DNA transposon activity is associated with increased mutation rates in genes of rice and other grasses
- PMID: 27599761
- PMCID: PMC5023962
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12790
DNA transposon activity is associated with increased mutation rates in genes of rice and other grasses
Abstract
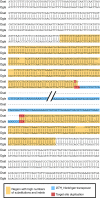
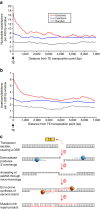
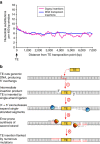
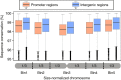
DNA (class 2) transposons are mobile genetic elements which move within their 'host' genome through excising and re-inserting elsewhere. Although the rice genome contains tens of thousands of such elements, their actual role in evolution is still unclear. Analysing over 650 transposon polymorphisms in the rice species Oryza sativa and Oryza glaberrima, we find that DNA repair following transposon excisions is associated with an increased number of mutations in the sequences neighbouring the transposon. Indeed, the 3,000 bp flanking the excised transposons can contain over 10 times more mutations than the genome-wide average. Since DNA transposons preferably insert near genes, this is correlated with increases in mutation rates in coding sequences and regulatory regions. Most importantly, we find this phenomenon also in maize, wheat and barley. Thus, these findings suggest that DNA transposon activity is a major evolutionary force in grasses which provide the basis of most food consumed by humankind.
Figures
References
-
- Grass Phylogeny Working Group. Phylogeny and subfamilial classification of the grasses (Poaceae). Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 88, 373–457 (2001).
-
- Schnable P. S. et al.. The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 326, 1112–1115 (2009). - PubMed
-
- International Brachypodium Initiative. Genome sequencing and analysis of the model grass Brachypodium distachyon. Nature 463, 763–768 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

