Neutralizing blood-borne polyphosphate in vivo provides safe thromboprotection
- PMID: 27596064
- PMCID: PMC5025862
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12616
Neutralizing blood-borne polyphosphate in vivo provides safe thromboprotection
Abstract
Polyphosphate is an inorganic procoagulant polymer. Here we develop specific inhibitors of polyphosphate and show that this strategy confers thromboprotection in a factor XII-dependent manner. Recombinant Escherichia coli exopolyphosphatase (PPX) specifically degrades polyphosphate, while a PPX variant lacking domains 1 and 2 (PPX_Δ12) binds to the polymer without degrading it. Both PPX and PPX_Δ12 interfere with polyphosphate- but not tissue factor- or nucleic acid-driven thrombin formation. Targeting polyphosphate abolishes procoagulant platelet activity in a factor XII-dependent manner, reduces fibrin accumulation and impedes thrombus formation in blood under flow. PPX and PPX_Δ12 infusions in wild-type mice interfere with arterial thrombosis and protect animals from activated platelet-induced venous thromboembolism without increasing bleeding from injury sites. In contrast, targeting polyphosphate does not provide additional protection from thrombosis in factor XII-deficient animals. Our data provide a proof-of-concept approach for combating thrombotic diseases without increased bleeding risk, indicating that polyphosphate drives thrombosis via factor XII.
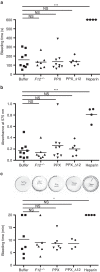
Figures
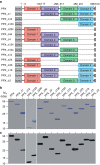

 =PPX variant,
=PPX variant,  =6xHis-tag antibody and
=6xHis-tag antibody and  =HRP-coupled detection antibody. Shown are relative amounts of PPX variants binding to polyP. Data blotted relative to full-size PPX, set to 1.0. Mean±s.e.m., n=4, ***P<0.001 by Student's t-test. (c) Gel mobility shift assay of full-size PPX, PPX_Δ1, PPX_Δ2, PPX_Δ12 and PPX_Δ124 binding to polyP. Increasing concentrations of PPX mutants (0–400 nM) were incubated with polyP (7.5 μg ml−1) for 30 min, and reaction mixtures containing 0–8 pmol mutant protein per lane were resolved on 1% agarose gels. PolyP was visualized with DAPI-negative staining and synthetic polyP with mean chain length of 383 and 637 phosphate units served as molecular size standard. (d) PPX_Δ12 (400 nM) was incubated for 30 min with increasing concentrations of various polyanions including LC polyP, SC polyP, dextran sulfate (DXS), oversulfated chondroitin sulfate (OSCS), DNA, RNA, chondroitin sulfate (CS), dermatan sulfate (DS) and heparan sulfate (HS). PPX_Δ12/polyanion complexes were dissolved on urea-polyacrylamide gels and PPX_Δ12 protein was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. The dashed line gives PPX_Δ12/polyanion complex formation assessed by densitometric scans. A representative gel of three independent experiments is shown.
=HRP-coupled detection antibody. Shown are relative amounts of PPX variants binding to polyP. Data blotted relative to full-size PPX, set to 1.0. Mean±s.e.m., n=4, ***P<0.001 by Student's t-test. (c) Gel mobility shift assay of full-size PPX, PPX_Δ1, PPX_Δ2, PPX_Δ12 and PPX_Δ124 binding to polyP. Increasing concentrations of PPX mutants (0–400 nM) were incubated with polyP (7.5 μg ml−1) for 30 min, and reaction mixtures containing 0–8 pmol mutant protein per lane were resolved on 1% agarose gels. PolyP was visualized with DAPI-negative staining and synthetic polyP with mean chain length of 383 and 637 phosphate units served as molecular size standard. (d) PPX_Δ12 (400 nM) was incubated for 30 min with increasing concentrations of various polyanions including LC polyP, SC polyP, dextran sulfate (DXS), oversulfated chondroitin sulfate (OSCS), DNA, RNA, chondroitin sulfate (CS), dermatan sulfate (DS) and heparan sulfate (HS). PPX_Δ12/polyanion complexes were dissolved on urea-polyacrylamide gels and PPX_Δ12 protein was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. The dashed line gives PPX_Δ12/polyanion complex formation assessed by densitometric scans. A representative gel of three independent experiments is shown.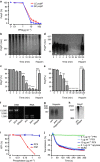


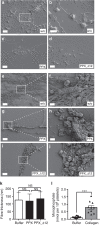
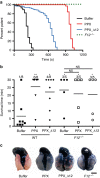
References
-
- Eikelboom J. W. & Weitz J. I. New anticoagulants. Circulation 121, 1523–1532 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Franchini M., Mengoli C., Cruciani M., Bonfanti C. & Mannucci P. M. Effects on bleeding complications of pharmacogenetic testing for initial dosing of vitamin K antagonists: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 12, 1480–1487 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Baber U., Mastoris I. & Mehran R. Balancing ischaemia and bleeding risks with novel oral anticoagulants. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 11, 693–703 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Kornberg A., Rao N. N. & Ault-Riche D. Inorganic polyphosphate: a molecule of many functions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 89–125 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

