Postauricular reflexes elicited by soft acoustic clicks and loud noise probes: Reliability, prepulse facilitation, and sensitivity to picture contents
- PMID: 27596354
- PMCID: PMC5819592
- DOI: 10.1111/psyp.12757
Postauricular reflexes elicited by soft acoustic clicks and loud noise probes: Reliability, prepulse facilitation, and sensitivity to picture contents
Abstract
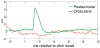
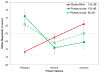
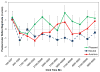
The startle blink reflex is facilitated during early picture viewing, then inhibited by attention during pleasant and aversive pictures compared to neutral pictures, and finally potentiated during aversive pictures specifically. However, it is unclear whether the postauricular reflex, which is elicited by the same loud acoustic probe as the startle blink reflex but enhanced by appetitive instead of defensive emotion, has the same pattern and time course of emotional modulation. We examined this issue in a sample of 90 undergraduates using serially presented soft acoustic clicks that elicited postauricular (but not startle blink) reflexes in addition to standard startle probes. Postauricular reflexes elicited by both clicks and probes correlated during food and nurturant contents, during which they were potentiated compared to neutral pictures, suggesting clicks effectively elicit emotionally modulated postauricular reflexes. The postauricular reflex was initially facilitated during the first 500 ms of picture processing but was larger during pleasant than neutral pictures throughout picture processing, with larger effect sizes during the latter half of picture processing. Across reflexes and eliciting stimuli, measures of emotional modulation had higher coefficient alphas than magnitudes during specific picture contents within each valence, indicating that only emotional modulation measures assess higher-order appetitive or defensive processing.
Keywords: Emotion; Internal consistency; Postauricular reflex; Prepulse facilitation; Startle blink reflex; Time course.
© 2016 Society for Psychophysiological Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postauricular and superior auricular reflex modulation during emotional pictures and sounds.Psychophysiology. 2011 Mar;48(3):410-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.01071.x. Psychophysiology. 2011. PMID: 20636290 Free PMC article.
-
Postauricular reflex responses to pictures varying in valence and arousal.Psychophysiology. 2009 May;46(3):487-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2009.00794.x. Epub 2009 Feb 17. Psychophysiology. 2009. PMID: 19226306
-
Prepulse inhibition and facilitation of the postauricular reflex, a vestigial remnant of pinna startle.Psychophysiology. 2017 Apr;54(4):566-577. doi: 10.1111/psyp.12819. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Psychophysiology. 2017. PMID: 28168713
-
Emotion, attention, and the startle reflex.Psychol Rev. 1990 Jul;97(3):377-95. Psychol Rev. 1990. PMID: 2200076 Review.
-
Heightened stress responsivity and emotional reactivity during pubertal maturation: Implications for psychopathology.Dev Psychopathol. 2009 Winter;21(1):87-97. doi: 10.1017/S0954579409000066. Dev Psychopathol. 2009. PMID: 19144224 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Measuring Pavlovian appetitive conditioning in humans with the postauricular reflex.Psychophysiology. 2018 Aug;55(8):e13073. doi: 10.1111/psyp.13073. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Psychophysiology. 2018. PMID: 29524234 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced positive emotion and underarousal are uniquely associated with subclinical depression symptoms: Evidence from psychophysiology, self-report, and symptom clusters.Psychophysiology. 2017 Jul;54(7):1010-1030. doi: 10.1111/psyp.12853. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Psychophysiology. 2017. PMID: 28322458 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the post-auricular reflex in response to social and CT-optimal touch.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 13;20(8):e0329625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329625. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40802700 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Mixed Emotions: Paradigms and Measures.Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2017 Jun;15:62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2017.05.016. Epub 2017 Jun 4. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2017. PMID: 28804752 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

