Kompis M. Factors improving the vibration transfer of the floating mass transducer at the round window. Otol. Neurotol. 2010b;31(1):122–128. - PubMed
-
- Backous DD, Duke W. Implantable middle ear hearing devices: current state of technology and market challenge. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006;14(5):314–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

