Direct detection of Helicobacter pylori in biopsy specimens using a high-throughput multiple genetic detection system
- PMID: 27599152
- PMCID: PMC5562010
- DOI: 10.2217/fmb-2016-0149
Direct detection of Helicobacter pylori in biopsy specimens using a high-throughput multiple genetic detection system
Abstract
Aim: We evaluated the direct high-throughput multiple genetic detection system (dHMGS) for Helicobacter pylori in gastric biopsies.
Materials & methods: One hundred and thirty-three specimens were concurrently analyzed by dHMGS, rapid urease test, culture and sequencing.
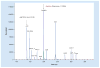
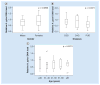
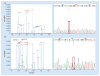
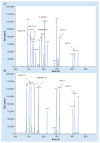
Results: dHMGS was highly sensitive and specific for H. pylori identification compared with culture and rapid urease test. The correlation coefficient of the quantitative standard curve was R2 = 0.983. A significant difference in the relative H. pylori DNA abundance was found in different gastroduodenal diseases. Concordance rates between dHMGS and sequencing for resistance mutations were 97.1, 100.0, 85.3 and 97.1%, respectively. Finally, dHMGS could efficiently distinguish mixed infection in biopsy specimens.
Conclusion: The dHMGS could efficiently diagnose and quantify H. pylori burden in biopsies, simultaneously screening for virulence, antibiotic resistance and presence of the multistrain infections.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; direct high-throughput multiple genetic detection system; gastric biopsy specimens; identification; mixed infection; quantitative analysis; resistance; virulence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of three PCR methods for detection of Helicobacter pylori DNA and detection of cagA gene in gastric biopsy specimens.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Jul 1;10(13):1958-60. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1958. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15222045 Free PMC article.
-
A high-throughput multiplex genetic detection system for Helicobacter pylori identification, virulence and resistance analysis.Future Microbiol. 2016 Oct;11:1261-1278. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2016-0023. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Future Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27023051
-
[Detection of Helicobacter pylori and antimicrobial resistance in gastric biopsy specimens].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2012 Jul;46(3):398-409. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2012. PMID: 22951652 Turkish.
-
Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori: invasive methods.Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998 Oct;30 Suppl 3:S320-3. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998. PMID: 10077765 Review.
-
Molecular methods for typing of Helicobacter pylori and their applications.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1999 Jun;24(2):193-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1999.tb01282.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10378420 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Diagnostic Modalities for Helicobacter pylori Infection.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 17;14(9):1170. doi: 10.3390/life14091170. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation and identification of a thyroid cancer cell line with stable expression of CCDC67 and luciferase reporter genes.Oncol Lett. 2019 Nov;18(5):4495-4502. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10839. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31611958 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and high-throughput multiplex genetic detection assay for detection, semi-quantification and virulence genotyping of Helicobacter pylori in non-invasive oral samples.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Sep 29;13:1267288. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1267288. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37842005 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Helicobacter pylori Plasticity in the Gastric Niche of Subjects at Increased Gastric Cancer Risk.Pathogens. 2019 May 18;8(2):65. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8020065. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31109082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Venerito M, Goni E, Malfertheiner P. Helicobacter pylori screening: options and challenges. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;10(4):497–503. - PubMed
-
- Rothenbacher D, Brenner H. Burden of Helicobacter pylori and H. pylori-related diseases in developed countries: recent developments and future implications. Microbes Infect. 2003;5(8):693–703. - PubMed
-
- Kim JJ, Kim JG, Dong HK. Mixed-infection of antibiotic susceptible and resistant Helicobacter pylori isolates in a single patient and underestimation of antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Helicobacter. 2003;8(3):202–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
