Genome-wide association study of antisocial personality disorder
- PMID: 27598967
- PMCID: PMC5048197
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2016.155
Genome-wide association study of antisocial personality disorder
Abstract
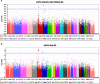
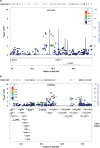
The pathophysiology of antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) remains unclear. Although the most consistent biological finding is reduced grey matter volume in the frontal cortex, about 50% of the total liability to developing ASPD has been attributed to genetic factors. The contributing genes remain largely unknown. Therefore, we sought to study the genetic background of ASPD. We conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) and a replication analysis of Finnish criminal offenders fulfilling DSM-IV criteria for ASPD (N=370, N=5850 for controls, GWAS; N=173, N=3766 for controls and replication sample). The GWAS resulted in suggestive associations of two clusters of single-nucleotide polymorphisms at 6p21.2 and at 6p21.32 at the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) region. Imputation of HLA alleles revealed an independent association with DRB1*01:01 (odds ratio (OR)=2.19 (1.53-3.14), P=1.9 × 10(-5)). Two polymorphisms at 6p21.2 LINC00951-LRFN2 gene region were replicated in a separate data set, and rs4714329 reached genome-wide significance (OR=1.59 (1.37-1.85), P=1.6 × 10(-9)) in the meta-analysis. The risk allele also associated with antisocial features in the general population conditioned for severe problems in childhood family (β=0.68, P=0.012). Functional analysis in brain tissue in open access GTEx and Braineac databases revealed eQTL associations of rs4714329 with LINC00951 and LRFN2 in cerebellum. In humans, LINC00951 and LRFN2 are both expressed in the brain, especially in the frontal cortex, which is intriguing considering the role of the frontal cortex in behavior and the neuroanatomical findings of reduced gray matter volume in ASPD. To our knowledge, this is the first study showing genome-wide significant and replicable findings on genetic variants associated with any personality disorder.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HTR3B is associated with alcoholism with antisocial behavior and alpha EEG power--an intermediate phenotype for alcoholism and co-morbid behaviors.Alcohol. 2009 Feb;43(1):73-84. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2008.09.005. Alcohol. 2009. PMID: 19185213 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between a functional MAOA locus and childhood sexual abuse predicts alcoholism and antisocial personality disorder in adult women.Mol Psychiatry. 2008 Mar;13(3):334-47. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002034. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Mol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 17592478
-
Genome-wide association study of susceptibility loci for cervical cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013 May 1;105(9):624-33. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djt051. Epub 2013 Mar 12. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013. PMID: 23482656
-
Update on Antisocial Personality Disorder.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2024 Oct;26(10):543-549. doi: 10.1007/s11920-024-01528-x. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2024. PMID: 39230801 Review.
-
HLA associations in schizophrenia: are we re-discovering the wheel?Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2014 Jan;165B(1):19-27. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32195. Epub 2013 Oct 19. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2014. PMID: 24142843 Review.
Cited by
-
Objective and subjective measures of sleep initiation are differentially associated with DNA methylation in adolescents.Clin Epigenetics. 2023 Aug 26;15(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01553-2. Clin Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 37634000 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of erythropoiesis and altered erythroblastic NMDA receptor-mediated calcium influx in Lrfn2-deficient mice.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 22;16(1):e0245624. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245624. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33481887 Free PMC article.
-
Sorting nexin-27 regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through the synaptic adhesion protein LRFN2.Elife. 2021 Jul 12;10:e59432. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59432. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34251337 Free PMC article.
-
Born this way? A review of neurobiological and environmental evidence for the etiology of psychopathy.Personal Neurosci. 2019 Oct 23;2:e8. doi: 10.1017/pen.2019.7. eCollection 2019. Personal Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 32435743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Life Stress Alters Gene Expression and Cytoarchitecture in the Prefrontal Cortex Leading to Social Impairment and Increased Anxiety.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 2;12:754198. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.754198. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34795694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fazel S, Danesh J. Serious mental disorder in 23000 prisoners: a systematic review of 62 surveys. Lancet 2002; 359: 545–550. - PubMed
-
- Joukamaa M, Aarnio J, von Gruenewaldt V, Hakamäki S, Hypén K, Lauerma H et al. Rikosseuraamusasiakkaiden Terveys, Työkyky ja Hoidontarve—Perustulosraportti. Rikosseuraamuslaitoksen julkaisuja; Rikosseuraamusvirasto: Helsinki, Finland, 2010.
-
- Hare RD. The Hare Psychopathy Checklist – Revised (PCL-R), 2nd edn, Multi-Health Systems: Toronto, ON, Canada.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

