Influence of the use of testosterone associated with physical training on some hematologic and physical parameters in older rats with alloxan-induced diabetes
- PMID: 27598977
- PMCID: PMC10522118
- DOI: 10.1590/2359-3997000000200
Influence of the use of testosterone associated with physical training on some hematologic and physical parameters in older rats with alloxan-induced diabetes
Abstract
Objective: This study investigated the possible blood changes in wistar rats elderly with and without treatment with anabolic steroids submitted physical training.
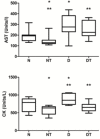
Materials and methods: Elderly rats (32) were divided into four groups: normal (N), treated normal (NT), diabetic (D) and treated diabetic (DT). They were submitted to 20 sessions of swimming with overload (5% body weight), 40 min/day for four weeks. The NT and DT groups received application of testosterone twice a week. At the end of the sessions, the animals were subjected to swimming until exhaustion and then killed for removal of blood and visceral fat. We evaluated maximum swim time, weight of visceral fat, erythrogram, leukogram, lipidogram and serum levels of glucose, lactate, aspartate aminotransferase and creatine kinase. The results were compared using one-way ANOVA followed by the post hoc Tukey test.
Results: In elderly diabetic rats, the use of anabolic associated with physical training in older rats resulted in improvement in erythrogram, lipidogram and physical performance for high-intensity aerobic exercise. However, it was related to changes in leukocyte count, probably associated with inflammation.
Conclusion: The combination of the use of testosterone with physical training, followed by maximal effort test caused changes hematological and biochemical can be associated with improvement in physiological characteristics, with increase of the swimming time and decrease of visceral fat levels, improvement in aerobic metabolism of fatty acids and glucose in normal and diabetic animals.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of exercise training on hippocampus concentrations of insulin and IGF-1 in diabetic rats.Hippocampus. 2009 Oct;19(10):981-7. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20636. Hippocampus. 2009. PMID: 19437499
-
Swimming Program on Mildly Diabetic Rats in Pregnancy.Reprod Sci. 2021 Aug;28(8):2223-2235. doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00462-0. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Reprod Sci. 2021. PMID: 33515208
-
Effects of swimming training at the intensity equivalent to aerobic/anaerobic metabolic transition in alloxan diabetic rats.J Diabetes Complications. 2007 Jul-Aug;21(4):258-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2006.07.007. J Diabetes Complications. 2007. PMID: 17616357
-
Swimming training potentiates the recovery of femoral neck strength in young diabetic rats under insulin therapy.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019;74:e829. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2019/e829. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019. PMID: 31038563 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial memory in sedentary and trained diabetic rats: molecular mechanisms.Hippocampus. 2014 Jun;24(6):703-11. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22261. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Hippocampus. 2014. PMID: 24916112
Cited by
-
The Effects of Testosterone Therapy Combined with Swimming Exercise on Adipose Tissue and Biochemical Parameters in Male Obese Wistar Rats.Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2021 Jul-Sep;17(3):304-312. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2021.304. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2021. PMID: 35342466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shahidi NT. A review of the chemistry, biological action, and clinical applications of anabolic-androgenic steroids. Clin Ther. 2001;23(9):1355-90. - PubMed
-
- Bardin CW. The anabolic action of testosterone. N Engl J Med. 1996;335(1):52-3. - PubMed
-
- Bhasin S, Woodhouse L, Storer TW. Proof of the effect of testosterone on skeletal muscle. J Endocrinol. 2001;170(1):27-38. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
