Veno-occlusive disease nurse management: development of a dynamic monitoring tool by the GITMO nursing group
- PMID: 27594906
- PMCID: PMC4990055
- DOI: 10.3332/ecancer.2016.661
Veno-occlusive disease nurse management: development of a dynamic monitoring tool by the GITMO nursing group
Abstract
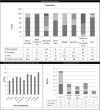
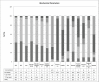
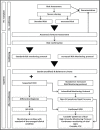
Veno-occlusive disease (VOD) is a complication arising from the toxicity of conditioning regimens that have a significant impact on the survival of patients who undergo stem cell transplantation. There are several known risk factors for developing VOD and their assessment before the start of conditioning regimens could improve the quality of care. Equally important are early identification of signs and symptoms ascribable to VOD, rapid diagnosis, and timely adjustment of support therapy and treatment. Nurses have a fundamental role at the stages of assessment and monitoring for signs and symptoms; therefore, they should have documented skills and training. The literature defines nurses' areas of competence in managing VOD, but in the actual clinical practice, this is not so clear. Moreover, there is an intrinsic difficulty in managing VOD due to its rapid and often dramatic evolution, together with a lack of care tools to guide nurses. Through a complex evidence-based process, the Gruppo Italiano per il Trapianto di Midollo Osseo (GITMO), cellule staminali emopoietiche e terapia cellulare nursing board has developed an operational flowchart and a dynamic monitoring tool applicable to haematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients, whether they develop this complication or not.
Keywords: assessment; monitoring; nurse management; stem cell transplantation; veno-occlusive disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nursing role in the assessment and care of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome patients: a consensus paper by the "Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo".Support Care Cancer. 2020 Nov;28(11):5125-5137. doi: 10.1007/s00520-020-05353-9. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Support Care Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32056012
-
BCSH/BSBMT guideline: diagnosis and management of veno-occlusive disease (sinusoidal obstruction syndrome) following haematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Br J Haematol. 2013 Nov;163(4):444-57. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12558. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Br J Haematol. 2013. PMID: 24102514
-
Veno-occlusive Disease in HSCT Patients: Consensus-based Recommendations for Risk Assessment, Diagnosis, and Management by the GITMO Group.Transplantation. 2021 Apr 1;105(4):686-694. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003569. Transplantation. 2021. PMID: 33273315
-
Histocompatibility assessment in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: recommendations from the Italian Society for Immunogenetics and Transplantation Biology (Associazione Italiana di Immunogenetica e Biologia dei Trapianti - AIBT).Blood Transfus. 2024 Jul 12;22(4):338-349. doi: 10.2450/BloodTransfus.495. Blood Transfus. 2024. PMID: 37458719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Best practice for peripheral blood progenitor cell mobilization and collection in adults and children: results of a Società Italiana Di Emaferesi e Manipolazione Cellulare (SIDEM) and Gruppo Italiano Trapianto Midollo Osseo (GITMO) consensus process.Transfusion. 2012 Apr;52(4):893-905. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2011.03385.x. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Transfusion. 2012. PMID: 21980921
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of VOD/SOS After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 3;11:489. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00489. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32318059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Operational procedure sharing pathway in veno-occlusive disease: a Delphi consensus-based recommendations.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 12;15:1498782. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1498782. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40144213 Free PMC article.
-
Nursing role in the assessment and care of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome patients: a consensus paper by the "Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo".Support Care Cancer. 2020 Nov;28(11):5125-5137. doi: 10.1007/s00520-020-05353-9. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Support Care Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32056012
References
-
- Baron F, Deprez M, Beguin Y. The veno-occlusive disease of the liver. Haematologica. 1997;82:718–725. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources