Effect of Ulinastatin in the Treatment of Postperative Cognitive Dysfunction: Review of Current Literature
- PMID: 27597957
- PMCID: PMC5002304
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/2571080
Effect of Ulinastatin in the Treatment of Postperative Cognitive Dysfunction: Review of Current Literature
Abstract
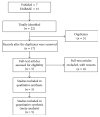
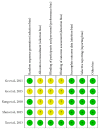
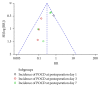
Background. Ulinastatin, identified as a urinary trypsin inhibitor, has been widely used in patients with inflammatory disorders. However, little is known about its effect on postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). The aim of our current work is to review the current body of literature. Methods. A systematic literature search in PubMed and EMBASE was performed to identify randomized controlled trials. Incidence of POCD, MMSE score, and laboratory indicators (IL-6, TNF-α, CRP, and S100β) were selected as outcomes. Results. Five RCTs involving 461 elderly patients that underwent surgical operations were identified. The meta-analysis suggested no statistical difference of incidence of POCD between ulinastatin and control groups on postoperative day 1; but ulinastatin could significantly decrease the incidence of POCD on postoperative day 3 and day 7 when compared with control treatment. Ulinastatin was effective in improving the MMSE score on day 1, day 3, and day 7 after operation. IL-6 and S100β concentrations were lower up to postoperative day 2. The incidences of postoperative complications in ulinastatin groups were lower than control. Conclusion. Ulinastatin administration was effective in treating early POCD (postoperative day 3 and day 7) and reducing IL-6 and S100β concentrations within two days after operations. Studies with larger-scale and rigorous design are urgently needed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A preliminary study of the effects of ulinastatin on early postoperative cognition function in patients undergoing abdominal surgery.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Apr 29;541:15-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.02.008. Epub 2013 Feb 16. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23422155 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of ulinastatin on cognitive dysfunction after general anesthesia in elderly patients: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Apr 2;100(13):e24814. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024814. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33787575 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ulinastatin on early postoperative cognitive function after one-lung ventilation surgery in elderly patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Metab Brain Dis. 2017 Apr;32(2):427-435. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9926-7. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Metab Brain Dis. 2017. PMID: 27830357 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Ulinastatin on Early Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction in Elderly Patients Undergoing Surgery: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jun 21;15:618589. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.618589. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34248475 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of parecoxib in the treatment of postoperative cognitive dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jan;98(1):e13812. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013812. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30608392 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation for postoperative cognitive dysfunction in geriatric patients with gastrointestinal tumor: a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Aug 23;22(1):563. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05534-9. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34425851 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ulinastatin May Significantly Improve Postoperative Cognitive Function of Elderly Patients Undergoing Spinal Surgery by Reducing the Translocation of Lipopolysaccharide and Systemic Inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 9;9:1007. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01007. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30356711 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of ulinastatin on isoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus of rats].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Jul 30;39(7):850-854. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.07.16. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31340920 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Insights into Advanced Neurological Dysfunction Mechanisms Following DBS Surgery in Parkinson's Patients: Neuroinflammation and Pyroptosis.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 May 20;45(5):4480-4494. doi: 10.3390/cimb45050284. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37232753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of anesthetic adjunctive agents on postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients undergoing noncardiac surgery: A Bayesian network meta-analysis.Brain Behav. 2023 Aug;13(8):e3149. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3149. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 37431799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Terrando N., Monaco C., Ma D., Foxwell B. M. J., Feldmannc M., Maze M. Tumor necrosis factor-a triggers a cytokine cascade yielding postoperative cognitive decline. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107(47):20518–20522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014557107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

