Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation with Polymethylmethacrylate Augmentation for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Intravertebral Pseudoarthrosis Associated with Kummell's Osteonecrosis
- PMID: 27595101
- PMCID: PMC4995318
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/3878063
Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation with Polymethylmethacrylate Augmentation for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Intravertebral Pseudoarthrosis Associated with Kummell's Osteonecrosis
Abstract
Purpose. The purpose of our study is to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of short-segment percutaneous pedicle screw fixation with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) augmentation for the treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar compression fracture with osteonecrosis. Methods. Osteoporotic thoracolumbar compression fractures with avascular necrosis were treated by short-segment PPF with PMMA augmentation. Eighteen were followed up for more than 2 years. The kyphotic angle, compression ratio, visual analog scale (VAS) score for back pain, and the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) were analyzed. In addition, radiologic and clinical parameters of PPF group were compared with percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP) group. Results. Vertebral height and kyphotic angle of the compressed vertebral bodies were significantly corrected after the operation (P < 0.05). Further, restored vertebral height was maintained during the 2 or more years of postoperative follow-up. Compared to the PVP group the postoperative compression ratio and kyphotic angle were significantly lower in the PPF group (P < 0.05). The postoperative ODI and VAS of the PVP group were significantly higher than the PPF (P < 0.05). Conclusions. According to our results, short-segment PPF with PMMA augmentation may be an effective minimally invasive treatment for osteoporosis in cases of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with Kummell's osteonecrosis.
Figures
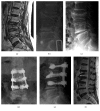


References
-
- Kim D.-Y., Lee S.-H., Jang J. S., Chung S. K., Lee H.-Y. Intravertebral vacuum phenomenon in osteoporotic compression fracture: report of 67 cases with quantitative evaluation of intravertebral instability. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2004;100(supplement 1):24–31. doi: 10.3171/jns.2004.100.1.0024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Becker S., Tuschel A., Chavanne A., Meissner J., Ogon M. Balloon kyphoplasty for vertebra plana with or without osteonecrosis. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery. 2008;16(1):14–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

