Gamma radiation at a human relevant low dose rate is genotoxic in mice
- PMID: 27596356
- PMCID: PMC5011728
- DOI: 10.1038/srep32977
Gamma radiation at a human relevant low dose rate is genotoxic in mice
Abstract
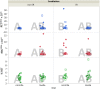
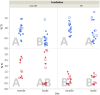
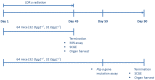
Even today, 70 years after Hiroshima and accidents like in Chernobyl and Fukushima, we still have limited knowledge about the health effects of low dose rate (LDR) radiation. Despite their human relevance after occupational and accidental exposure, only few animal studies on the genotoxic effects of chronic LDR radiation have been performed. Selenium (Se) is involved in oxidative stress defence, protecting DNA and other biomolecules from reactive oxygen species (ROS). It is hypothesised that Se deficiency, as it occurs in several parts of the world, may aggravate harmful effects of ROS-inducing stressors such as ionising radiation. We performed a study in the newly established LDR-facility Figaro on the combined effects of Se deprivation and LDR γ exposure in DNA repair knockout mice (Ogg1(-/-)) and control animals (Ogg1(+/-)). Genotoxic effects were seen after continuous radiation (1.4 mGy/h) for 45 days. Chromosomal damage (micronucleus), phenotypic mutations (Pig-a gene mutation of RBC(CD24-)) and DNA lesions (single strand breaks/alkali labile sites) were significantly increased in blood cells of irradiated animals, covering three types of genotoxic activity. This study demonstrates that chronic LDR γ radiation is genotoxic in an exposure scenario realistic for humans, supporting the hypothesis that even LDR γ radiation may induce cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
S.D.D. is an employee of Litron Laboratories; Litron holds patents covering flow cytometric methods for scoring GPI anchor-deficient erythrocytes and sells kits based on this technology (In Vivo MutaFlow); Litron holds patents covering flow cytometric methods for scoring micronucleated erythrocytes and sells kits based on this technology (In Vivo MicroFlow).
Figures



References
-
- Suzuki K. & Yamashita S. Low-dose radiation exposure and carcinogenesis. Japanese journal of clinical oncology 42, 563–568 (2012). - PubMed
-
- UNSCEAR. Report of the United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation 2010: 57th session: summary of low-dose radiation effects on health. (2010).
-
- UNSCEAR. Sources, effects and risks of ionizing radiation. Annex A: Levels and effects of radiation exposure due to the nuclear accident after the 2011 great east-Japan earthquake and tsunami. (United Nations, New York, 2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

