Oxidative Stress, DNA Damage and DNA Repair in Female Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
- PMID: 27598300
- PMCID: PMC5012603
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162082
Oxidative Stress, DNA Damage and DNA Repair in Female Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2DM) is associated with oxidative stress which in turn can lead to DNA damage. The aim of the present study was to analyze oxidative stress, DNA damage and DNA repair in regard to hyperglycemic state and diabetes duration.
Methods: Female T2DM patients (n = 146) were enrolled in the MIKRODIAB study and allocated in two groups regarding their glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level (HbA1c≤7.5%, n = 74; HbA1c>7.5%, n = 72). In addition, tertiles according to diabetes duration (DD) were created (DDI = 6.94±3.1 y, n = 49; DDII = 13.35±1.1 y, n = 48; DDIII = 22.90±7.3 y, n = 49). Oxidative stress parameters, including ferric reducing ability potential, malondialdehyde, oxidized and reduced glutathione, reduced thiols, oxidized LDL and F2-Isoprostane as well as the activity of antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase were measured. Damage to DNA was analyzed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and whole blood with single cell gel electrophoresis. DNA base excision repair capacity was tested with the modified comet repair assay. Additionally, mRNA expressions of nine genes related to base excision repair were analyzed in a subset of 46 matched individuals.
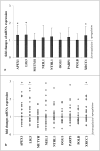
Results: No significant differences in oxidative stress parameters, antioxidant enzyme activities, damage to DNA and base excision repair capacity, neither between a HbA1c cut off />7.5%, nor between diabetes duration was found. A significant up-regulation in mRNA expression was found for APEX1, LIG3 and XRCC1 in patients with >7.5% HbA1c. Additionally, we observed higher total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, LDL/HDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, Framingham risk score, systolic blood pressure, BMI and lower HDL-cholesterol in the hyperglycemic group.
Conclusion: BMI, blood pressure and blood lipid status were worse in hyperglycemic individuals. However, no major disparities regarding oxidative stress, damage to DNA and DNA repair were present which might be due to good medical treatment with regular health checks in T2DM patients in Austria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parameters of oxidative stress, DNA damage and DNA repair in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2011 Oct;117(4):222-30. doi: 10.3109/13813455.2010.551135. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21338322
-
Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Genes Involved in Repair of Oxidative DNA Damage and the Risk of Recurrent Depressive Disorder.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Nov 20;22:4455-4474. doi: 10.12659/msm.898091. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27866211 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage is increased in lymphocytes of patients with metabolic syndrome.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015 Apr;782:30-5. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015. PMID: 25868129
-
Variant base excision repair proteins: contributors to genomic instability.Semin Cancer Biol. 2010 Oct;20(5):320-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.10.010. Epub 2010 Oct 16. Semin Cancer Biol. 2010. PMID: 20955798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enzymology of mitochondrial base excision repair.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;68:257-71. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)68105-4. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11554302 Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Clinical Studies on Type 2 Diabetes and Its Complications.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 May 12;2019:5953685. doi: 10.1155/2019/5953685. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31214280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Genomic Instability with HbA1c levels and Medication in Diabetic Patients.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 2;7:41985. doi: 10.1038/srep41985. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28150817 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Micronuclei Frequency in Oral and Lingual Epithelium of Treated Diabetes Mellitus Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jan 9;2018:4898153. doi: 10.1155/2018/4898153. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29546061 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress and Related Biomarkers in Gilbert's Syndrome: A Secondary Analysis of Two Case-Control Studies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Sep 15;10(9):1474. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091474. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573106 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the expression of genes associated with iron metabolism in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.Free Radic Biol Med. 2024 Jan;210:344-351. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.11.042. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38056574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kahn SE. Clinical review 135—The importance of beta-cell failure in the development and progression of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(9):4047–58. WOS:000170951600002. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

