Regulation of inflammatory responses by neuregulin-1 in brain ischemia and microglial cells in vitro involves the NF-kappa B pathway
- PMID: 27596278
- PMCID: PMC5011915
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0703-7
Regulation of inflammatory responses by neuregulin-1 in brain ischemia and microglial cells in vitro involves the NF-kappa B pathway
Abstract
Background: We previously demonstrated that neuregulin-1 (NRG-1) was neuroprotective in rats following ischemic stroke. Neuroprotection by NRG-1 was associated with the suppression of pro-inflammatory gene expression in brain tissues. Over-activation of brain microglia can induce pro-inflammatory gene expression by activation of transcriptional regulators following stroke. Here, we examined how NRG-1 transcriptionally regulates inflammatory gene expression by computational bioinformatics and in vitro using microglial cells.
Methods: To identify transcriptional regulators involved in ischemia-induced inflammatory gene expression, rats were sacrificed 24 h after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and NRG-1 treatment. Gene expression profiles of brain tissues following ischemia and NRG-1 treatment were examined by microarray technology. The Conserved Transcription Factor-Binding Site Finder (CONFAC) bioinformatics software package was used to predict transcription factors associated with inflammatory genes induced following stroke and suppressed by NRG-1 treatment. NF-kappa B (NF-kB) was identified as a potential transcriptional regulator of NRG-1-suppressed genes following ischemia. The involvement of specific NF-kB subunits in NRG-1-mediated inflammatory responses was examined using N9 microglial cells pre-treated with NRG-1 (100 ng/ml) followed by lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 10 μg/ml) stimulation. The effects of NRG-1 on cytokine production were investigated using Luminex technology. The levels of the p65, p52, and RelB subunits of NF-kB and IkB-α were determined by western blot analysis and ELISA. Phosphorylation of IkB-α was investigated by ELISA.
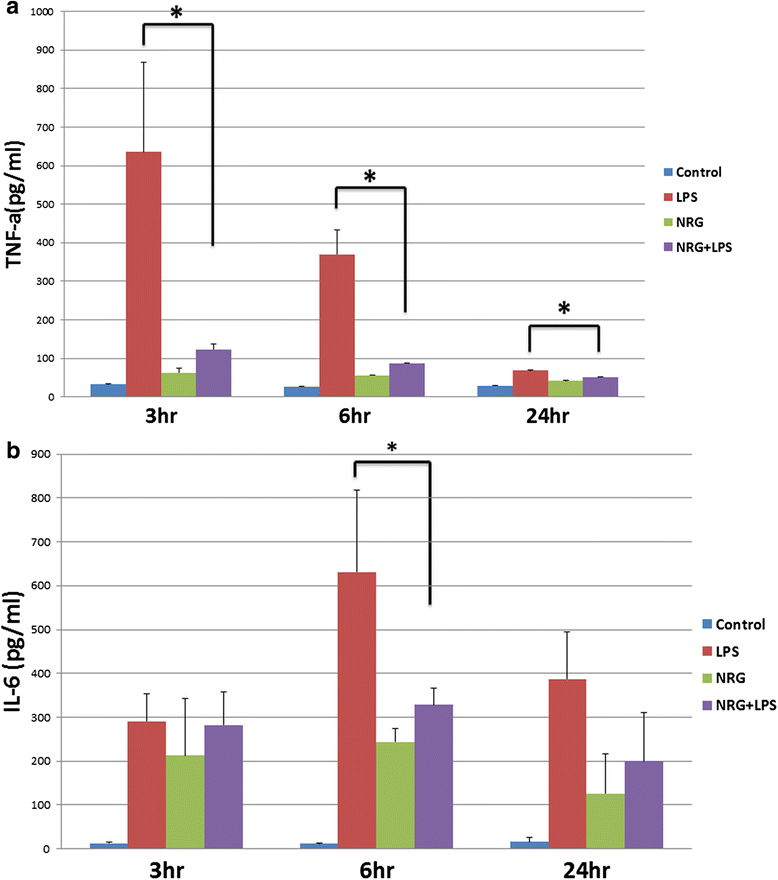
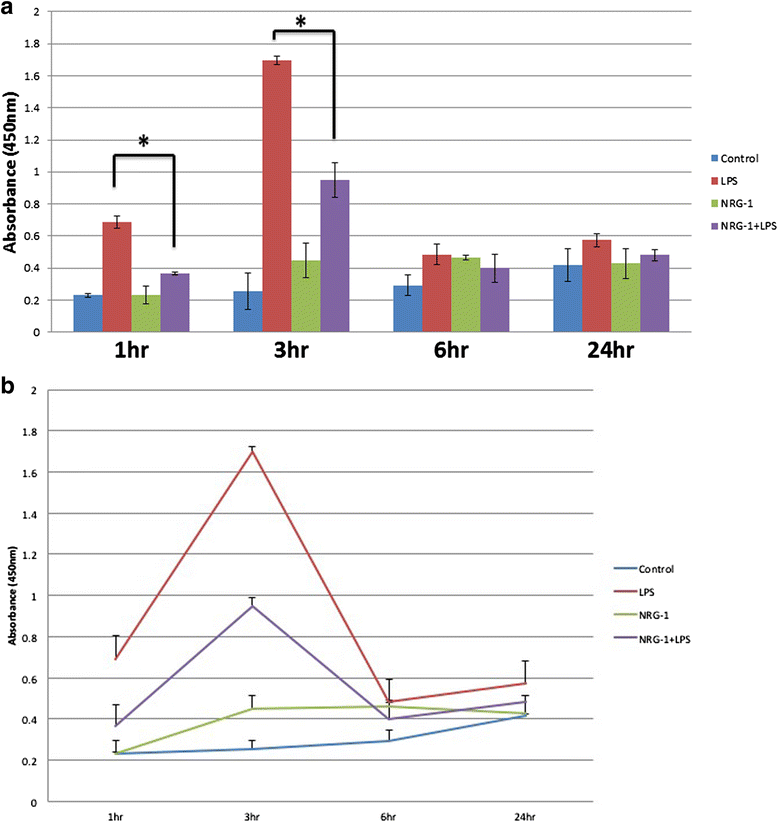
Results: CONFAC identified 12 statistically over-represented transcription factor-binding sites (TFBS) in our dataset, including NF-kBP65. Using N9 microglial cells, we observed that NRG-1 significantly inhibited LPS-induced TNFα and IL-6 release. LPS increased the phosphorylation and degradation of IkB-α which was blocked by NRG-1. NRG-1 also prevented the nuclear translocation of the NF-kB p65 subunit following LPS administration. However, NRG-1 increased production of the neuroprotective cytokine granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) and the nuclear translocation of the NF-kB p52 subunit, which is associated with the induction of anti-apoptotic and suppression of pro-inflammatory gene expression.
Conclusions: Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of NRG-1 are associated with the differential regulation of NF-kB signaling pathways in microglia. Taken together, these findings suggest that NRG-1 may be a potential therapeutic treatment for treating stroke and other neuroinflammatory disorders.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Gene expression; Inflammation; Ischemia; Microarray; Neuregulin; Stroke; Transcription factor-binding site (TFBS).
Figures






Similar articles
-
Neuregulin-1 inhibits neuroinflammatory responses in a rat model of organophosphate-nerve agent-induced delayed neuronal injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Apr 2;12:64. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0283-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 25880399 Free PMC article.
-
Lentivirus-mediated overexpression of OTULIN ameliorates microglia activation and neuroinflammation by depressing the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Mar 15;15(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1117-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29544517 Free PMC article.
-
Kellerin from Ferula sinkiangensis exerts neuroprotective effects after focal cerebral ischemia in rats by inhibiting microglia-mediated inflammatory responses.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113718. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113718. Epub 2020 Dec 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33352239
-
The Impact of Nuclear Factor Kappa B on the Response of Microglia in Spinal Cord Injuries.Cureus. 2025 Feb 20;17(2):e79367. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79367. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40125122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RUNX1: A Regulator of NF-kB Signaling in Pulmonary Diseases.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018;19(2):172-178. doi: 10.2174/1389203718666171009111835. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 28990531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuregulin-1 attenuates hemolysis- and ischemia induced-cerebrovascular inflammation associated with sickle cell disease.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2023 Feb;32(2):106912. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2022.106912. Epub 2022 Dec 5. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2023. PMID: 36473396 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Anthocyanins Extracted from Oryza sativa L. in Primary Dermal Fibroblasts.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Jul 31;2019:2089817. doi: 10.1155/2019/2089817. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31467631 Free PMC article.
-
Neuregulin-1/ErbB4 signaling modulates Plasmodium falciparum HRP2-induced damage to brain cortical organoids.iScience. 2022 May 14;25(6):104407. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104407. eCollection 2022 Jun 17. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35663028 Free PMC article.
-
The case for neuregulin-1 as a clinical treatment for stroke.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Apr 4;18:1325630. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1325630. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38638304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gonadotropin-Dependent Neuregulin-1 Signaling Regulates Female Rat Ovarian Granulosa Cell Survival.Endocrinology. 2017 Oct 1;158(10):3647-3660. doi: 10.1210/en.2017-00065. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28938399 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

