The combination of serum insulin, osteopontin, and hepatocyte growth factor predicts time to castration-resistant progression in androgen dependent metastatic prostate cancer- an exploratory study
- PMID: 27599544
- PMCID: PMC5013640
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2723-1
The combination of serum insulin, osteopontin, and hepatocyte growth factor predicts time to castration-resistant progression in androgen dependent metastatic prostate cancer- an exploratory study
Abstract
Background: We hypothesized that pretreatment serum levels of insulin and other serum markers would predict Progression-free survival (PFS), defined as time to castration-resistant progression or death, in metastatic androgen-dependent prostate cancer (mADPC).
Methods: Serum samples from treatment-naïve men participating in a randomized phase 3 trial of ADT +/- chemotherapy were retrospectively analyzed using multiplex assays for insulin and multiple other soluble factors. Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to identify associations between individual factor levels and PFS.
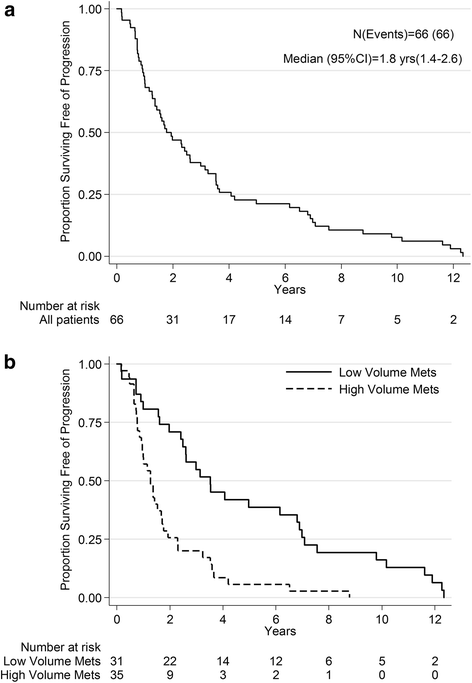
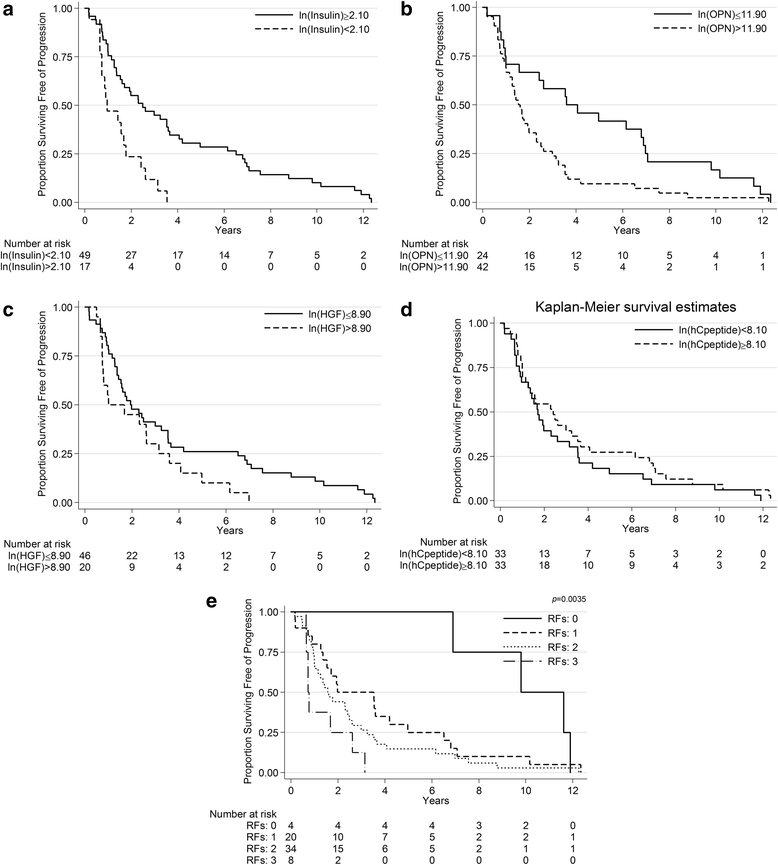
Results: Sixty six patients were evaluable (median age = 72 years; median prostate surface antigen [PSA] = 31.5 ng/mL; Caucasian = 86 %; Gleason score ≥8 = 77 %). In the univariable analysis, higher insulin (HR = 0.81 [0.67, 0.98] p = 0.03) and C-peptide (HR = 0.62 [0.39, 1.00]; p = 0.05) levels were associated with a longer PFS, while higher Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF; HR = 1.63 [1.06, 2.51] p = 0.03) and Osteopontin (OPN; HR = 1.56 [1.13, 2.15]; p = 0.01) levels were associated with a shorter PFS. In multivariable analysis, insulin below 2.1 (ln scale; HR = 2.55 [1.24, 5.23]; p = 0.011) and HGF above 8.9 (ln scale; HR = 2.67 [1.08, 3.70]; p = 0.027) levels were associated with longer PFS, while adjusted by OPN, C-peptide, trial therapy and metastatic volume. Four distinct risk groups were identified by counting the number of risk factors (RF) including low insulin, high HGF, high OPN levels, and low C-peptide levels (0, 1, 2, and 3). Median PFS was 9.8, 2.0, 1.6, and 0.7 years for each, respectively (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Pretreatment serum insulin, HGF, OPN, and C-peptide levels can predict PFS in men with mADPC treated with ADT. Risk groups based on these factors are superior predictors of PFS than each marker alone.
Keywords: Castration resistance; Hepatocyte growth factor; Insulin; Metastatic prostate cancer; Osteopontin; Prognostic marker.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating Tumor Cells as a Marker for Progression-free Survival in Metastatic Castration-naïve Prostate Cancer.Prostate. 2017 Jun;77(8):849-858. doi: 10.1002/pros.23325. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Prostate. 2017. PMID: 28295408
-
Plasma macrophage-stimulating protein and hepatocyte growth factor levels are associated with prostate cancer progression.Hum Cell. 2016 Jan;29(1):22-9. doi: 10.1007/s13577-015-0123-5. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Hum Cell. 2016. PMID: 26250899
-
Elevated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) in men with metastatic prostate cancer starting androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is associated with shorter time to castration resistance and overall survival.Prostate. 2014 Feb;74(3):225-34. doi: 10.1002/pros.22744. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Prostate. 2014. PMID: 24132762
-
Biomarkers in prostate cancer - Current clinical utility and future perspectives.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017 Dec;120:180-193. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.11.007. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017. PMID: 29198331 Review.
-
Prostate cancer: Validating radiographic progression-free survival.Nat Rev Urol. 2018 May;15(5):263. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2018.46. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Nat Rev Urol. 2018. PMID: 29620058 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Optimized Identification of High-Grade Prostate Cancer by Combining Different PSA Molecular Forms and PSA Density in a Deep Learning Model.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Feb 18;11(2):335. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11020335. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670632 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Levels of Omentin, Leptin, VEGF, and HGF and Their Clinical Relevance with PSA Marker in Prostate Cancer.Dis Markers. 2018 Aug 16;2018:3852401. doi: 10.1155/2018/3852401. eCollection 2018. Dis Markers. 2018. PMID: 30186533 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SPP1 as an Extracellular Matrix Signature for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Front Oncol. 2019 Sep 18;9:924. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00924. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31620371 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Extracellular Matrix- and Integrin Adhesion Complex-Related Molecules for Prostate Cancer Biomarker Discovery.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 28;12(1):79. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010079. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38255186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis at the single-cell level indicates an important role of heterogeneous global DNA methylation status on the progression of lung adenocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 2;11(1):23337. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02786-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34857857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hussain M, Goldman B, Tangen C, Higano CS, Petrylak DP, Wilding G, Akdas AM, Small EJ, Donnelly BJ, Sundram SK, et al. Prostate-specific antigen progression predicts overall survival in patients with metastatic prostate cancer: data from Southwest Oncology Group Trials 9346 (Intergroup Study 0162) and 9916. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(15):2450–2456. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.9810. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hussain M, Tangen CM, Higano C, Schelhammer PF, Faulkner J, Crawford ED, Wilding G, Akdas A, Small EJ, Donnelly B, et al. Absolute prostate-specific antigen value after androgen deprivation is a strong independent predictor of survival in new metastatic prostate cancer: data from Southwest Oncology Group Trial 9346 (INT-0162) J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(24):3984–3990. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.06.4246. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

